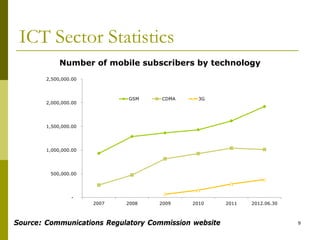
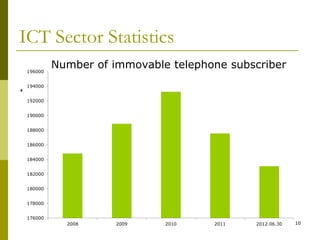
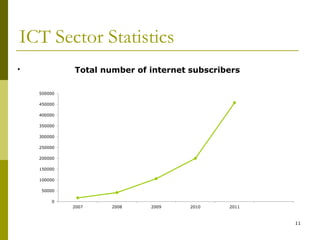
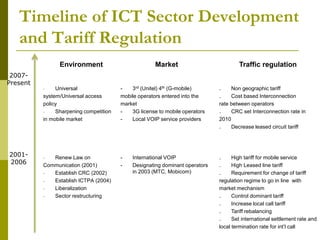
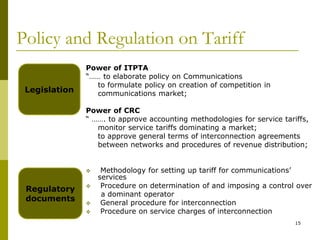
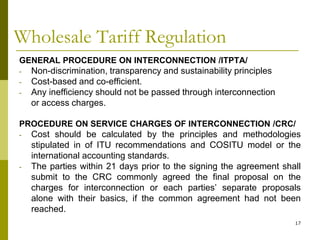
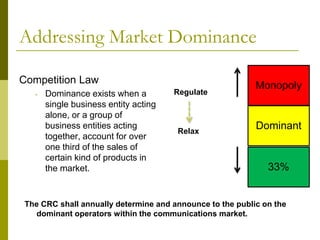
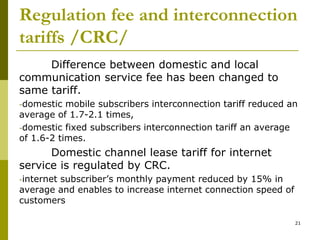
The document presents a comprehensive overview of Mongolia's tariff policy and regulatory framework in the ICT sector, highlighting key authorities, market structure, and historical developments. It discusses the roles of the Information Technology, Post and Telecommunications Authority and the Communications Regulatory Commission in fostering competition and regulating tariffs. Additionally, it provides statistics on mobile and internet subscribers and outlines methodologies for setting and monitoring service tariffs.