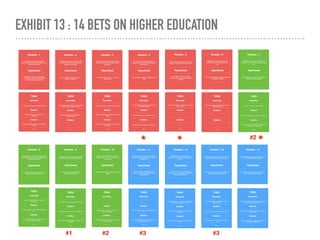
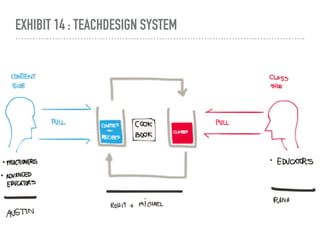
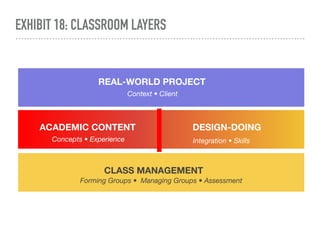
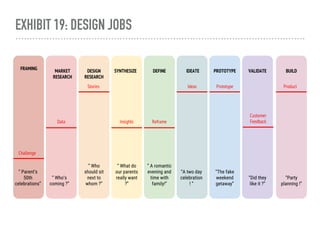
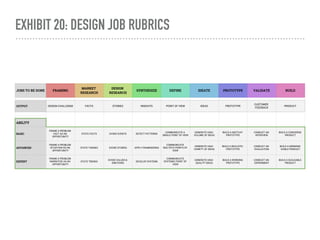
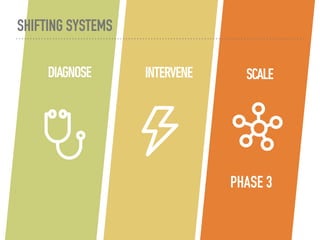
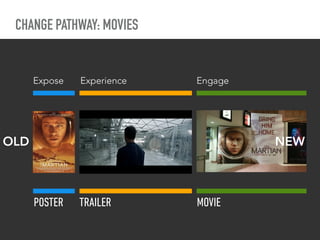
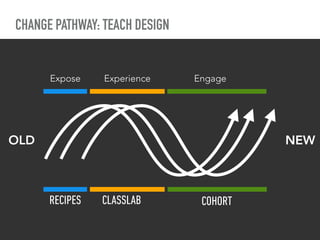
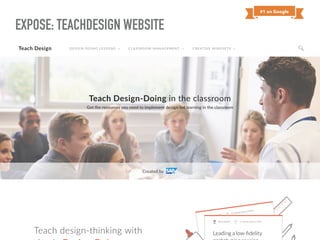
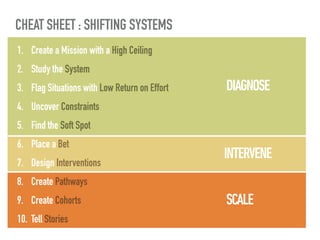
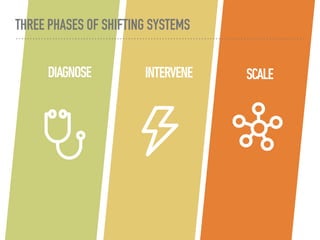
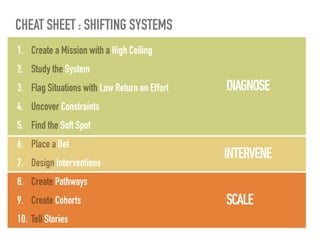
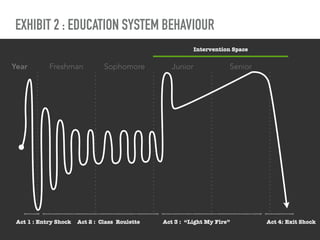
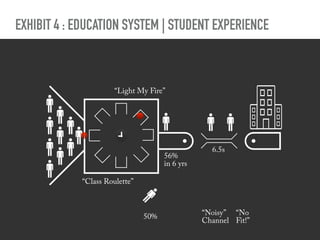
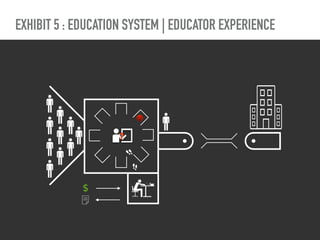
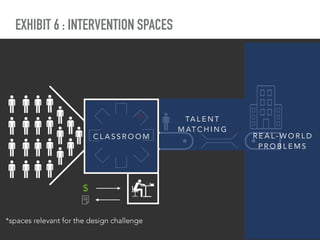
The document discusses a framework for intervening in educational systems through design-thinking, detailing a historical timeline from 2016 to 2018, as well as key steps for effective interventions. It outlines specific phases including diagnosing the system, flagging low-effort situations, uncovering constraints, and creating pathways for change. The approach seeks to empower students and promote effective learning through real-world experiences and collaborative efforts among educators.



![INTERVENTION
UNIT OF SCALE
intervene | ˌin(t)ərˈvēn |
verb [no object]
1 come between so as to prevent or alter a result or course of events:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190226042320/85/Shifting-Education-4-320.jpg)














![BIO-COST
Where are you
leaking energy ?
Bio-cost is the energy, attention, and stress that people
expend over time to achieve their goals—to get what they
want” in Ashby’s sense. [Ashby 1956]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190226042320/85/Shifting-Education-26-320.jpg)