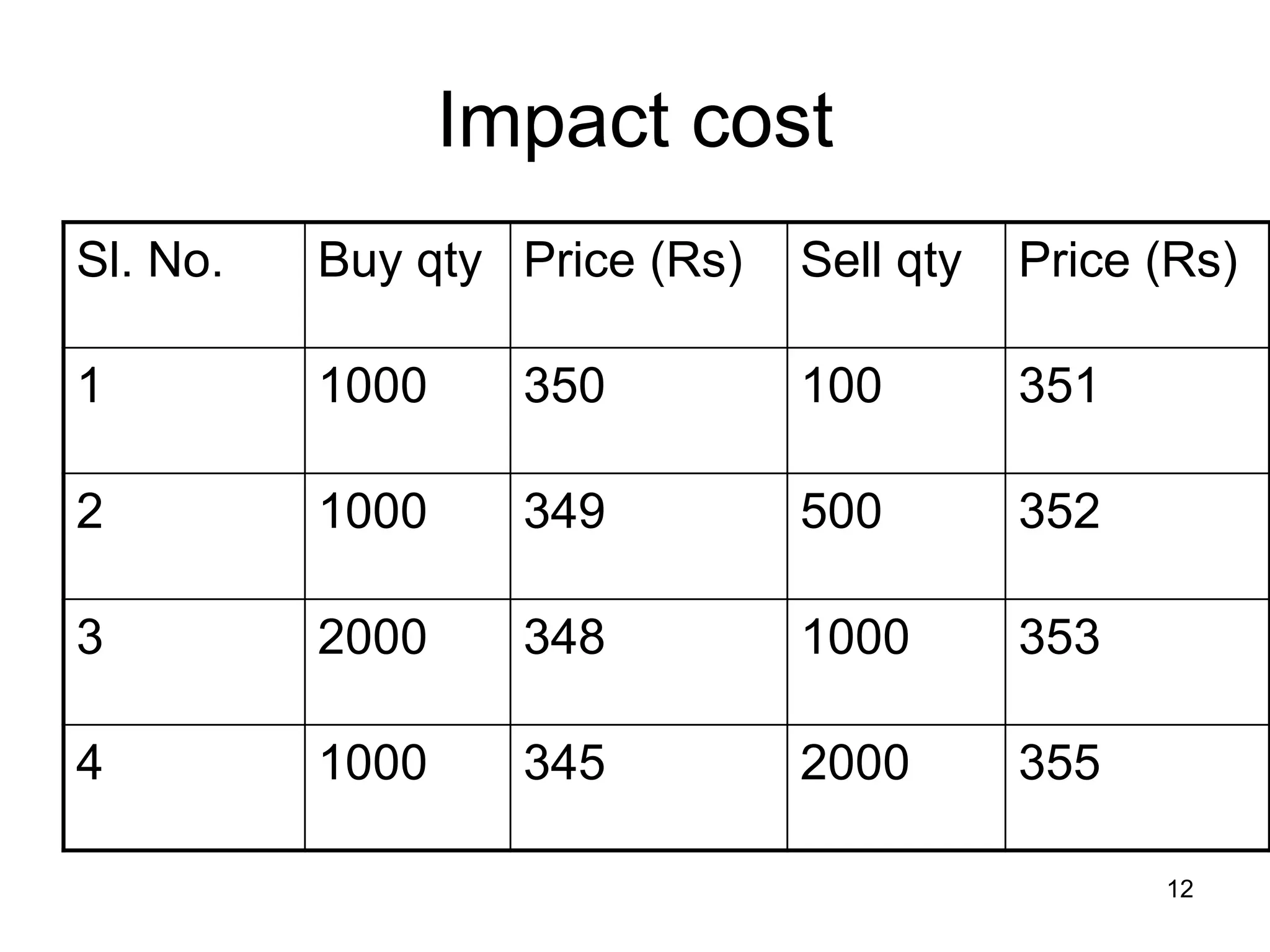
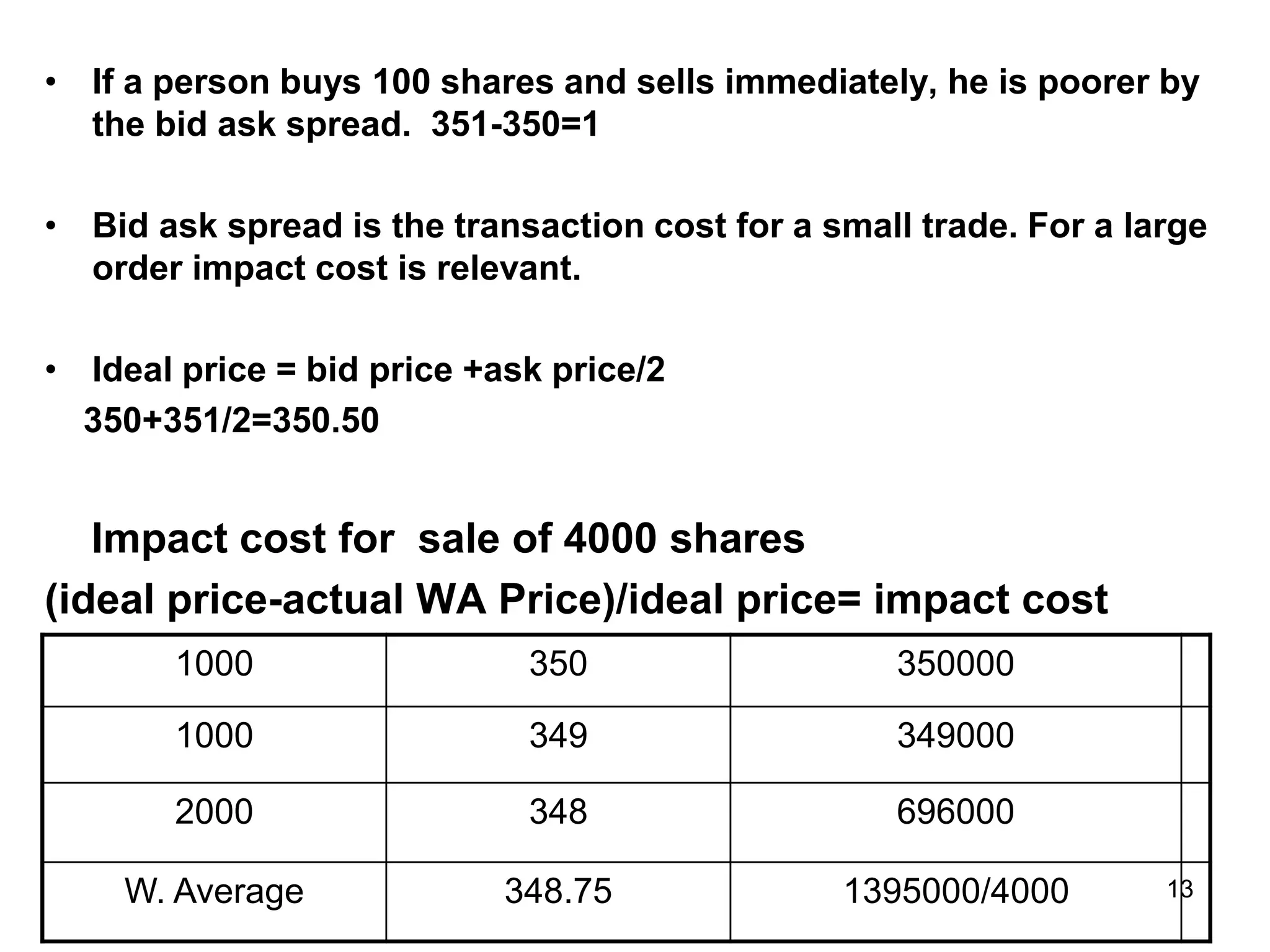
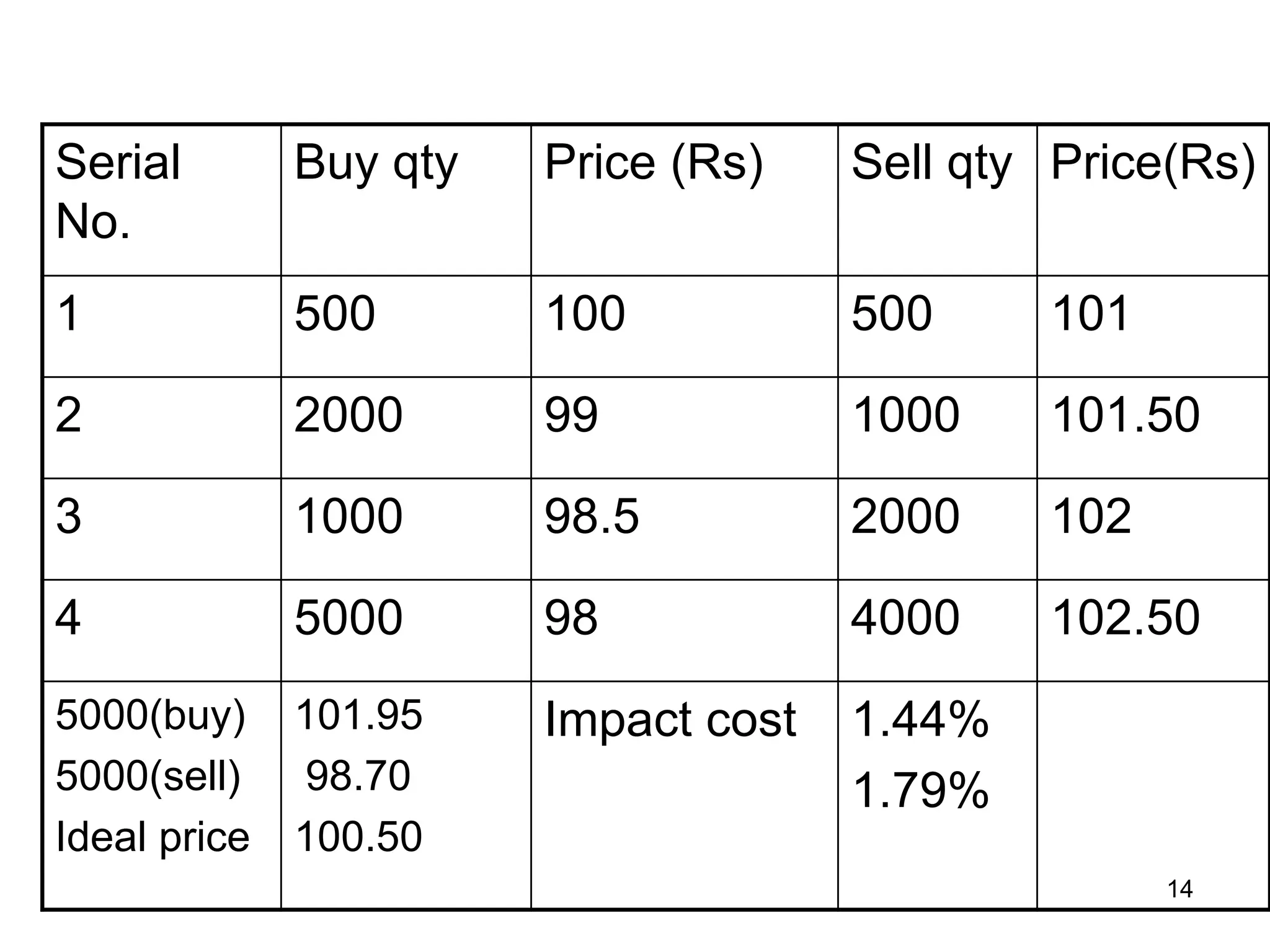
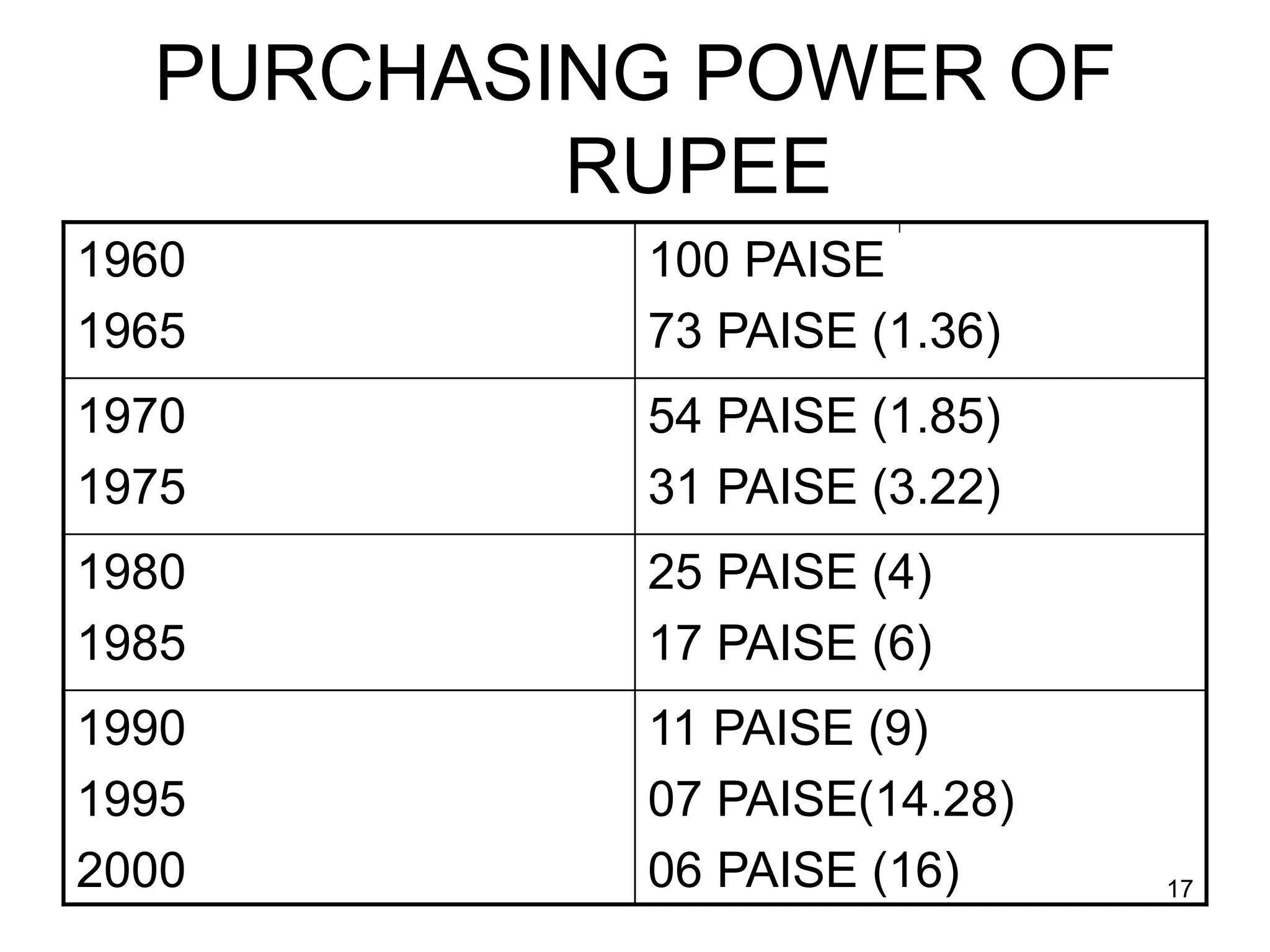
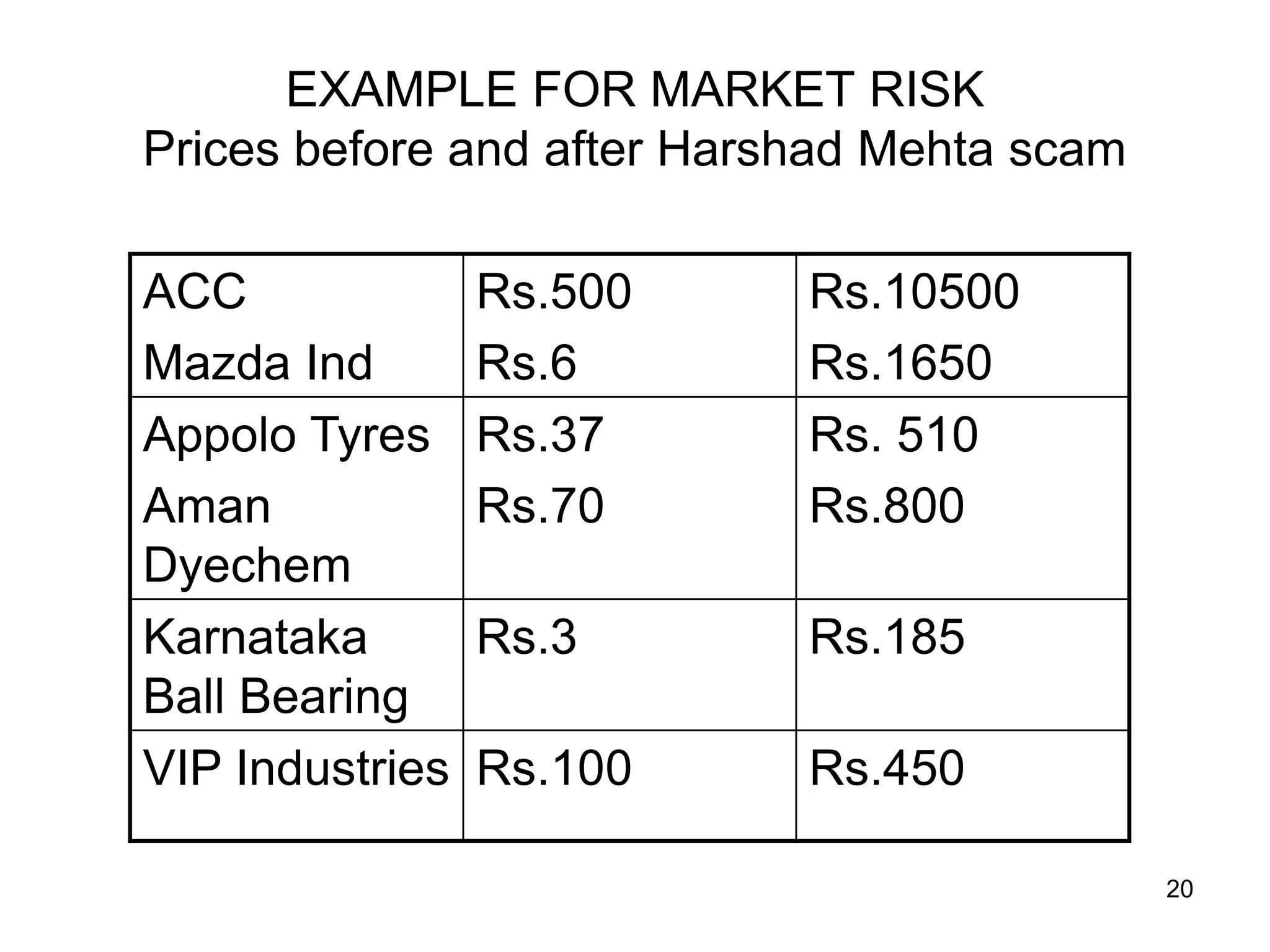
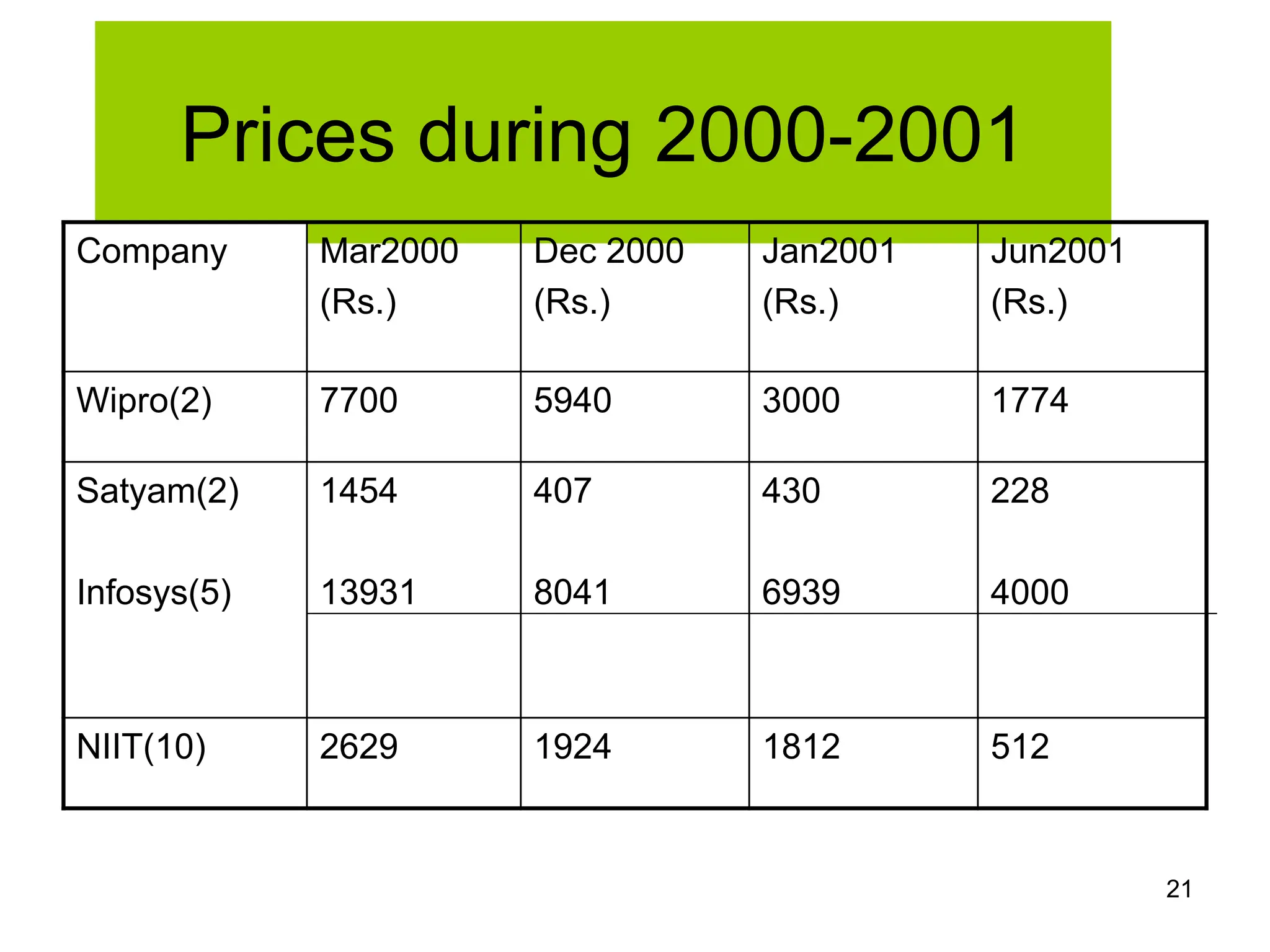
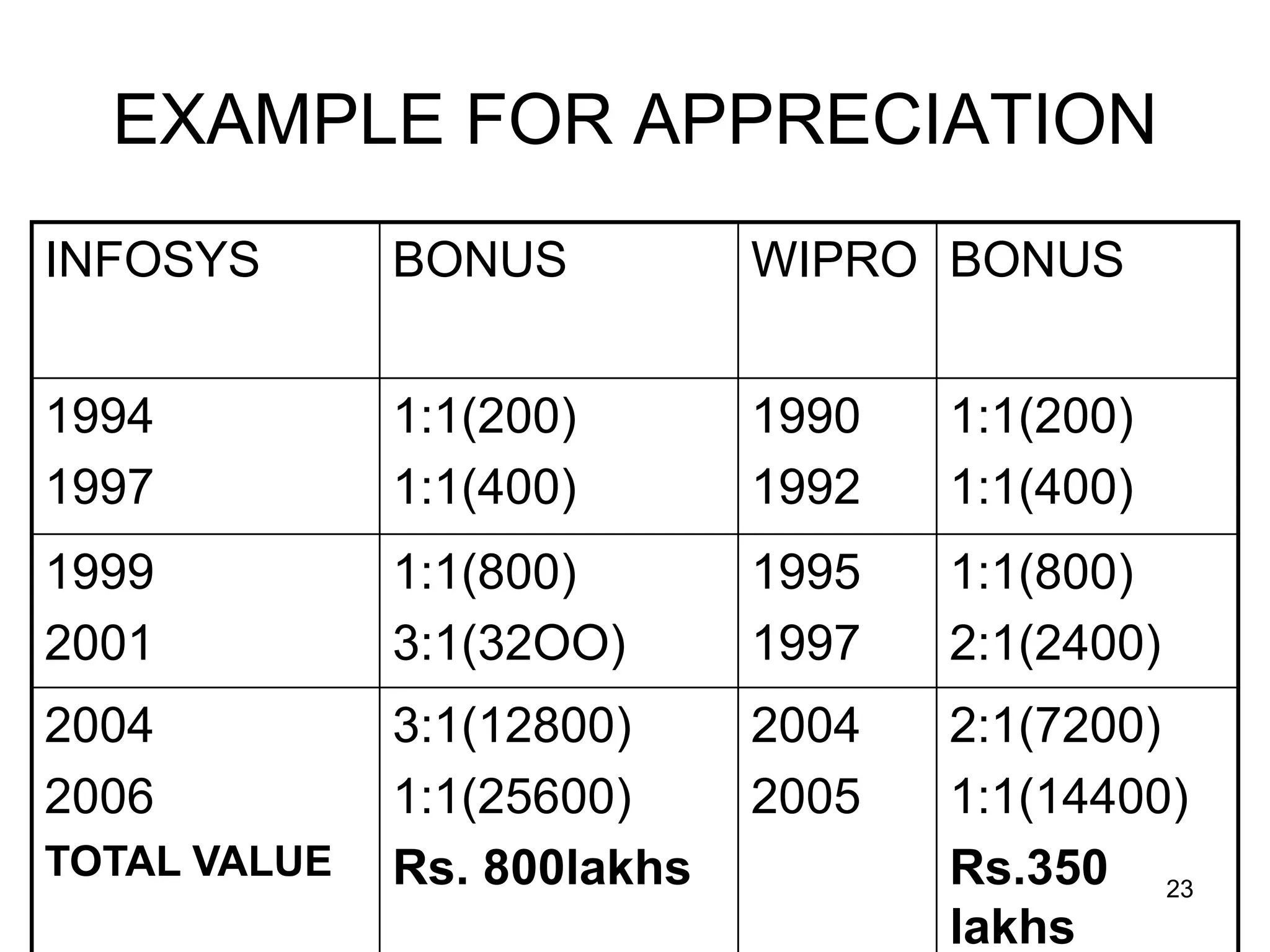
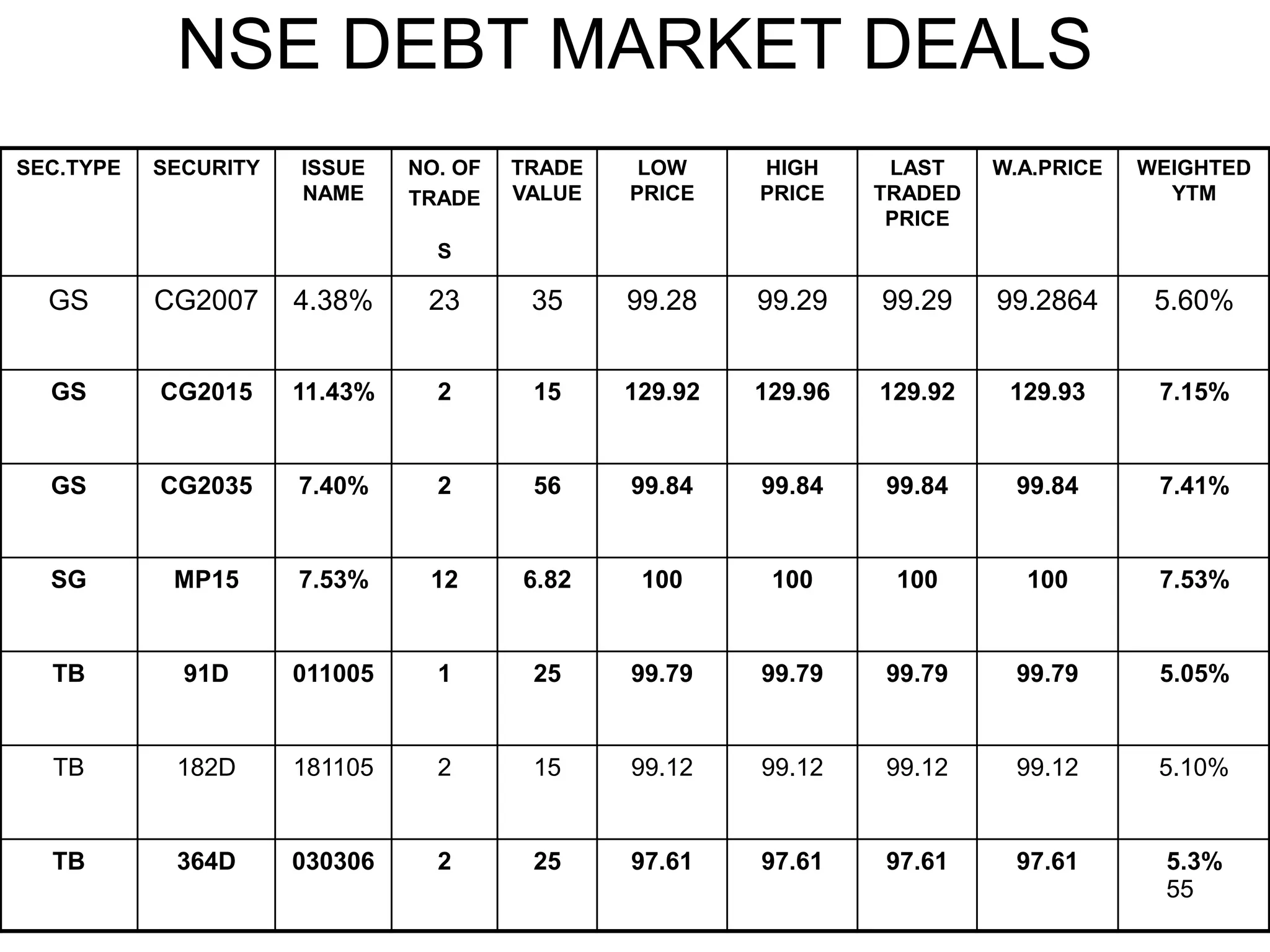
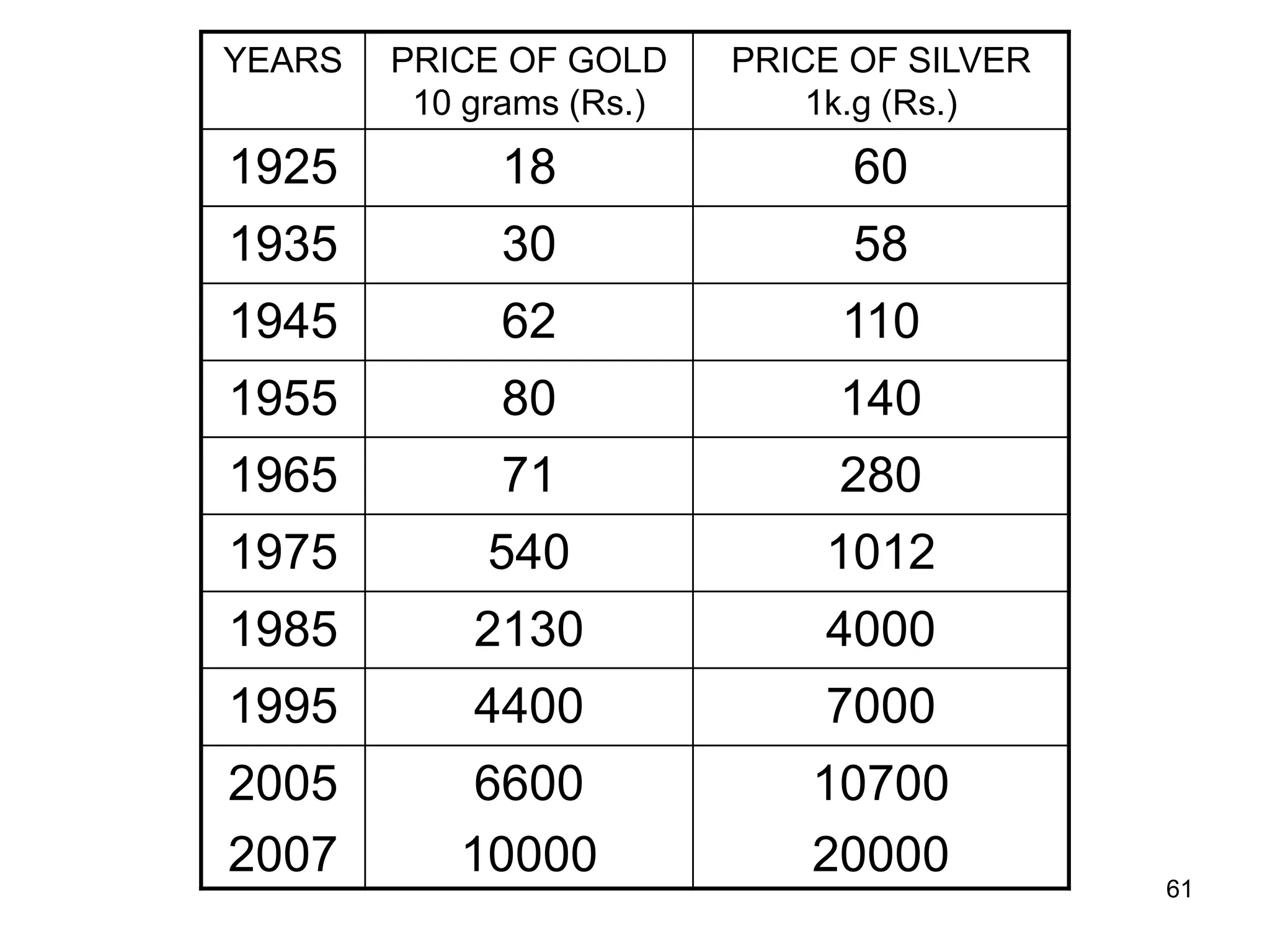
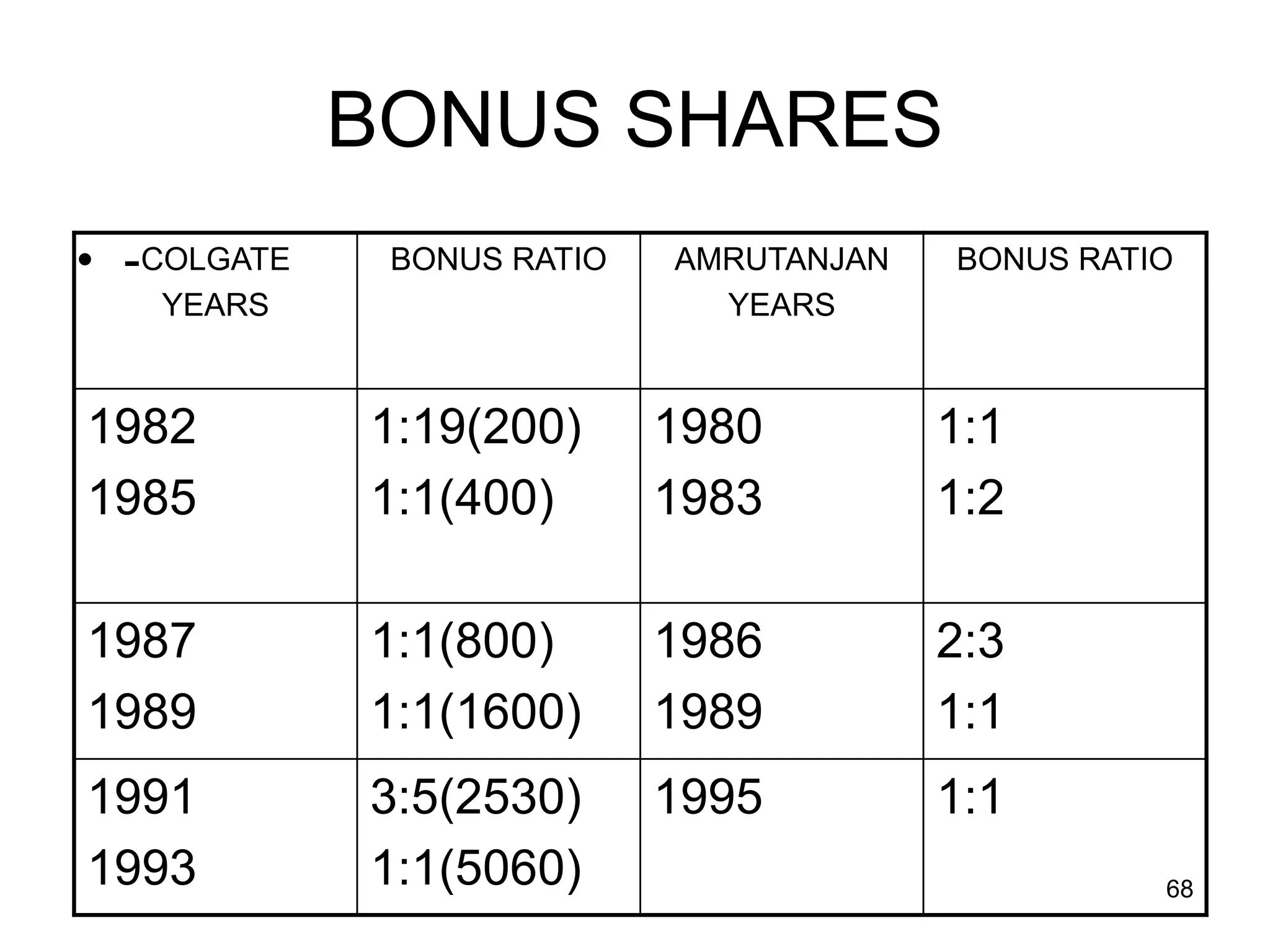
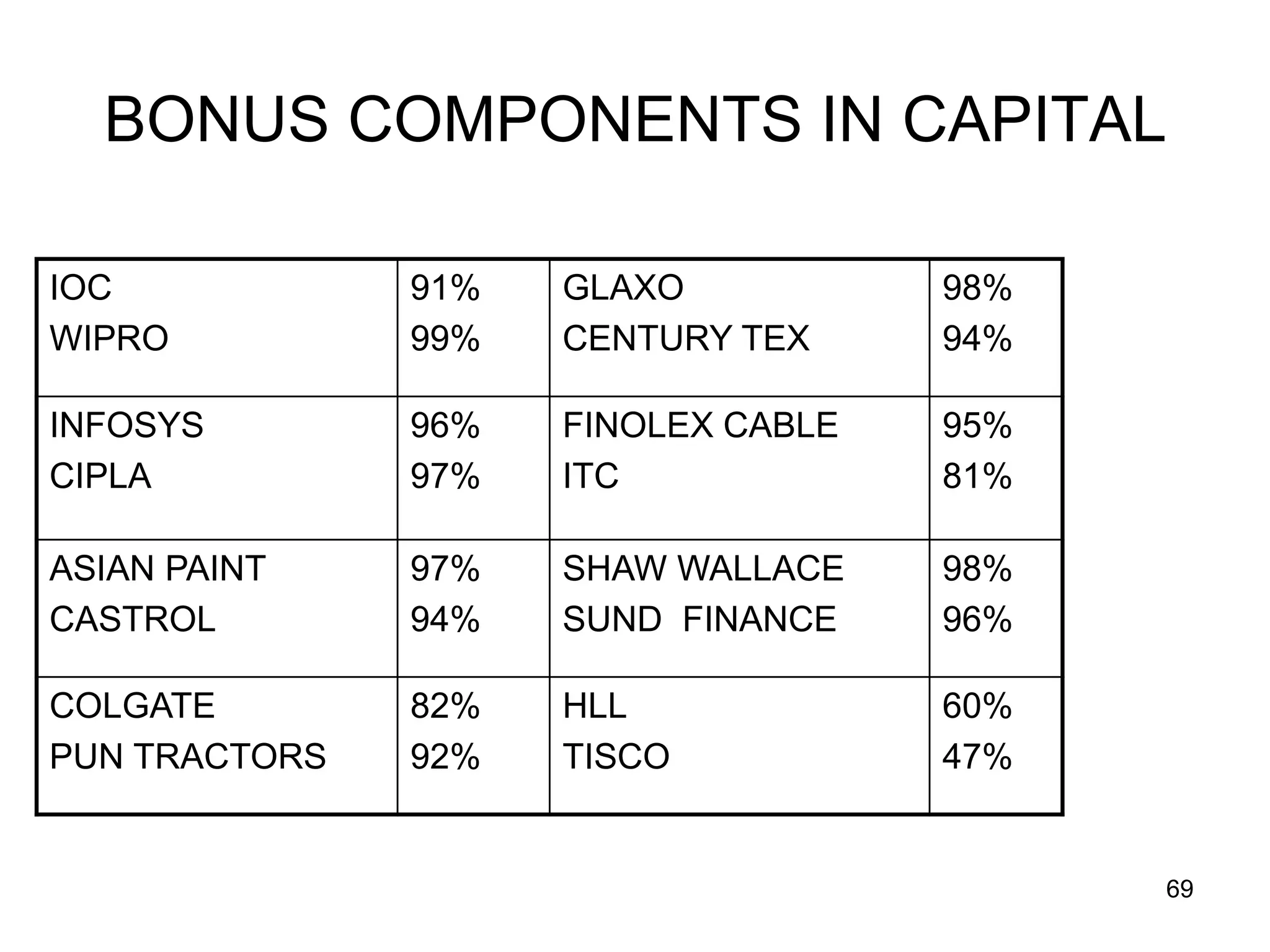
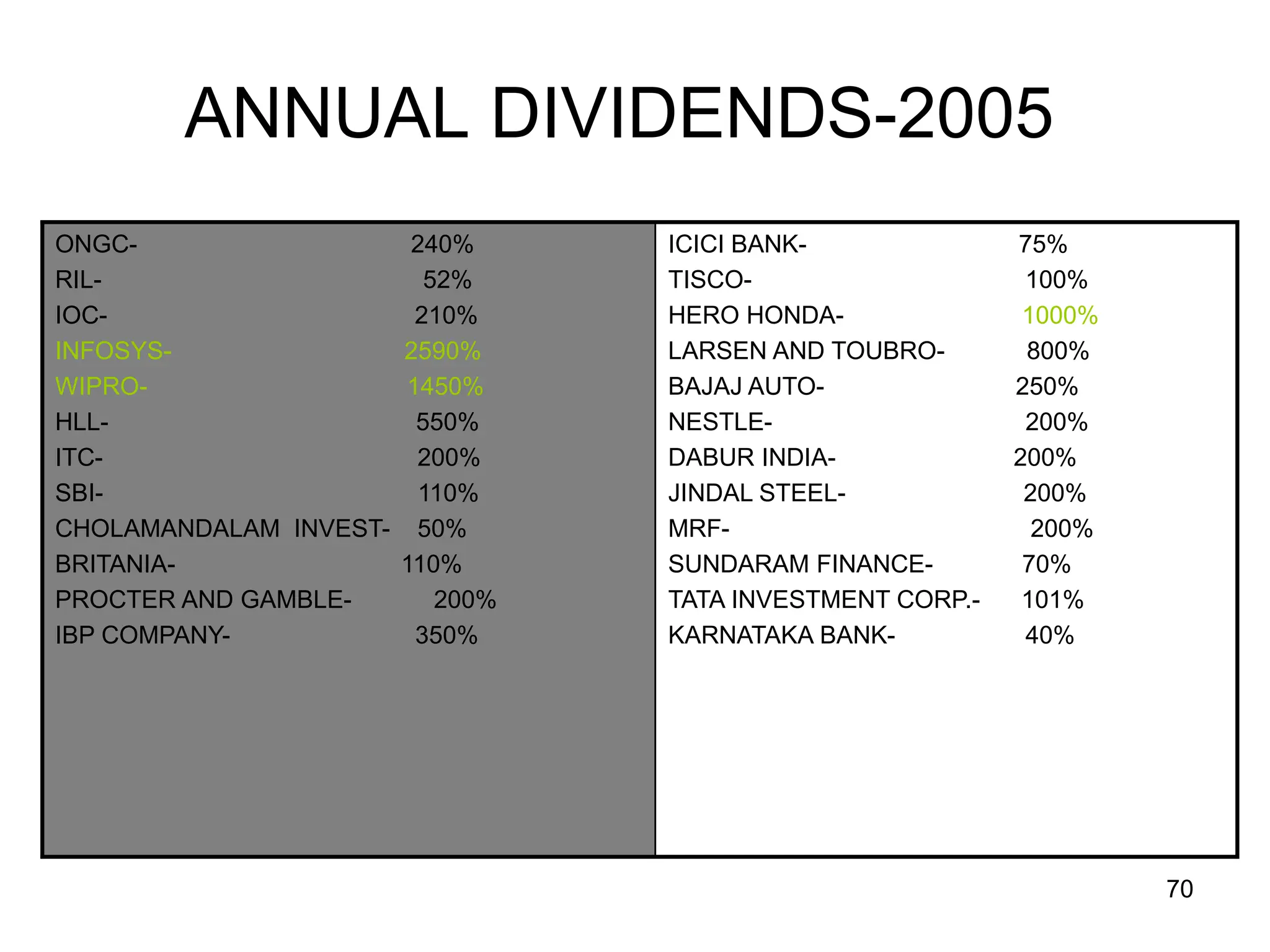
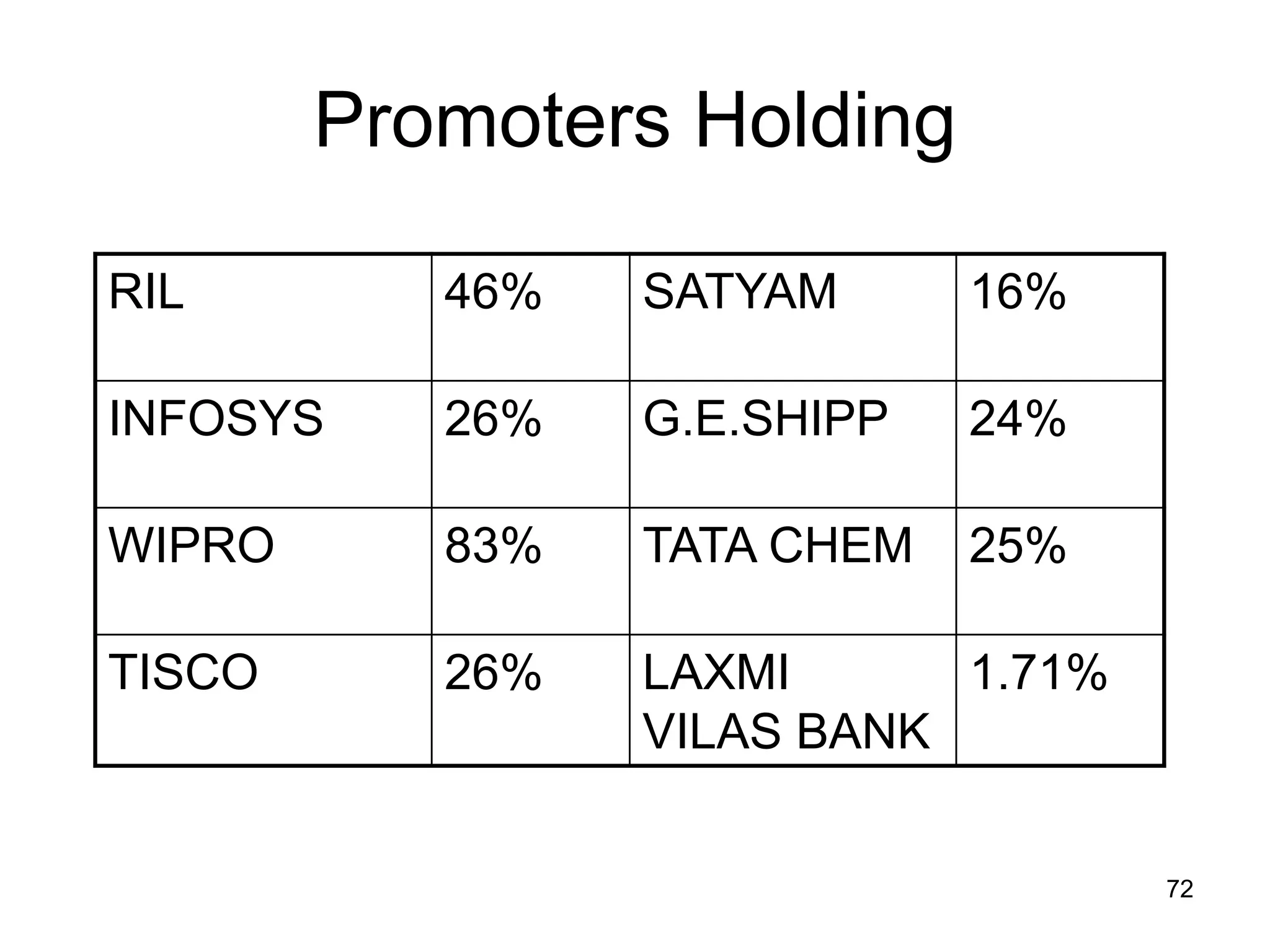
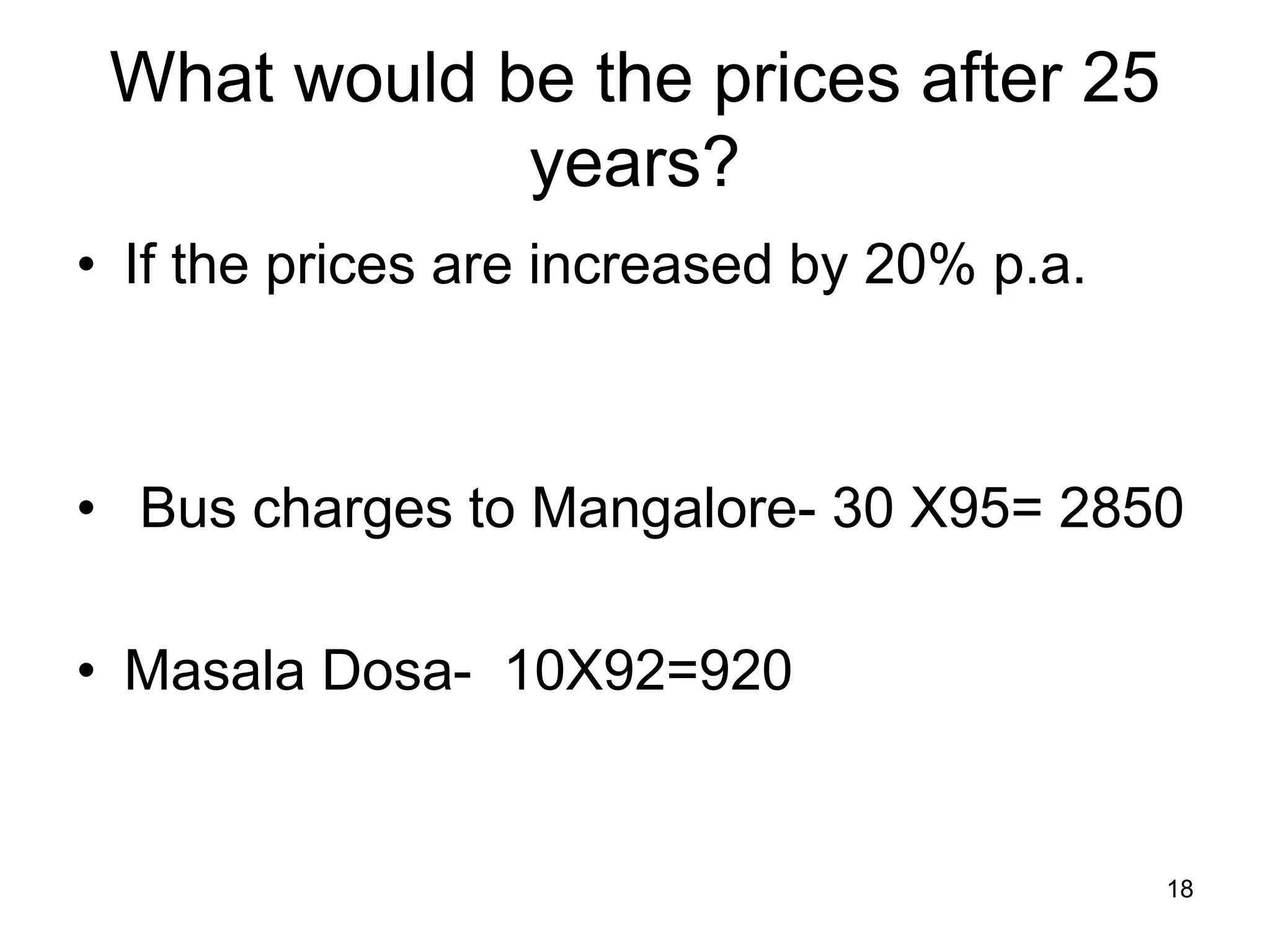The document discusses various aspects of finance, including investment strategies, risks, and financial instruments like debentures, shares, and mutual funds. It provides insights into market behavior, the impact of interest rates, and different types of investments while emphasizing the importance of strategic financial planning. Key concepts such as investment risk, speculation, and the characteristics of various financial products are also covered.