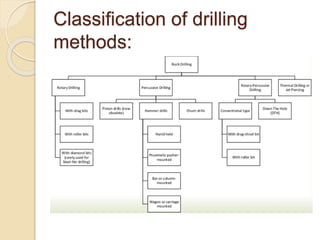
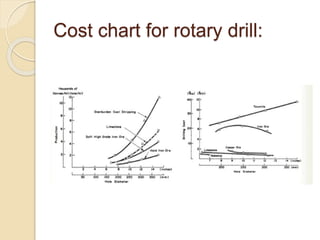
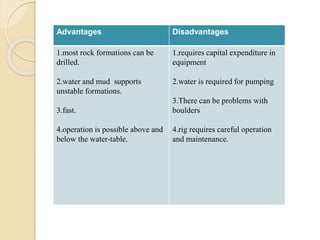
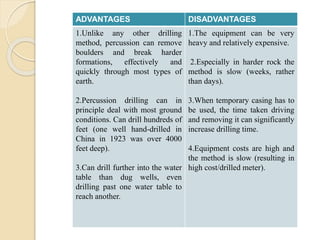
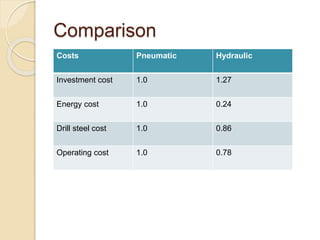
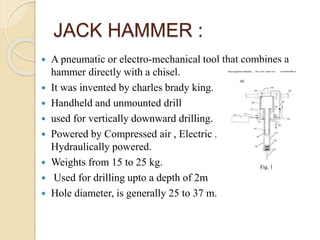
This document discusses methods for selecting drilling equipment and operations for rock breakage. It describes various drilling classification systems including mechanical, thermal, hydraulic, sonic, chemical, electrical and nuclear. The main types of drilling operations covered are rotary and percussion. Factors for selecting drills include site conditions, rock type, drillability, operating variables, performance, availability and cost. Advantages and disadvantages of rotary and percussion drilling are provided. Examples of drilling equipment like jackhammers and wagon drills are also described.