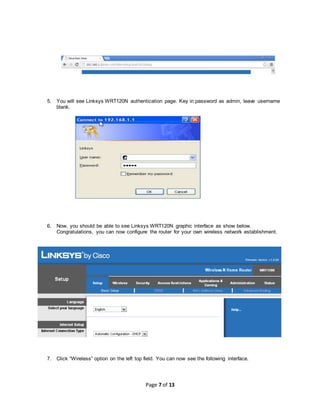
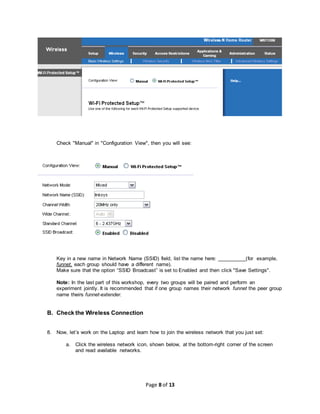
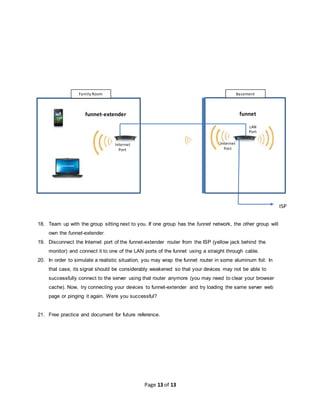
This document provides instructions for setting up a wireless network in a workshop setting. It describes connecting a wireless router and configuring it to broadcast a wireless signal with a chosen name. It then guides configuring laptops and phones to connect to the wireless network. The document also covers adding security by configuring a wireless password and restricting connections by MAC address. Finally, it discusses extending the wireless range by connecting a second wireless router to the first one via Ethernet cable.