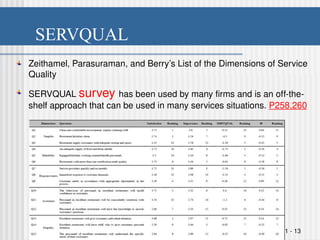
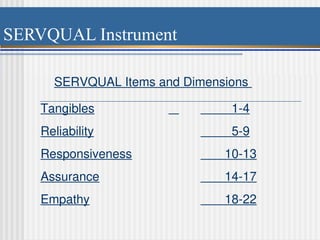
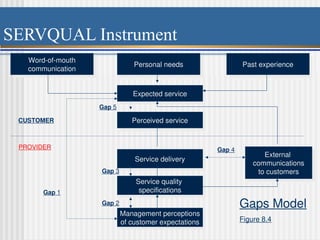
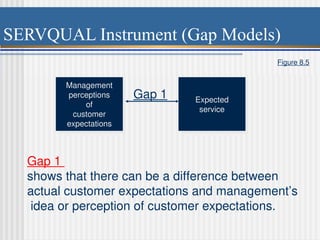
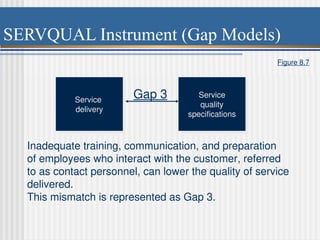
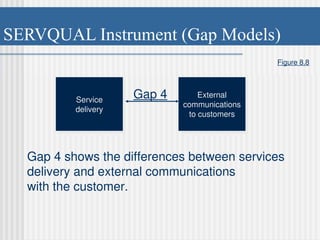
Chapter 8 discusses designing quality services, comparing service quality issues to manufacturing, emphasizing that customer needs are central to both. It presents the SERVQUAL model, which assesses service quality dimensions such as tangibles, reliability, and responsiveness, highlighting potential gaps between customer expectations and management perceptions. The chapter emphasizes the uniqueness of services, challenges in quality assessment due to intangibility, and the importance of effective communication and training to enhance service delivery.