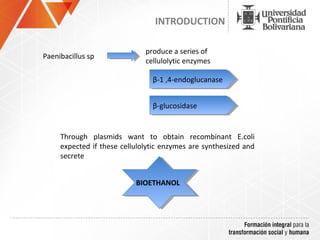
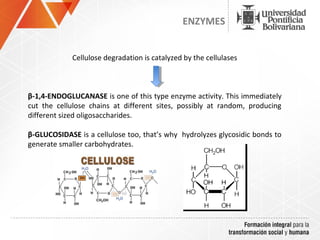
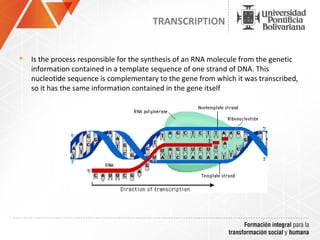
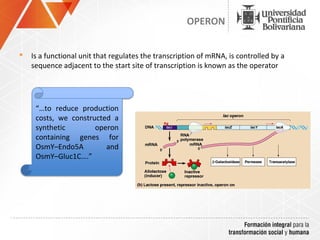
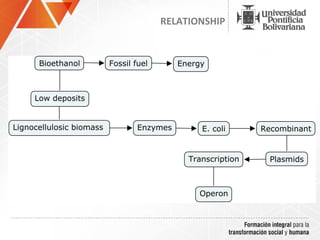
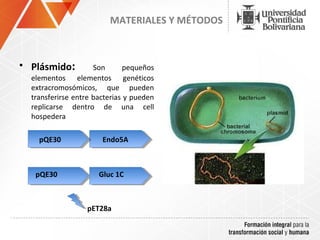
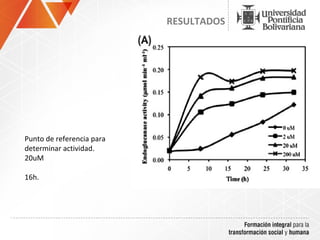
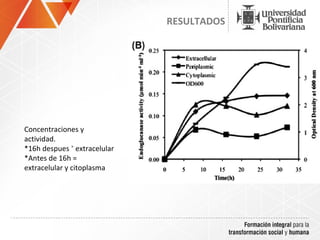
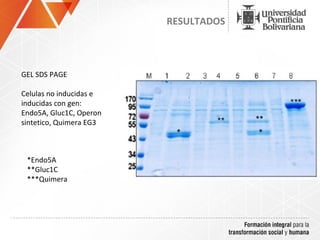
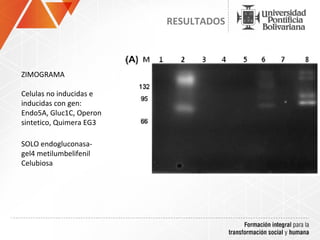
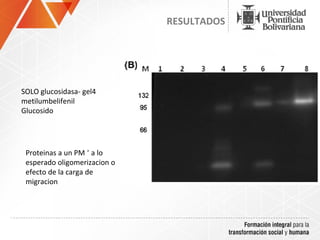
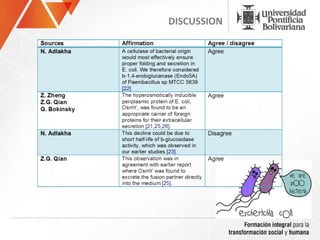
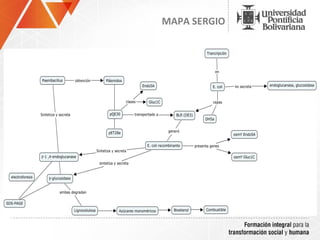
The document summarizes a study on efficiently secreting endoglucanase and beta-glucosidase enzymes extracellularly in E. coli. The researchers constructed a synthetic operon containing genes for OsmY–Endo5A and OsmY–Gluc1C enzymes. They transformed E. coli with plasmids expressing these enzymes individually and as a synthetic operon. Results showed the synthetic operon was more effective at secreting the enzymes extracellularly than a chimeric construct, as measured by enzyme activity assays and SDS-PAGE gels. The study demonstrates the potential for E. coli to efficiently secrete cellulolytic enzymes for the production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic biomass