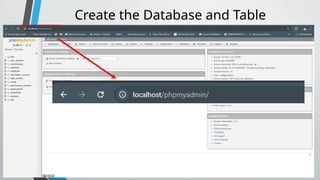
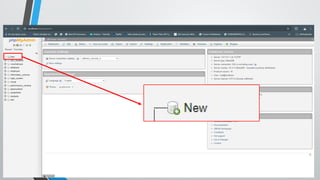
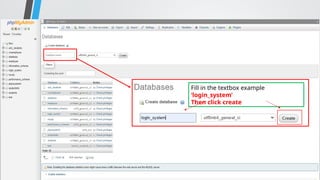
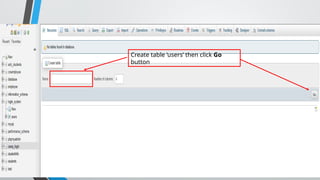
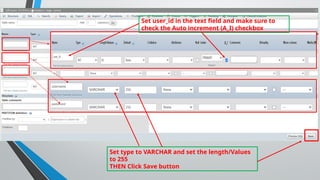
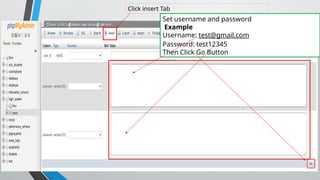
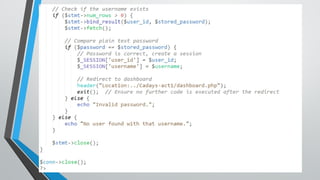
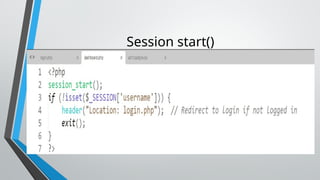
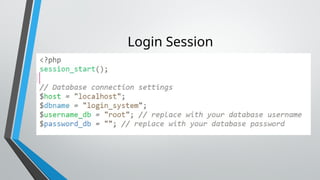
PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is an open-source scripting language widely used for web development, executing on the server to create dynamic websites. Key features include its free use, compatibility with major operating systems, and ability to handle databases, making it suitable for various applications like content management systems and e-commerce platforms. A basic understanding of HTML, PHP, and SQL is necessary for creating functionalities like user login systems, incorporating security measures like prepared statements to prevent SQL injection.