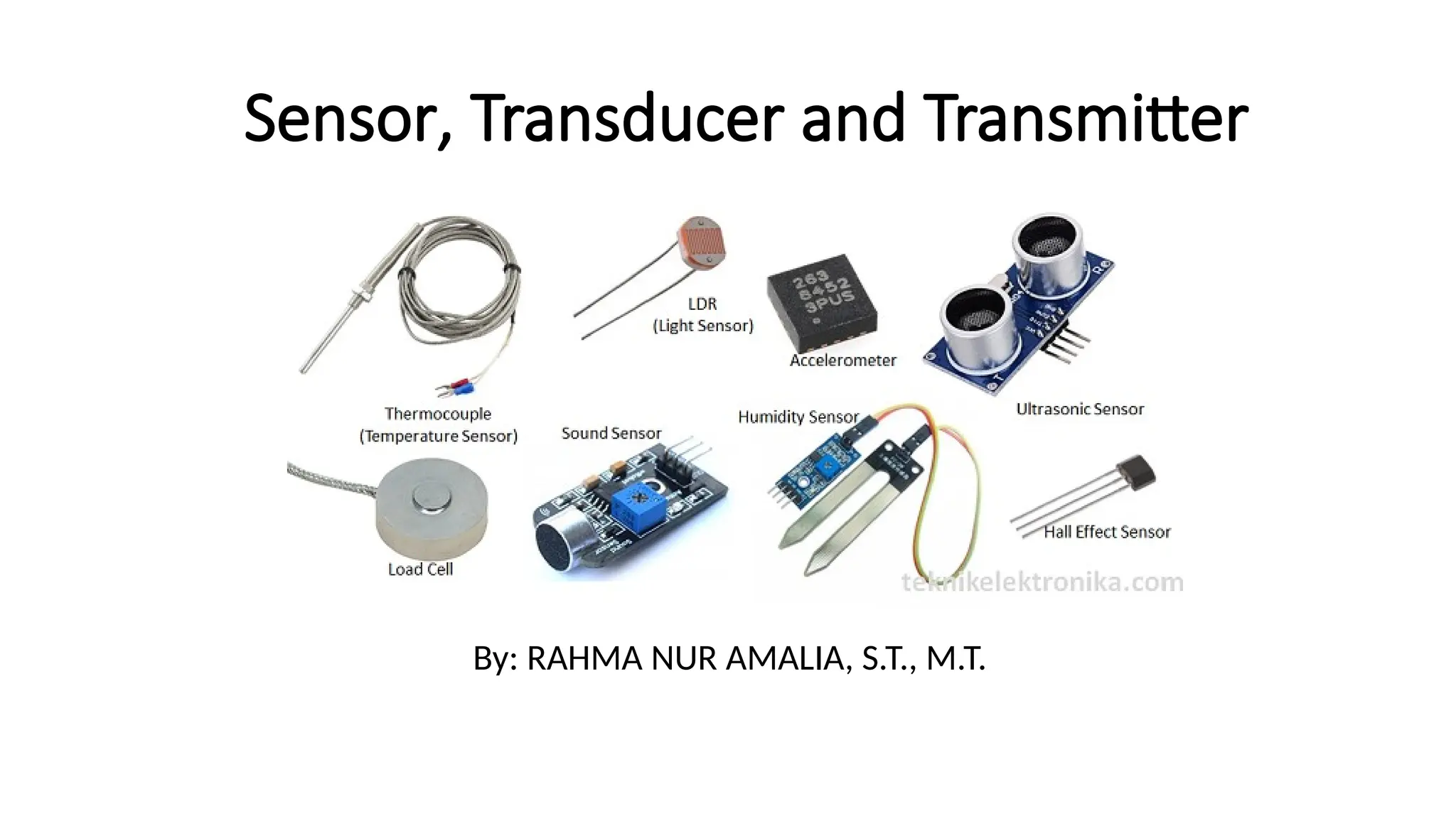
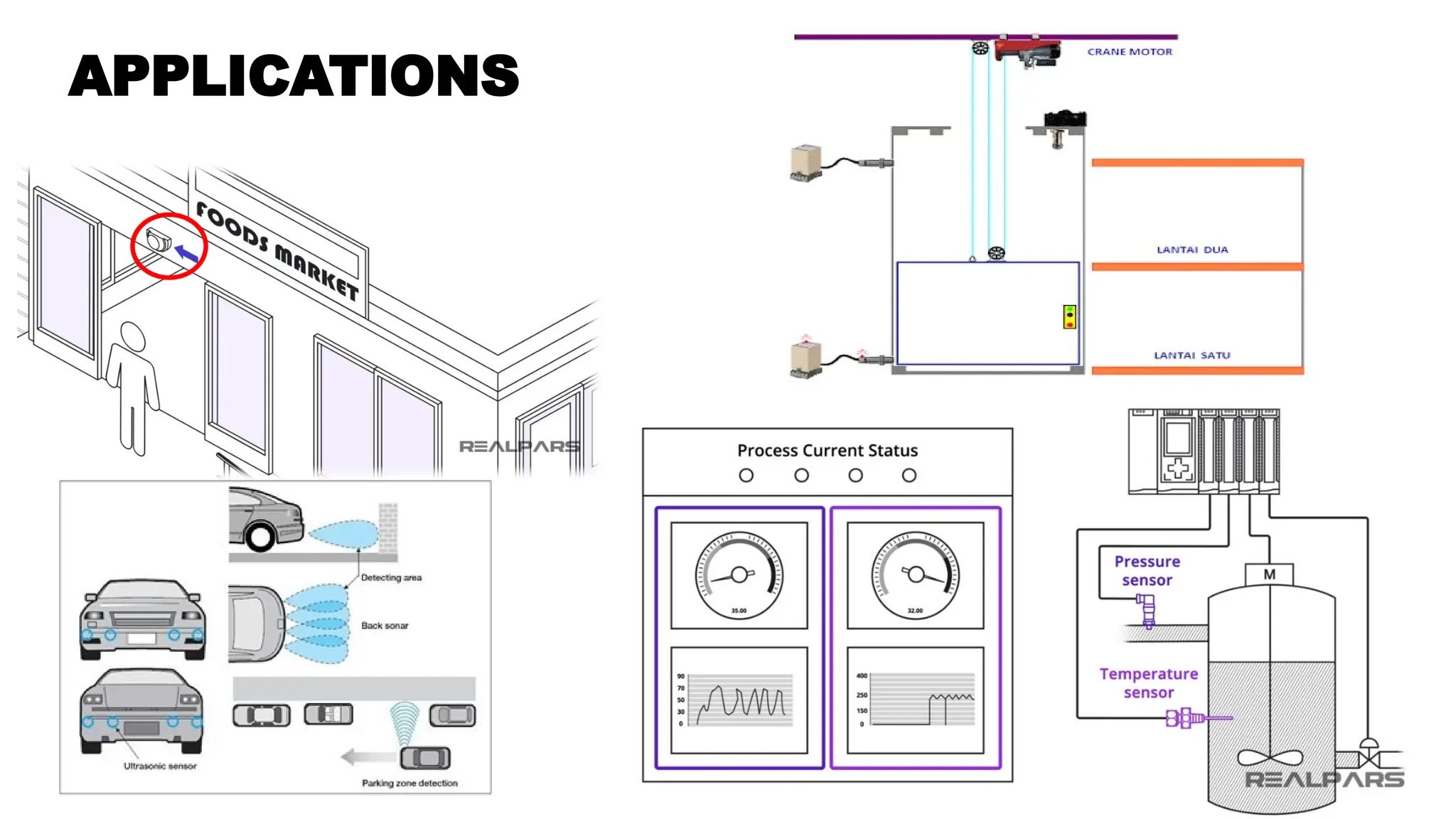
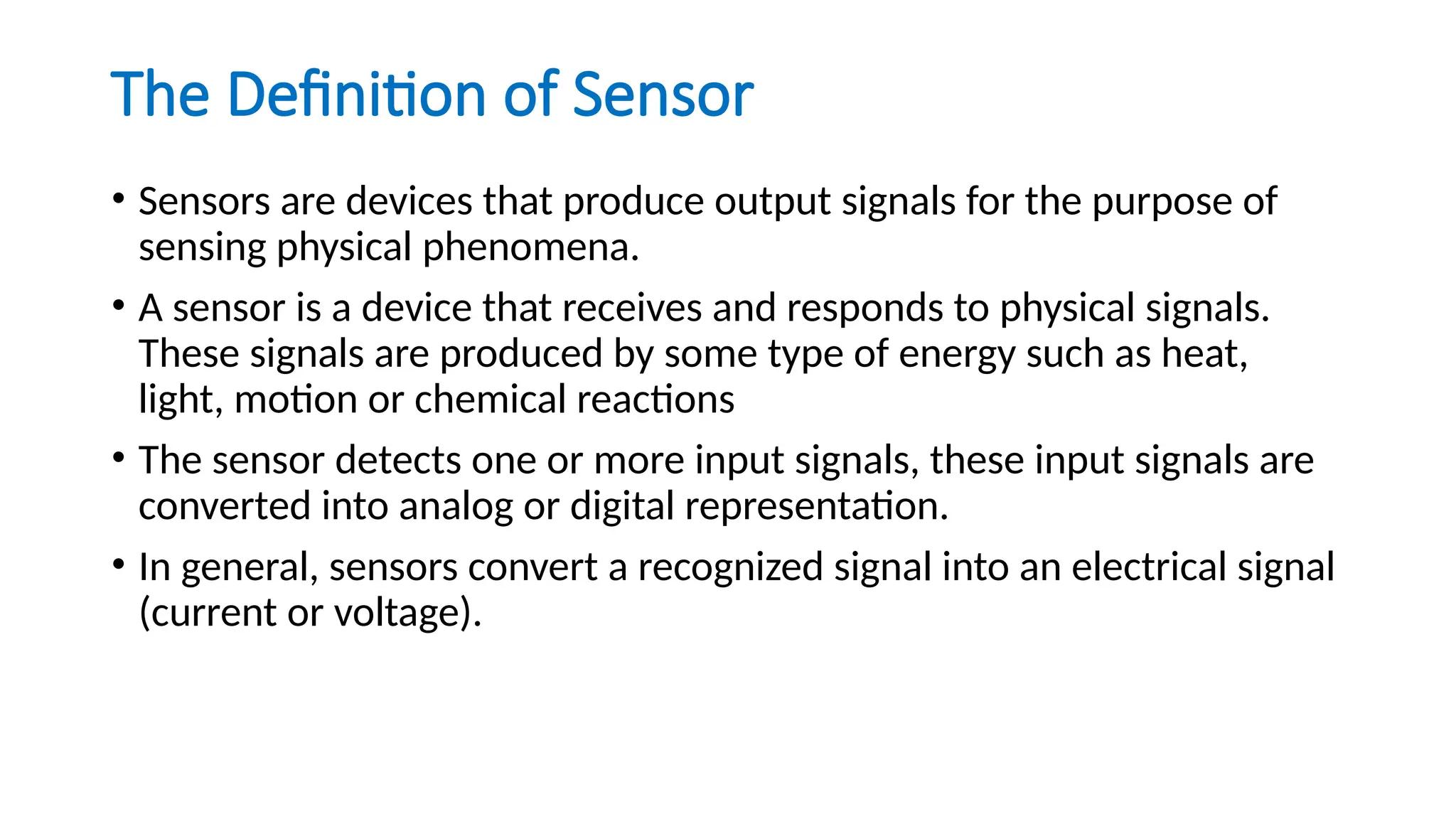
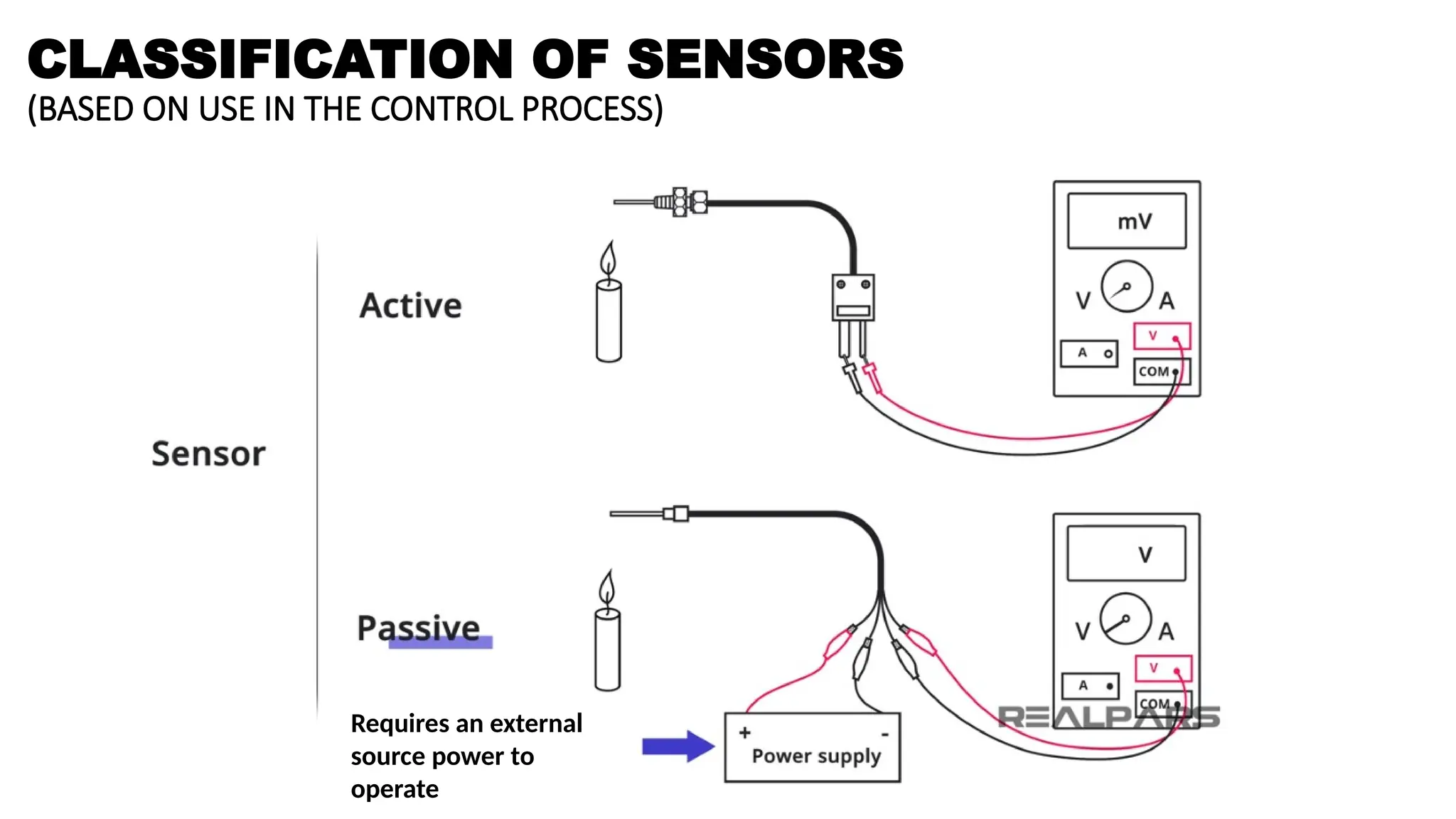
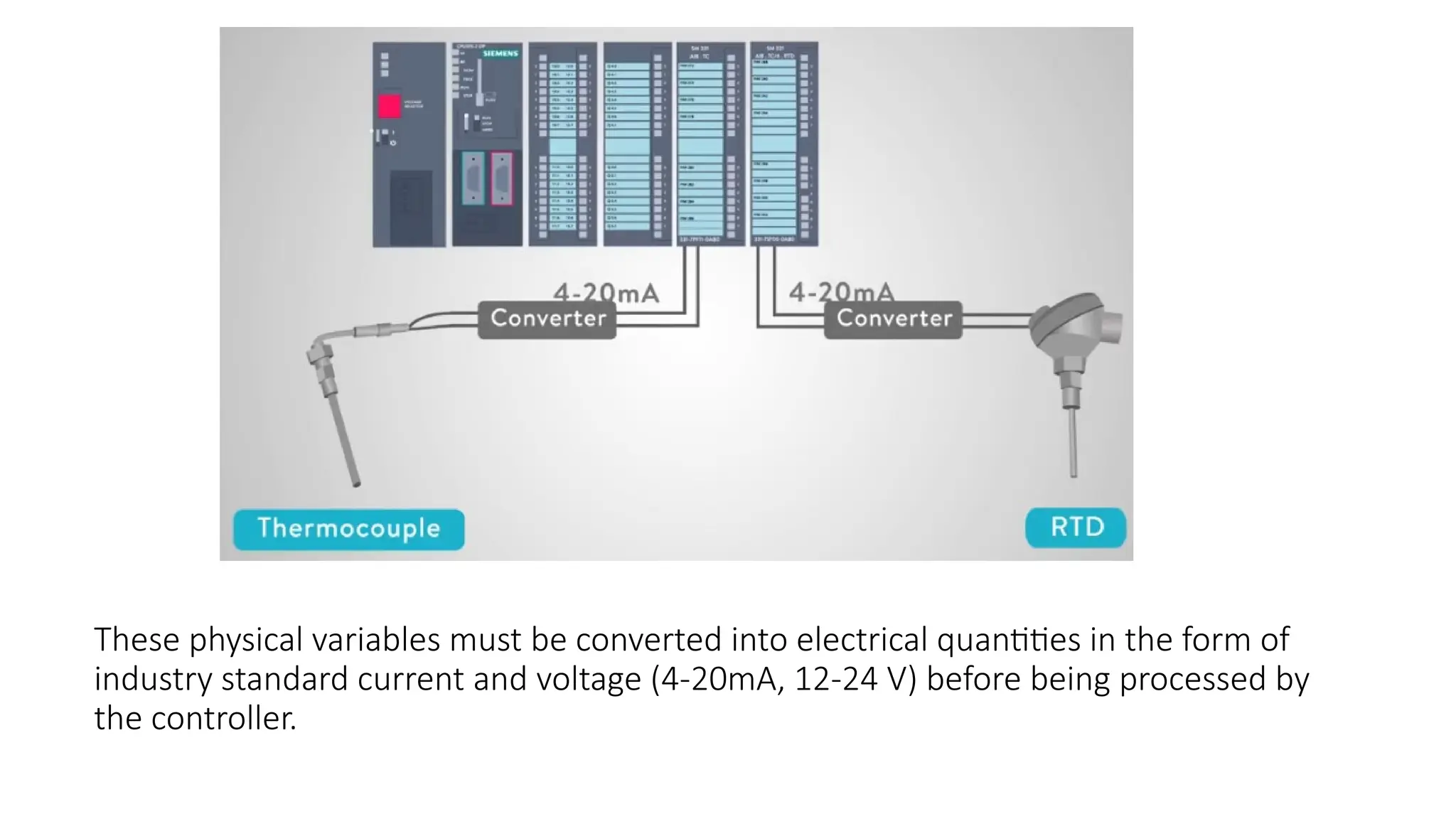
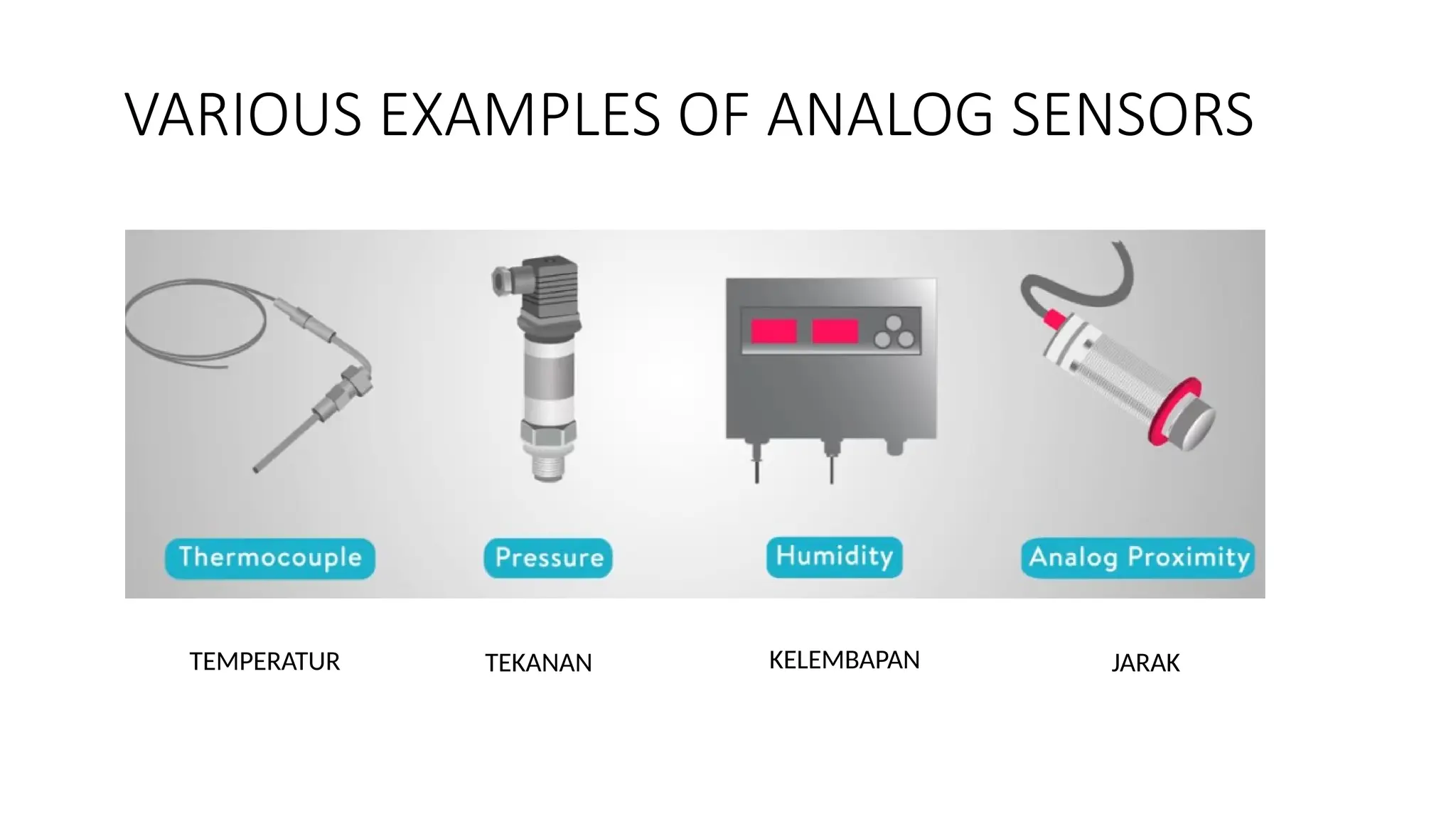
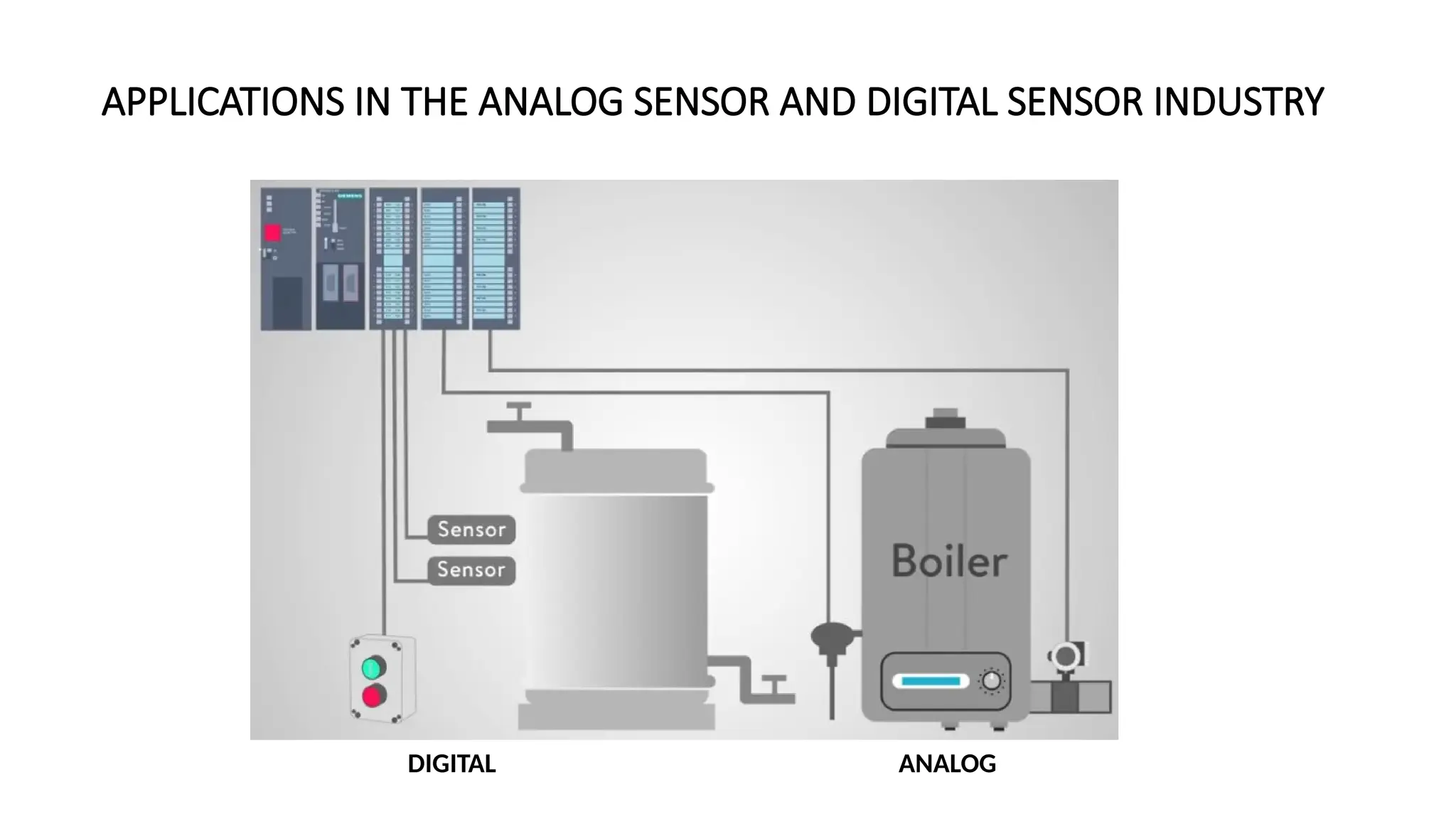
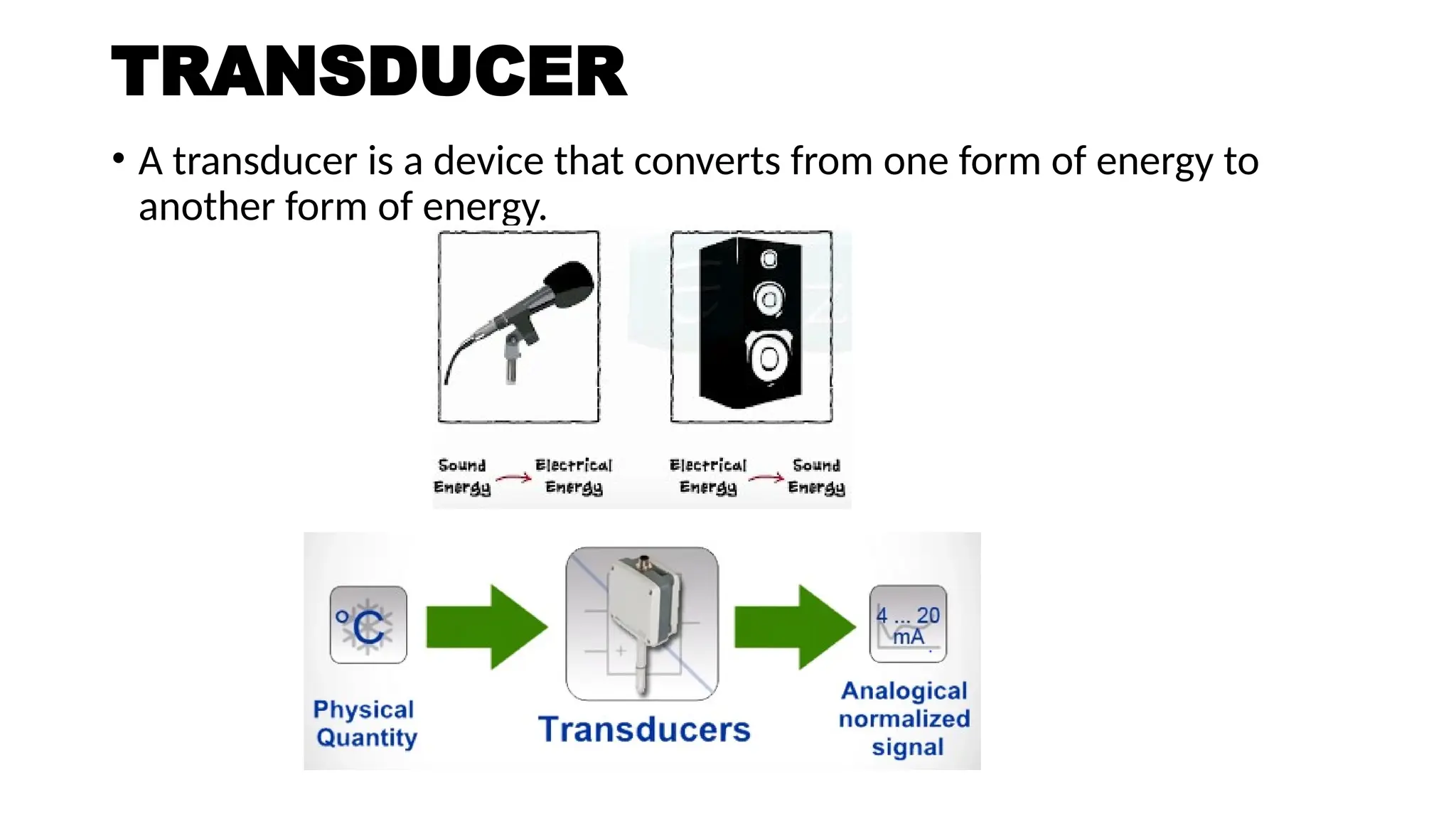
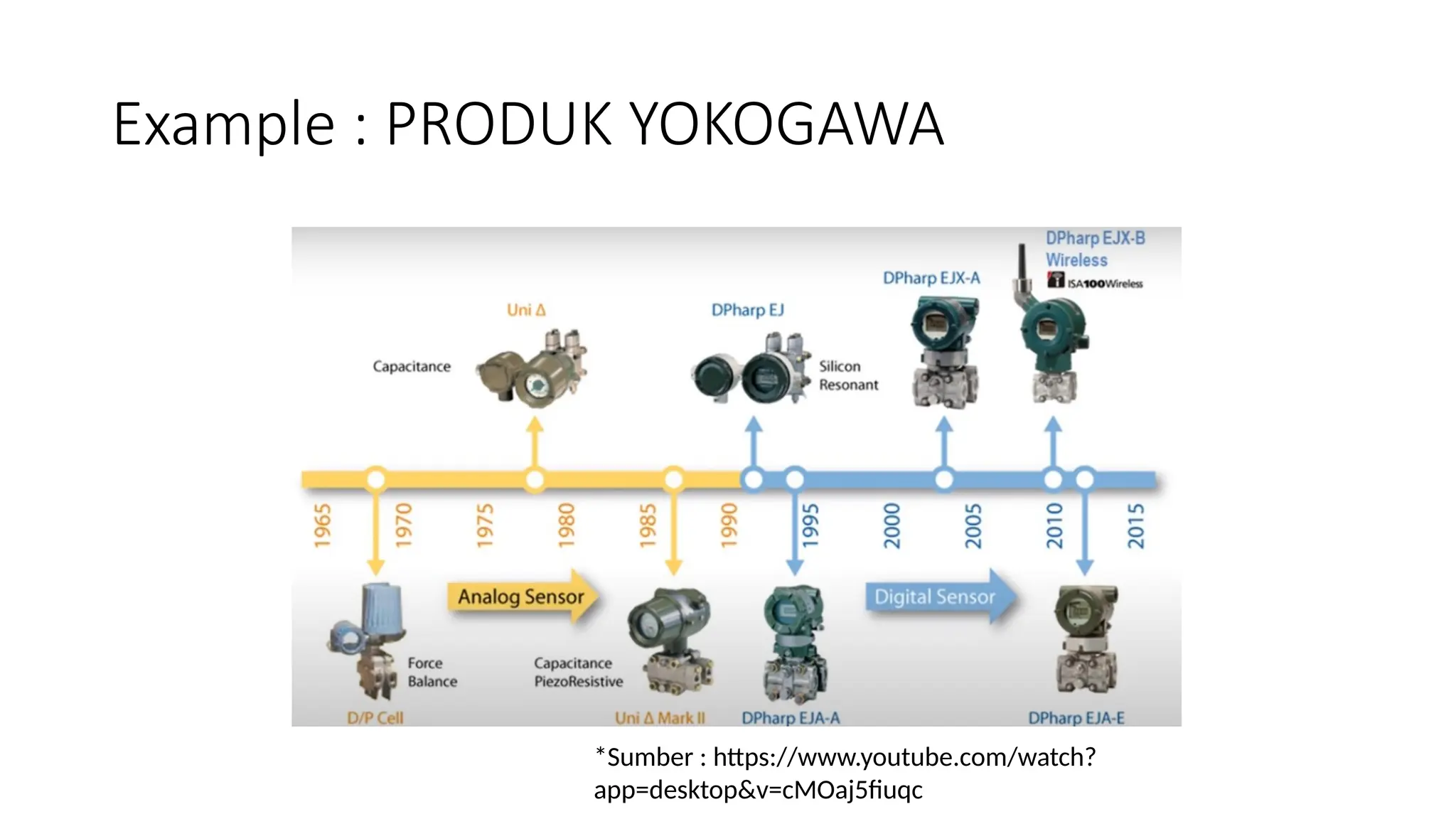
The document discusses sensors, transducers, and transmitters, detailing their definitions, classifications, and applications in various industries. It explains the differences between active and passive sensors, as well as digital and analog sensors, highlighting their roles in converting physical phenomena into electrical signals. Additionally, the text outlines the function of transducers in energy conversion and provides examples of their use in pressure measurement within industries such as oil and gas and pharmaceuticals.

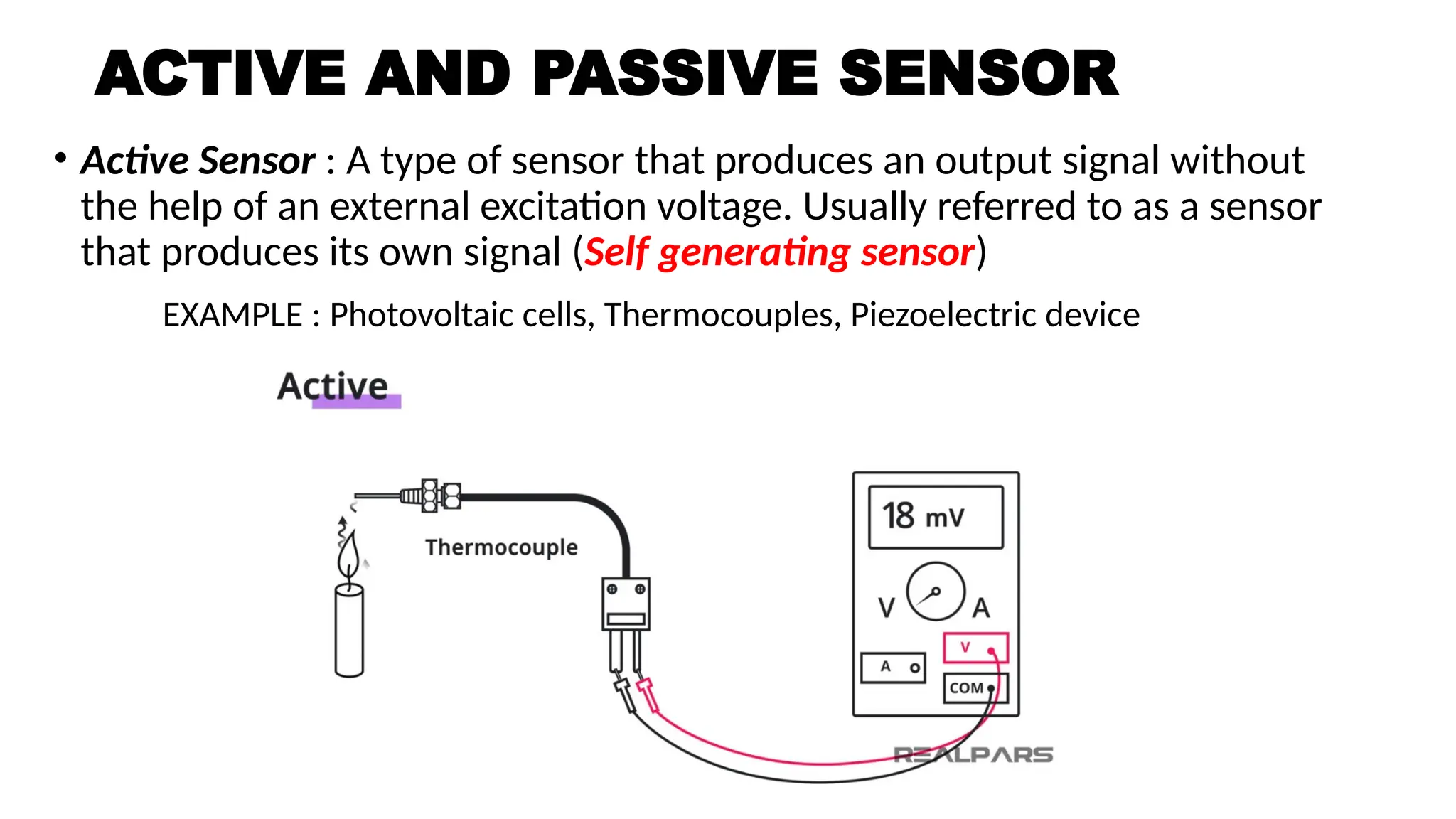
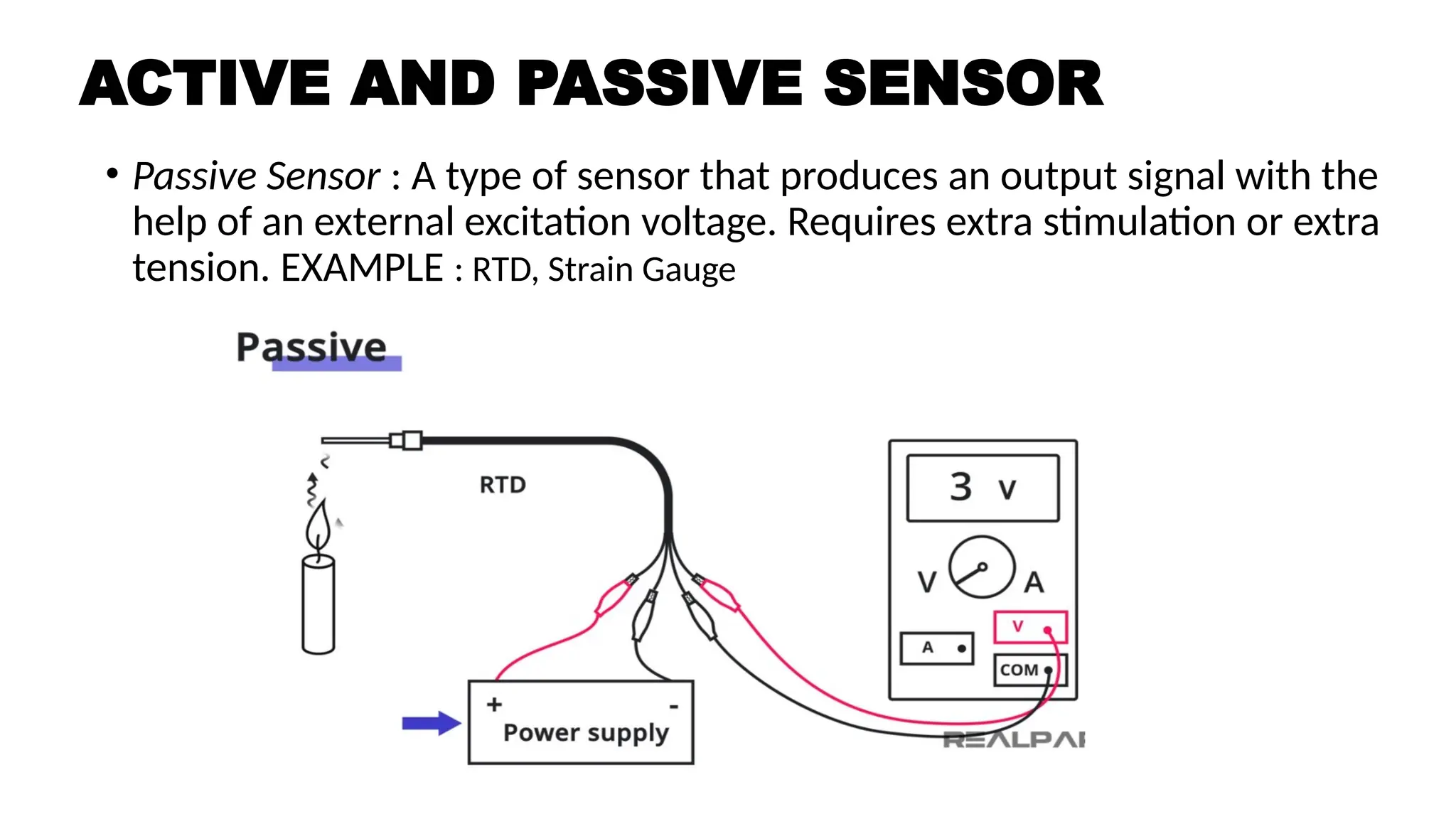
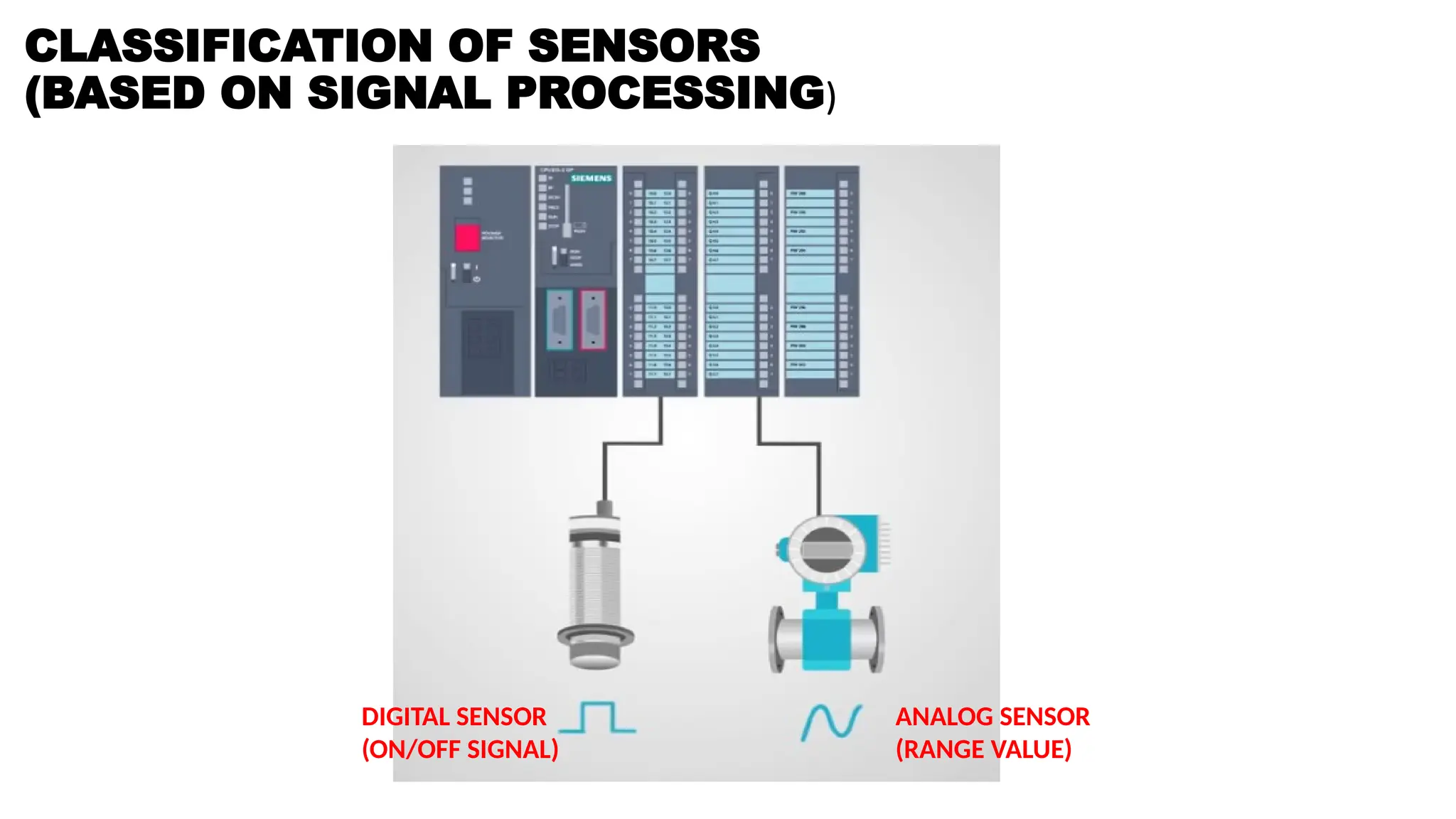
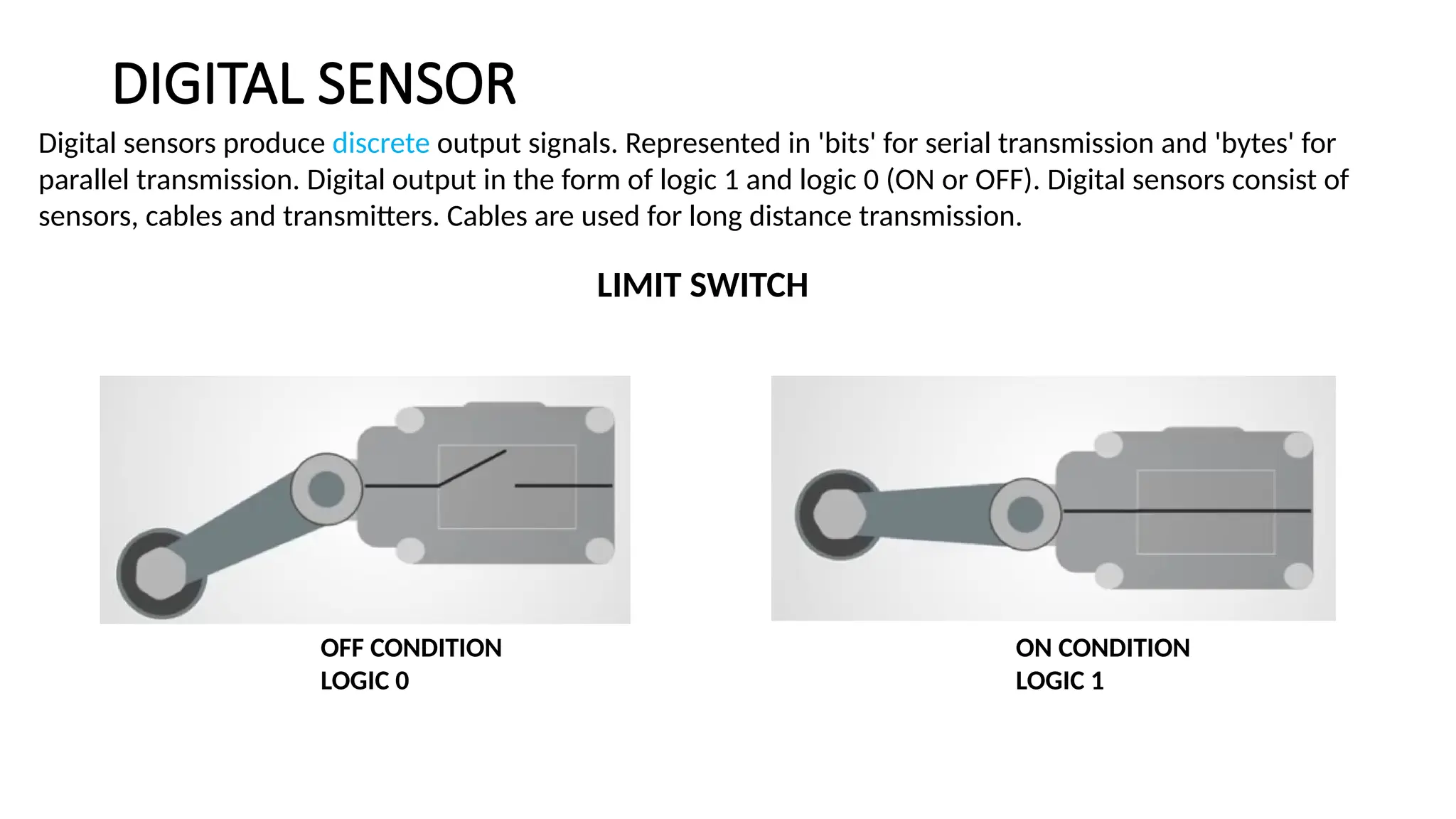
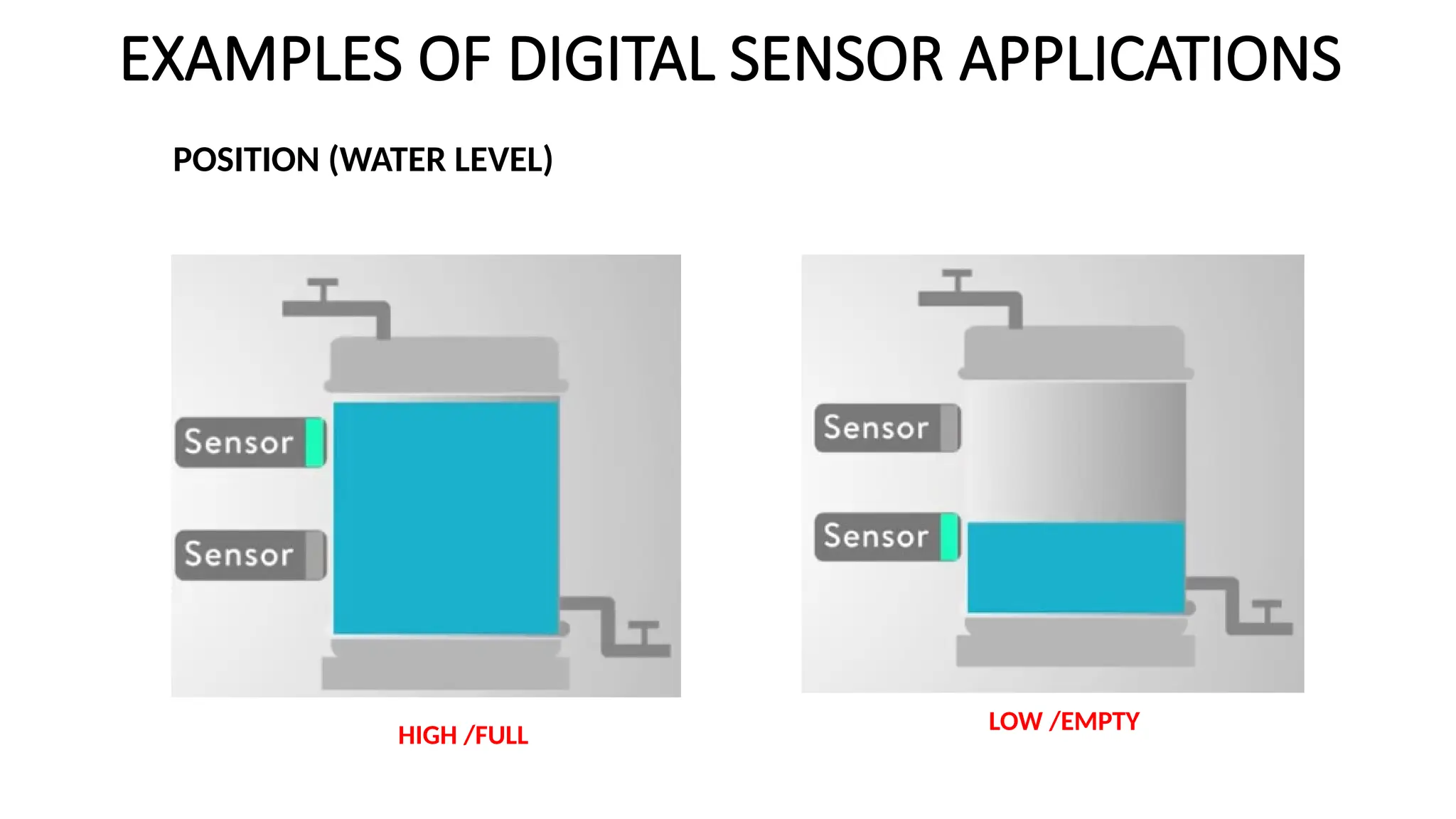
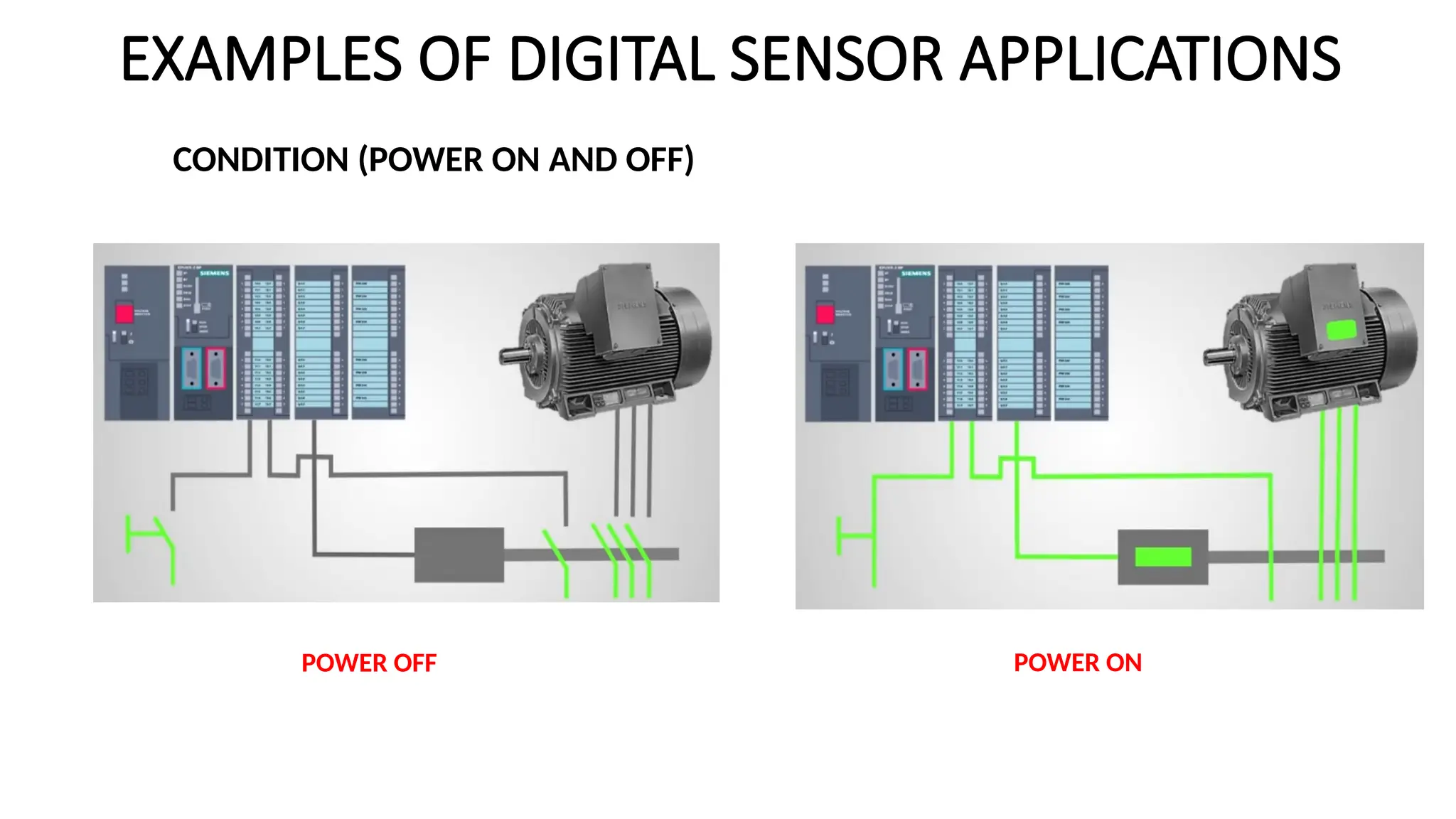
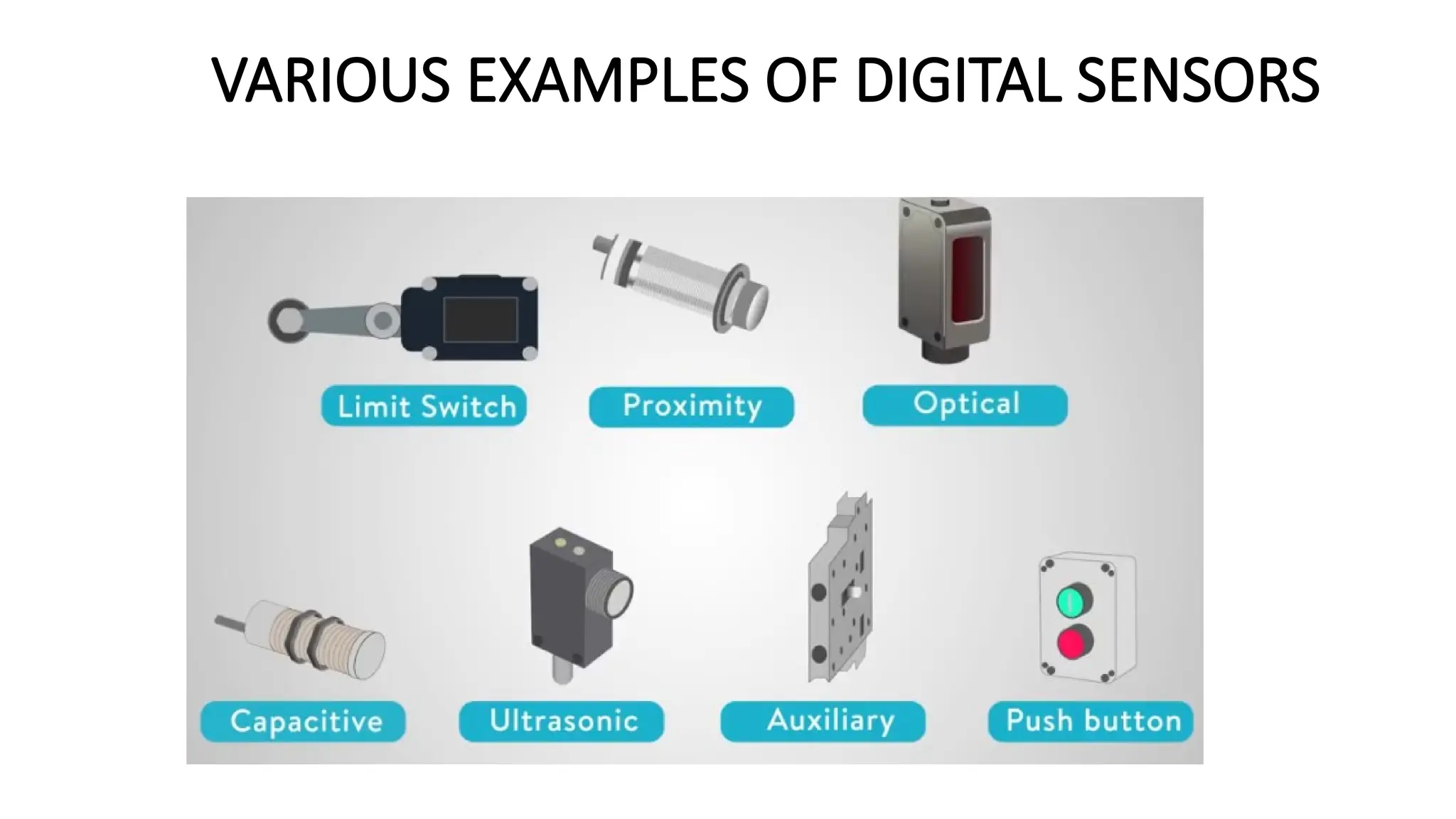
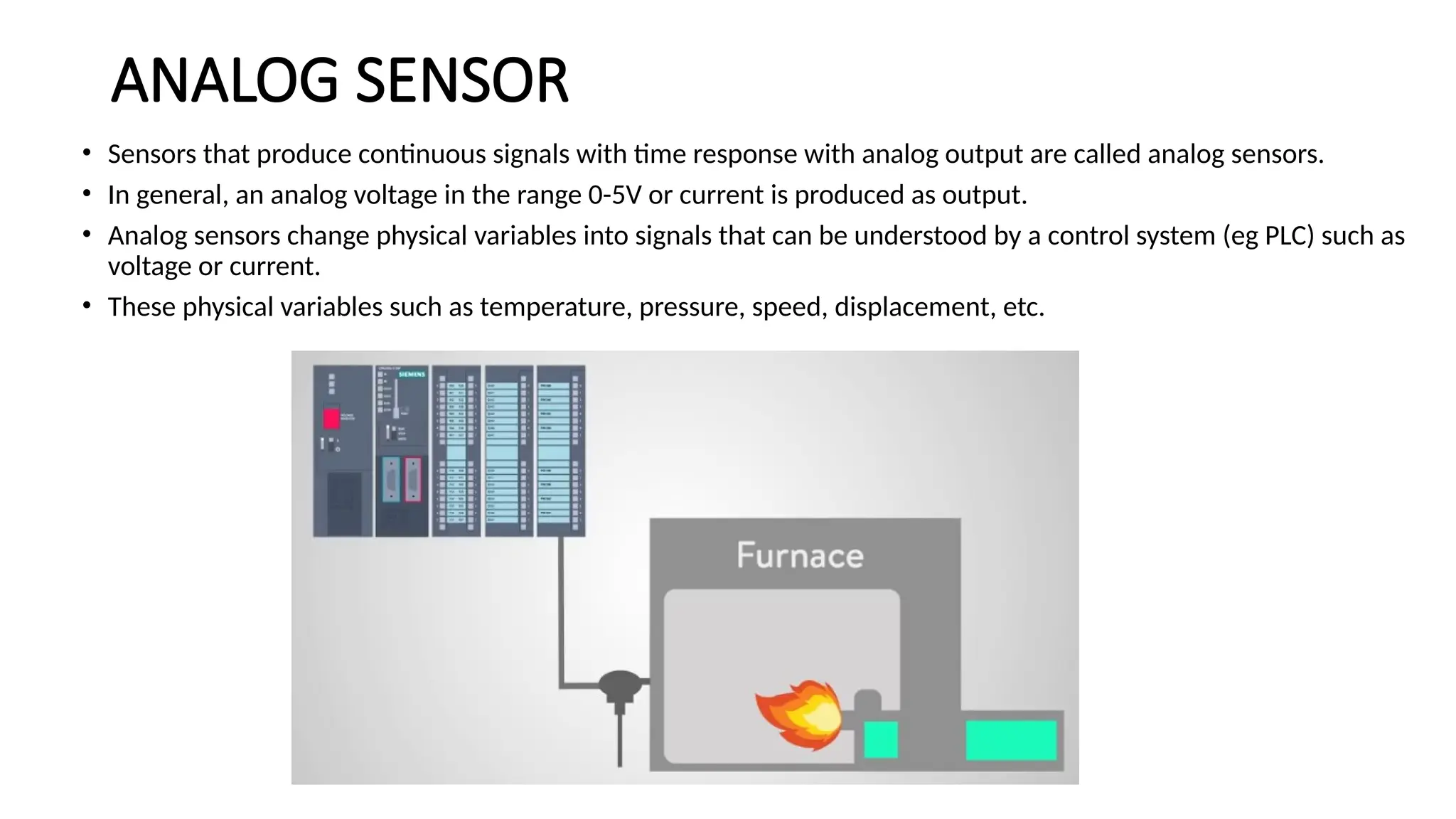

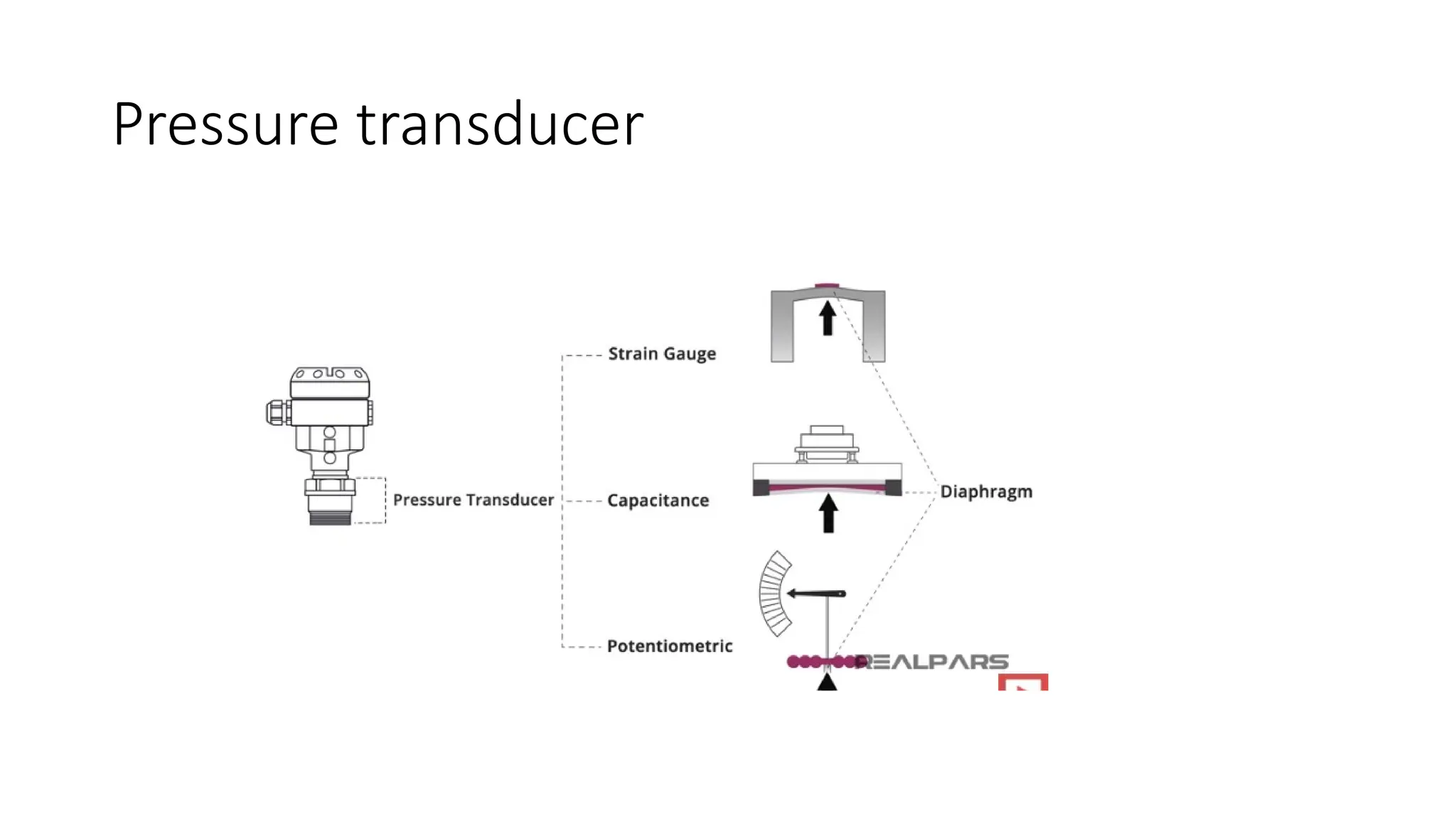
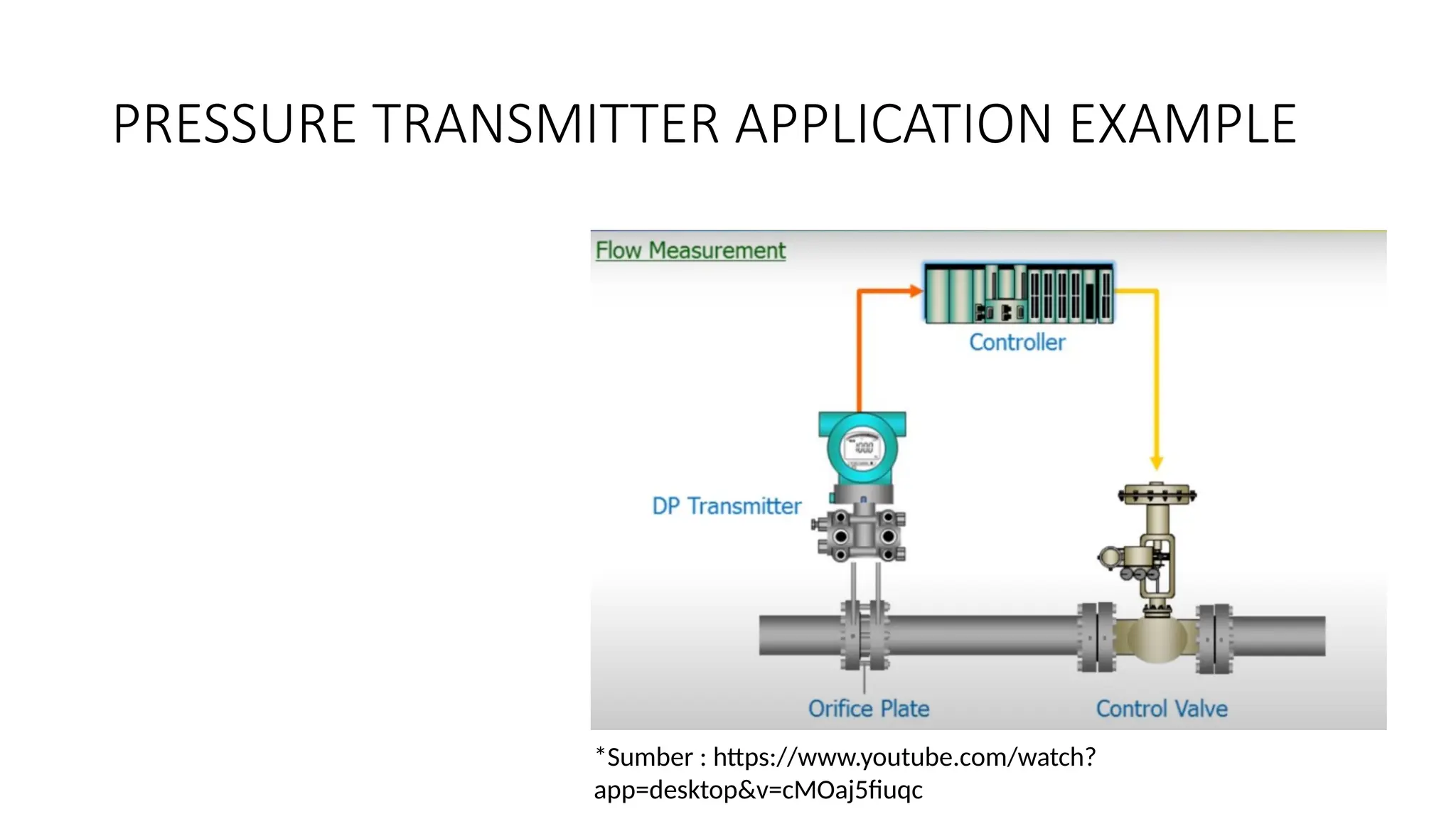
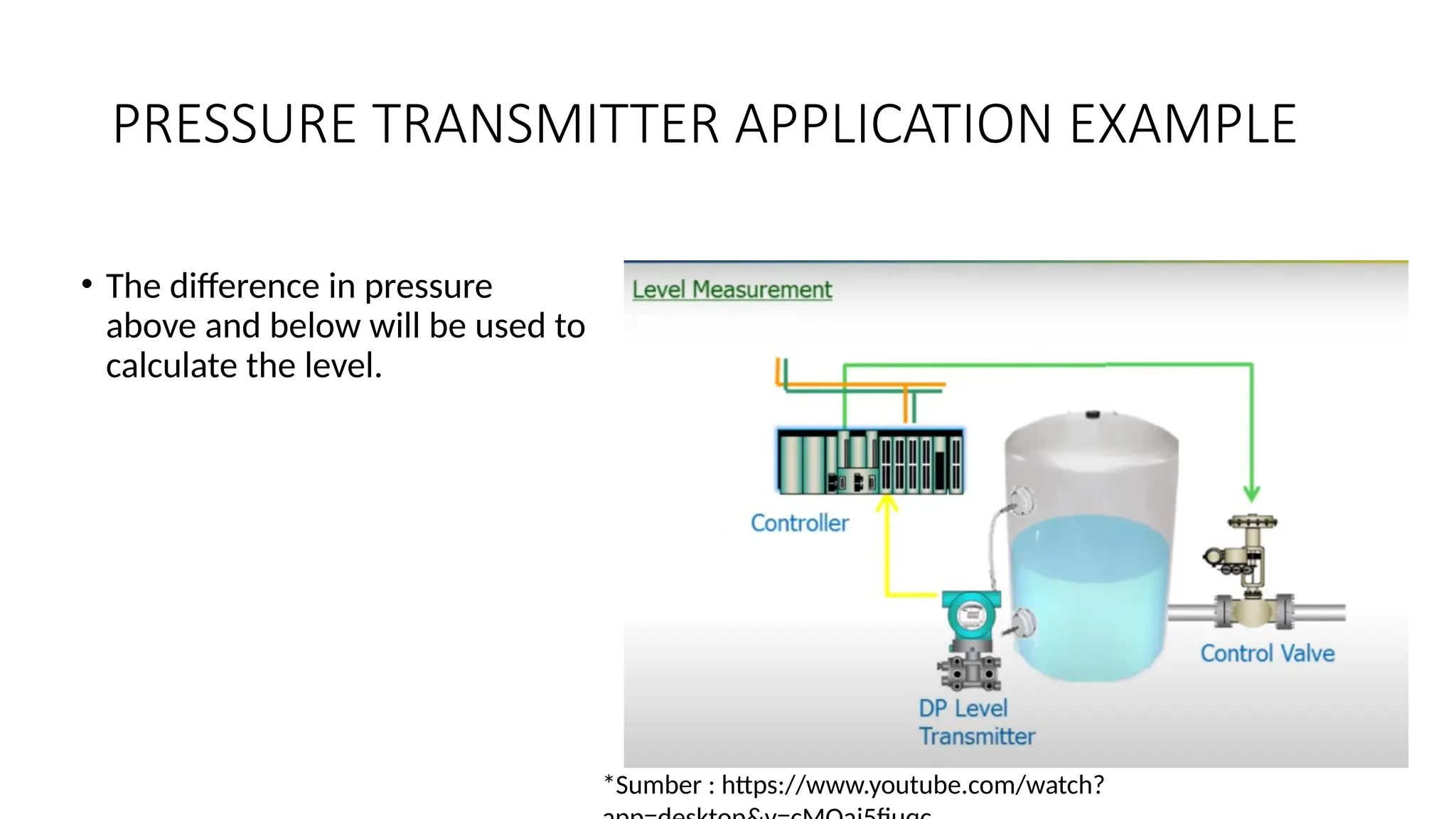
![SENSOR_TRANSDUCER_AND_TRANSMITTER[1].pptx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sensortransducerandtransmitter1-240916094527-d63ff0b6/75/SENSOR_TRANSDUCER_AND_TRANSMITTER-1-pptx-36-2048.jpg)