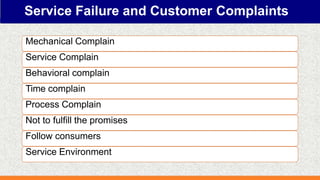
Service failures occur when a company's performance falls below a customer's expectations, creating dissatisfaction. There are many types of service failures including mechanical, behavioral, time-related, and process failures. In response, customers may complain informally or take more formal actions.
When service failures happen, companies should engage in service recovery strategies. This involves fixing both the customer and the underlying problem. To fix the customer, companies should respond quickly, communicate understanding, treat customers fairly, and build customer relationships. To fix the problem, companies should encourage complaints to identify issues, learn from recovery experiences, make services more reliable, and consider service guarantees. Effective guarantees are unconditional, meaningful, easy to understand, and supported by employee training.