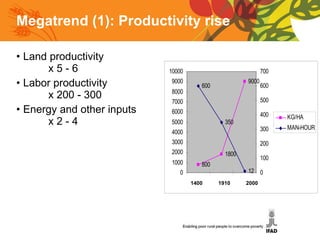
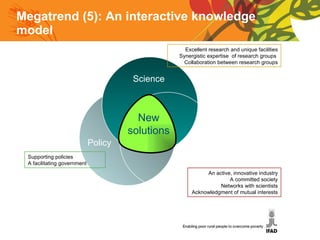
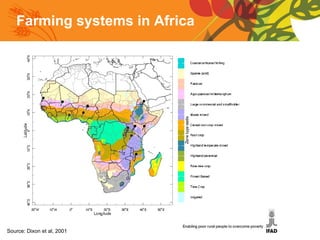
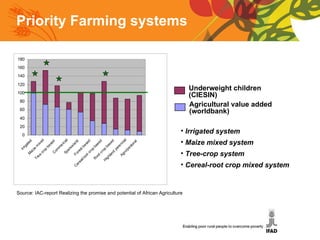
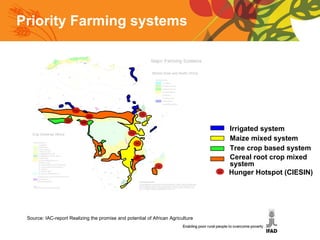
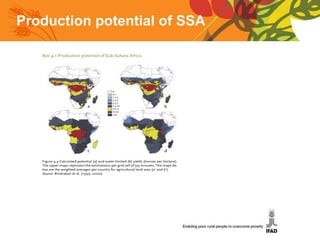
The document summarizes a conference on new directions for smallholder agriculture. It discusses trends in agriculture including rising productivity and the shift from craft to industry. It examines farming systems in different regions, noting challenges for small farmers like lack of access to credit and markets. The document calls for science and technologies tailored for smallholders, and roles for both the private sector in investment and supply chains, and public sector in knowledge and cooperatives. It concludes with recommendations like increased investment in agriculture and research, and strengthened institutions and entrepreneurship.