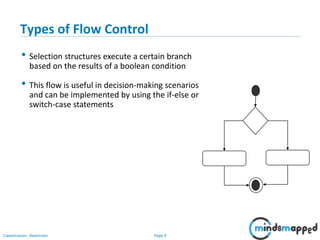
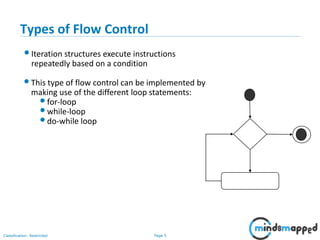
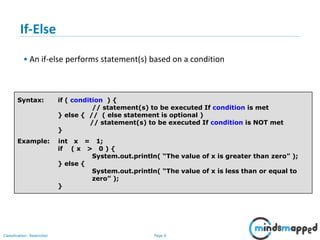
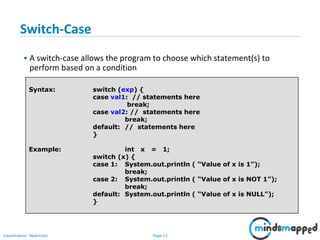
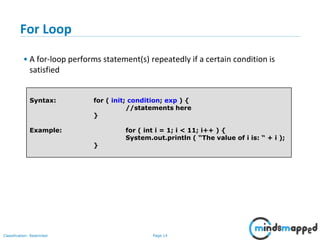
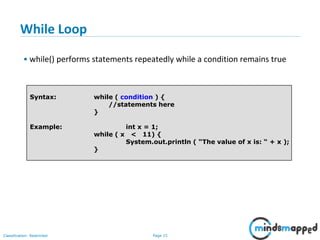
The document outlines flow control statements in programming, focusing on different types such as sequential execution, selection structures (if-else, switch-case), and iteration structures (for loop, while loop, do-while loop). It explains the purpose of flow control in modifying the execution path based on conditions and provides syntax and examples for each type. Additionally, it includes activities to reinforce understanding of conditions and expected outputs.