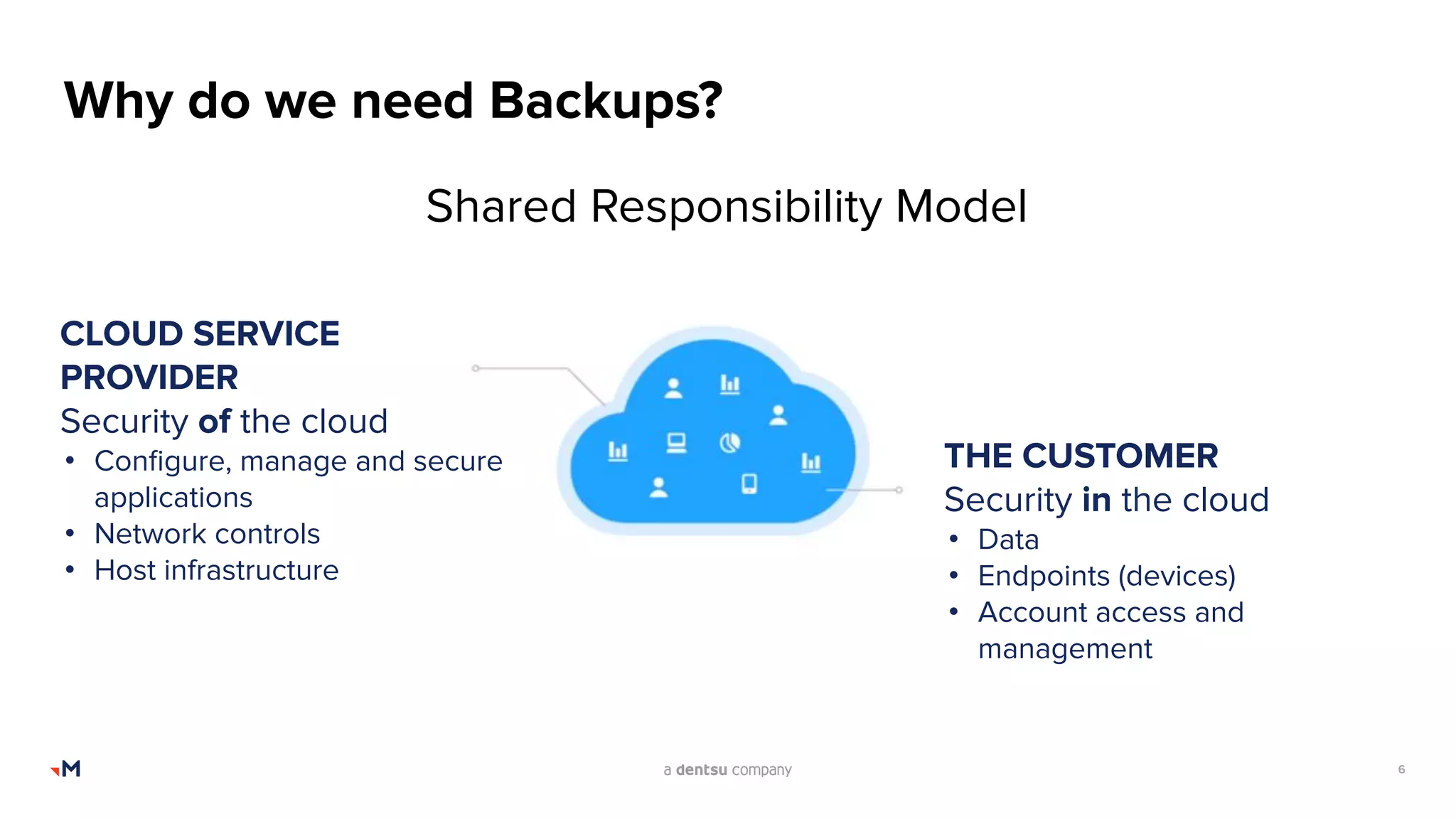
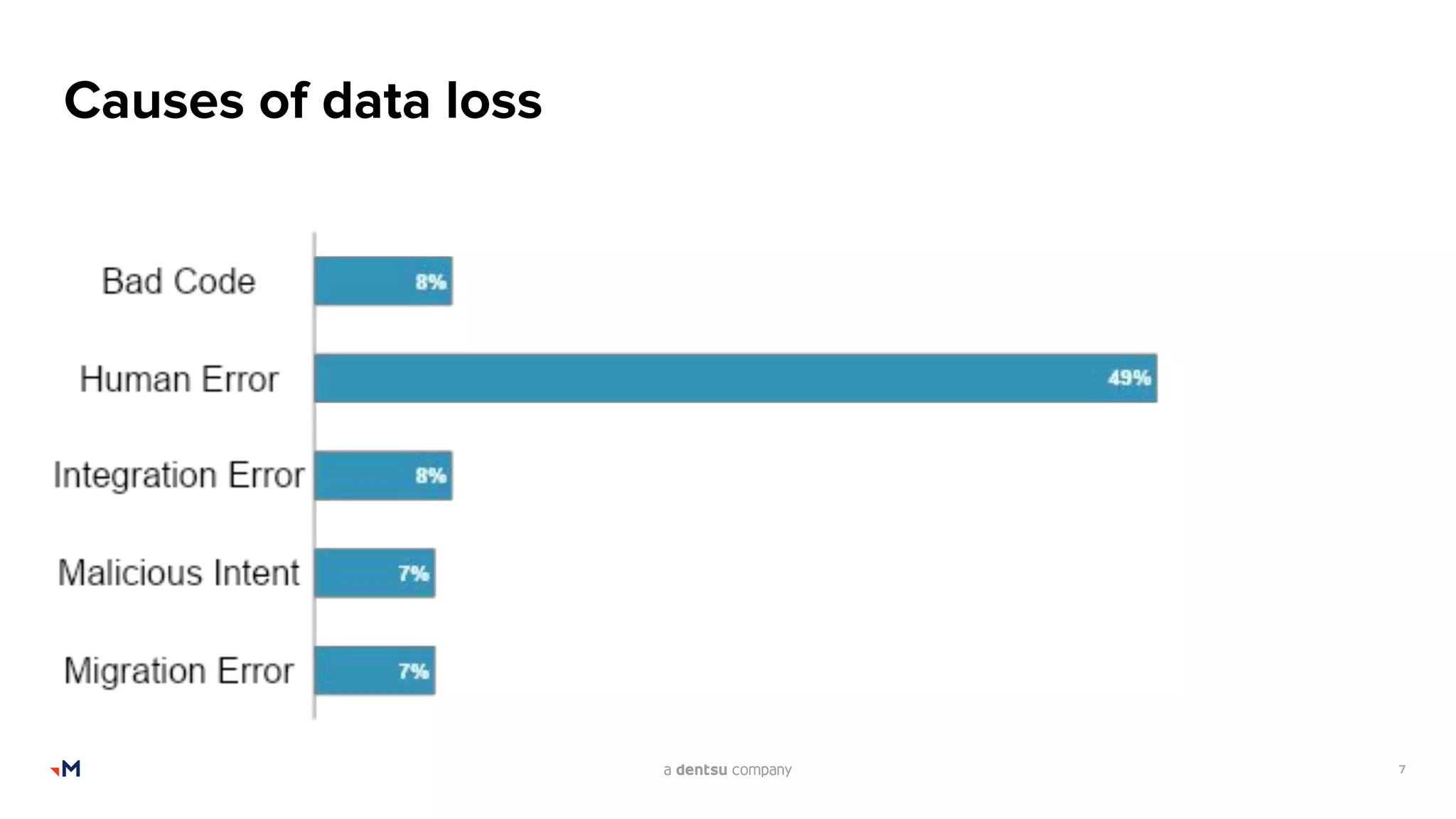
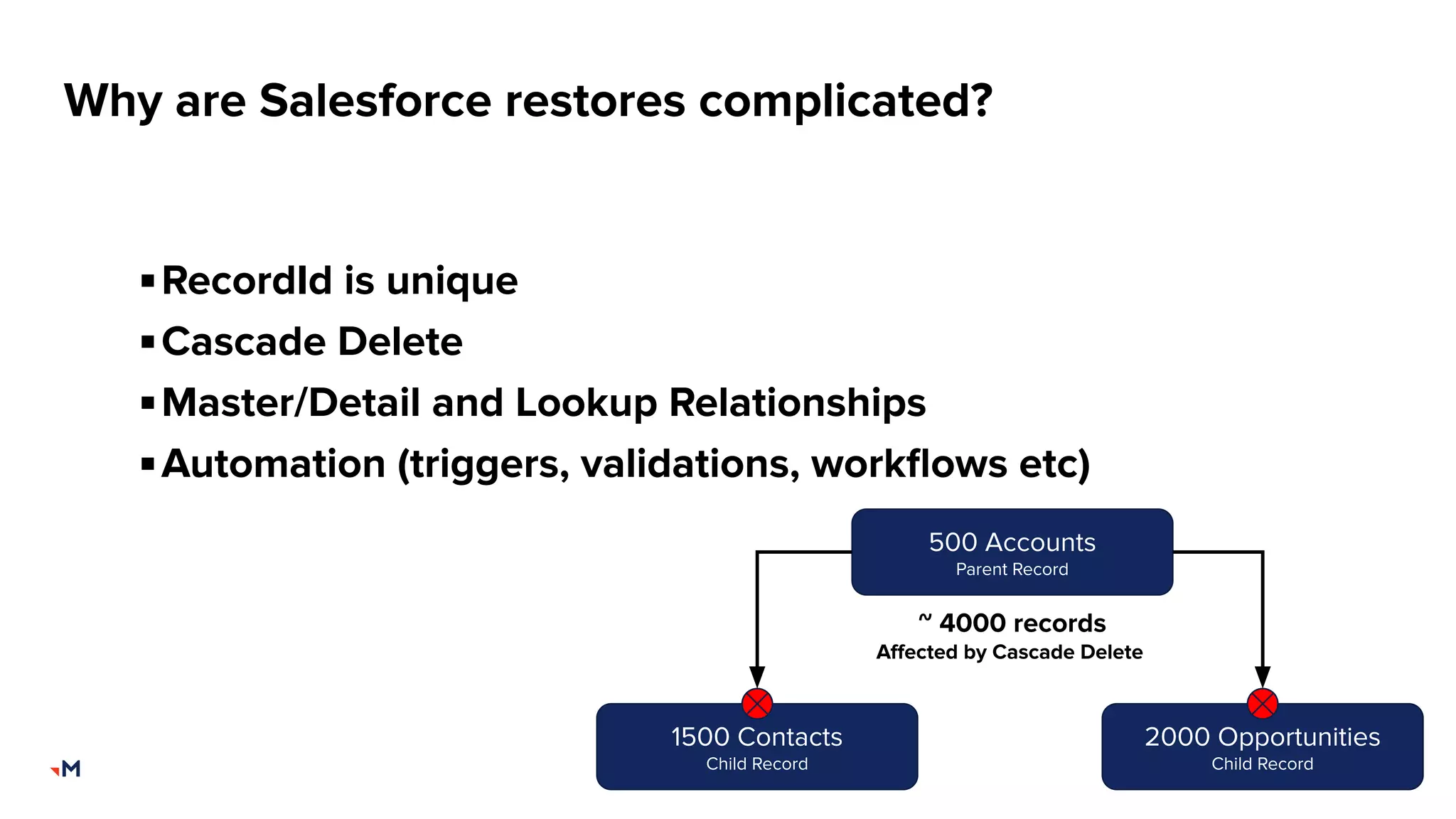
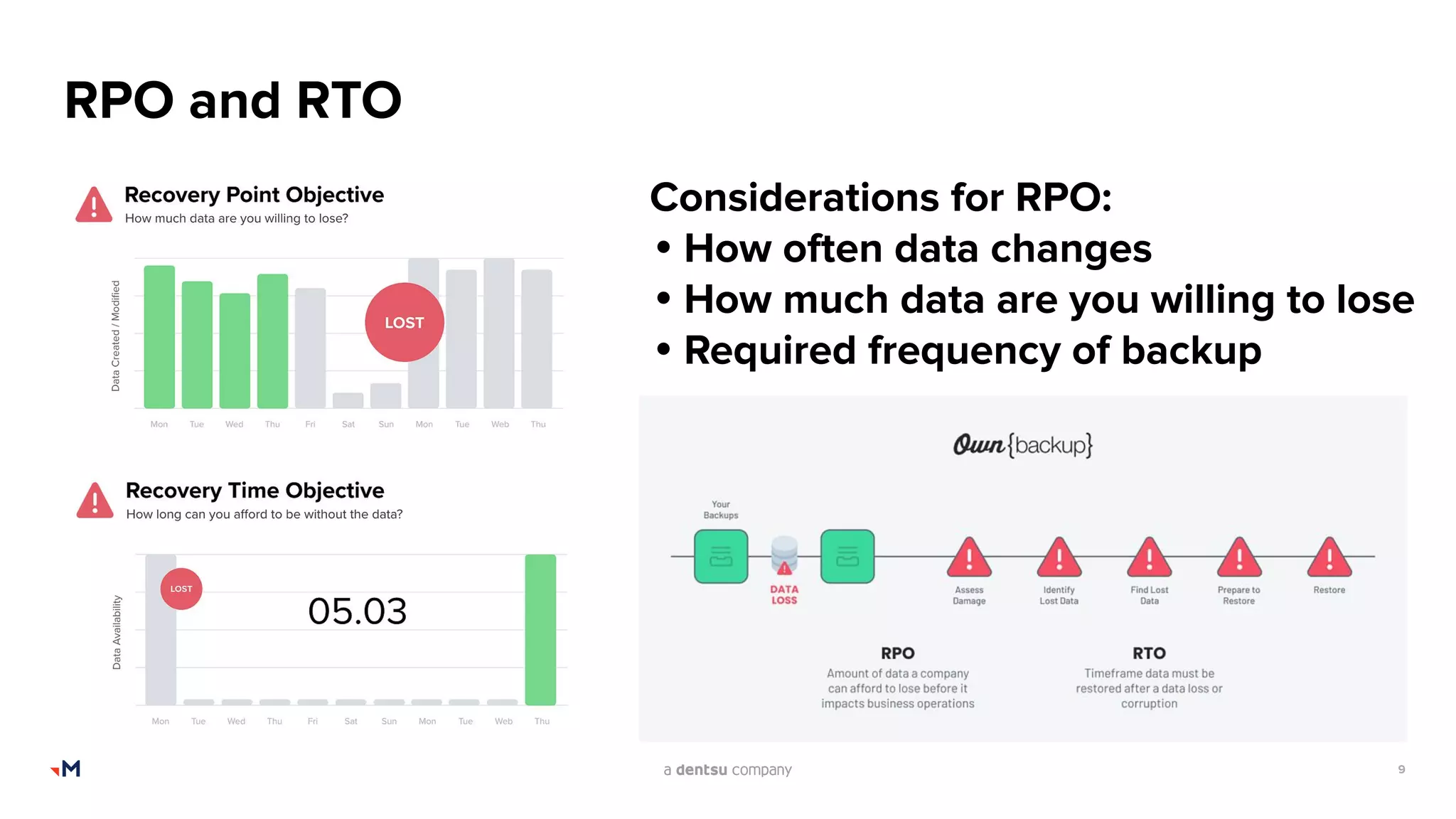
The document presents an admin's guide on backups by Mark Barcham from Merkle Aotearoa, addressing the importance of backup and recovery solutions for Salesforce users. It highlights the current lack of comprehensive strategies among users, the complexities involved in restoring Salesforce data, and key considerations for implementing effective backup solutions. Additionally, it discusses the types of backups needed, the frequency of backups, and various factors to consider when selecting backup tools.