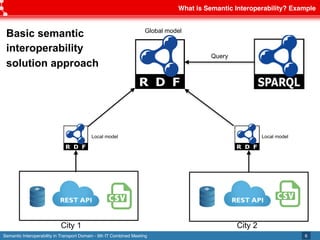
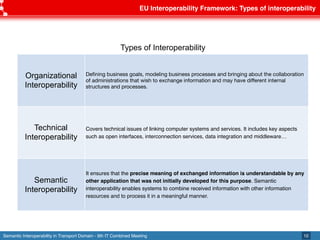
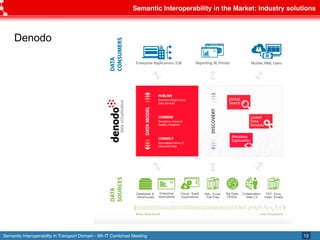
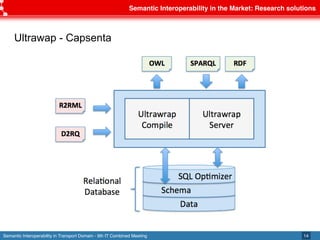
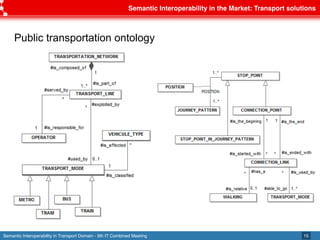
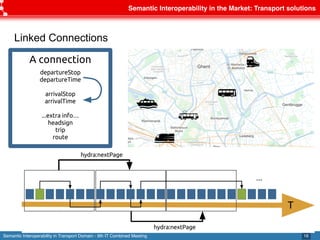
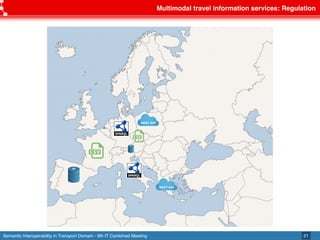
The document discusses semantic interoperability in the transport domain, defining it as the ability of systems to exchange information based on its meaning. It outlines the European Interoperability Framework and its principles, types of interoperability, and key challenges and enablers for multimodal travel information services. Additionally, it highlights both industry and research solutions aimed at improving interoperability in the transport sector.