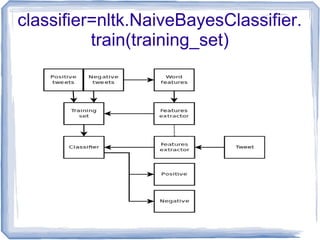
The document outlines a presentation on sentiment analysis of tweets using Python and NLTK, focusing on classifying tweets as positive or negative. It discusses the necessity of training a classifier with manually classified tweets, the extraction of features from the tweets, and utilizes a Naive Bayes classifier to determine the sentiment based on the frequency of words. An example is provided to demonstrate how the classifier identifies the sentiment of a tweet by analyzing the presence of certain words.