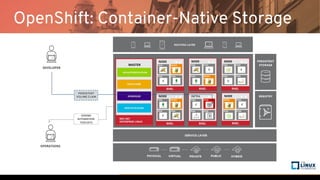
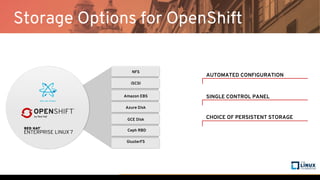
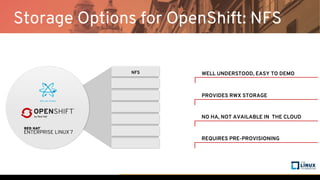
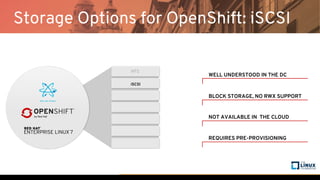
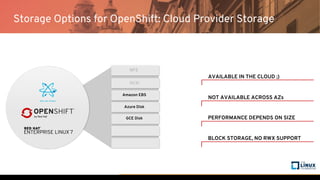
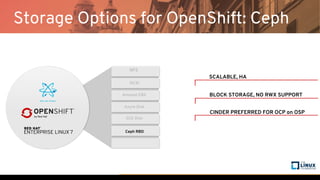
The document discusses the importance of persistent storage for containerized applications, detailing types of persistent volumes and their access modes. It highlights the need for persistent storage due to containers being stateless and the necessity to retain data across runs. Various storage options, including NFS, iSCSI, and GlusterFS, are presented, along with their respective performance characteristics and use cases.