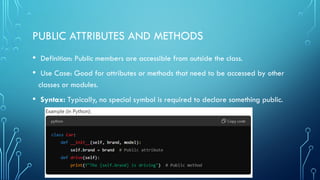
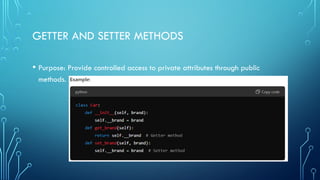
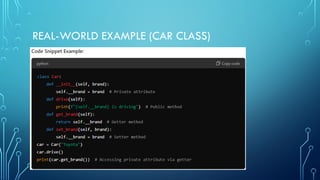
The document discusses object-oriented programming (OOP), focusing on the concepts of public and private attributes and methods. Public members are accessible from outside the class, while private members are restricted to the defining class, ensuring data encapsulation and integrity. The use of getter and setter methods is emphasized for controlled access to private attributes.