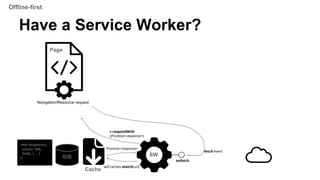
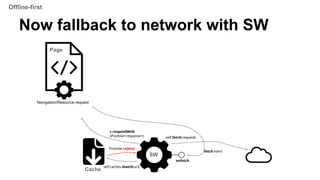
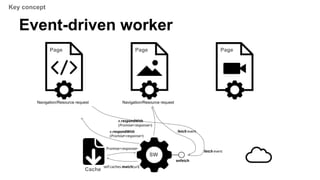
The document provides an overview of service workers, including their purpose for offline usage, background processing, and caching strategies. It explains the lifecycle events of service workers, registration, installation, and how to handle fetch events, along with security considerations. Additionally, it discusses the development environment for service workers and various resources for further reference.




![// scope defaults to "/*"
navigator.serviceWorker.register("/assets/v1/serviceworker.js").then(
function(serviceWorker) {
console.log("success!");
serviceWorker.postMessage("Howdy from your installing page.");
// To use the serviceWorker immediately, you might call
// window.location.reload()
}, function(why) {
console.error("Installing the worker failed!", why);
});
Registration
● In the page
“/*” /assets/v1/serviceworker.js
[ Registration map ]
Scope Script URL
Service Worker Lifecycle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/service-workers-140530220326-phpapp01/85/Service-workers-12-320.jpg)
![Registration
● In the page
navigator.serviceWorker.register("/sw.js");
“/*” /sw.js
[ Registration map ]
Scope Script URL
“/foo/*” /foo/sw.js
“/*” /bar/sw.js
Service Worker Lifecycle
navigator.serviceWorker.register("/foo/sw.js", { scope: “/foo/*” });
navigator.serviceWorker.register("/bar/sw.js");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/service-workers-140530220326-phpapp01/85/Service-workers-13-320.jpg)


![Programmable cache control
● new Cache()
[Constructor]
interface Cache {
Promise<AbstractResponse>
match((Request or ScalarValueString) request, optional QueryParams params);
Promise<sequence<AbstractResponse>>
matchAll((Request or ScalarValueString) request, optional QueryParams params);
Promise<any> add((Request or ScalarValueString)... requests);
Promise<any> put((Request or ScalarValueString) request, AbstractResponse response);
Promise<any>
delete((Request or ScalarValueString) request, optional QueryParams params);
Promise<any> each(CacheIterationCallback callback, optional object thisArg);
};
Service Worker Lifecycle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/service-workers-140530220326-phpapp01/85/Service-workers-16-320.jpg)


![Fetch: navigation request
onfetch
sw.js
Cache
self.caches.match(url)
Promise<response>
e.respondWith
(Promise<response>)
“/*” /sw.js
[ Registration map ]
Scope Script URL
“/foo/*” /foo/sw.js
Page Hit “https://example.com/index.html
fetch event
Scope matching
Run SW
Functional event processing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/service-workers-140530220326-phpapp01/85/Service-workers-19-320.jpg)
![Fetch: subresource request
onfetch
sw.js
Cache
self.caches.match(url)
Promise<response>
e.respondWith
(Promise<response>)
“/*” /sw.js
[ Registration map ]
Scope Script URL
“/foo/*” /foo/sw.js
Page
Fetch “https://example.com/img/flower.png
fetch event
Control
Run SW
Functional event processing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/service-workers-140530220326-phpapp01/85/Service-workers-20-320.jpg)

![Updating
onfetch
sw-v2
Cache
self.caches.match(url)
Promise<response>
e.respondWith
(Promise<response>)
“/*” /sw-v1
[ Registration map ]
Scope active
fetch event
-
waiting
Page
sw-v1
_Update
_Install
Page
sw-v1
/sw-v2 /sw-v2-
Page
sw-v2
Fetch “https://example.com/img/flower.png
Run SW
Service Worker Lifecycle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/service-workers-140530220326-phpapp01/85/Service-workers-22-320.jpg)



