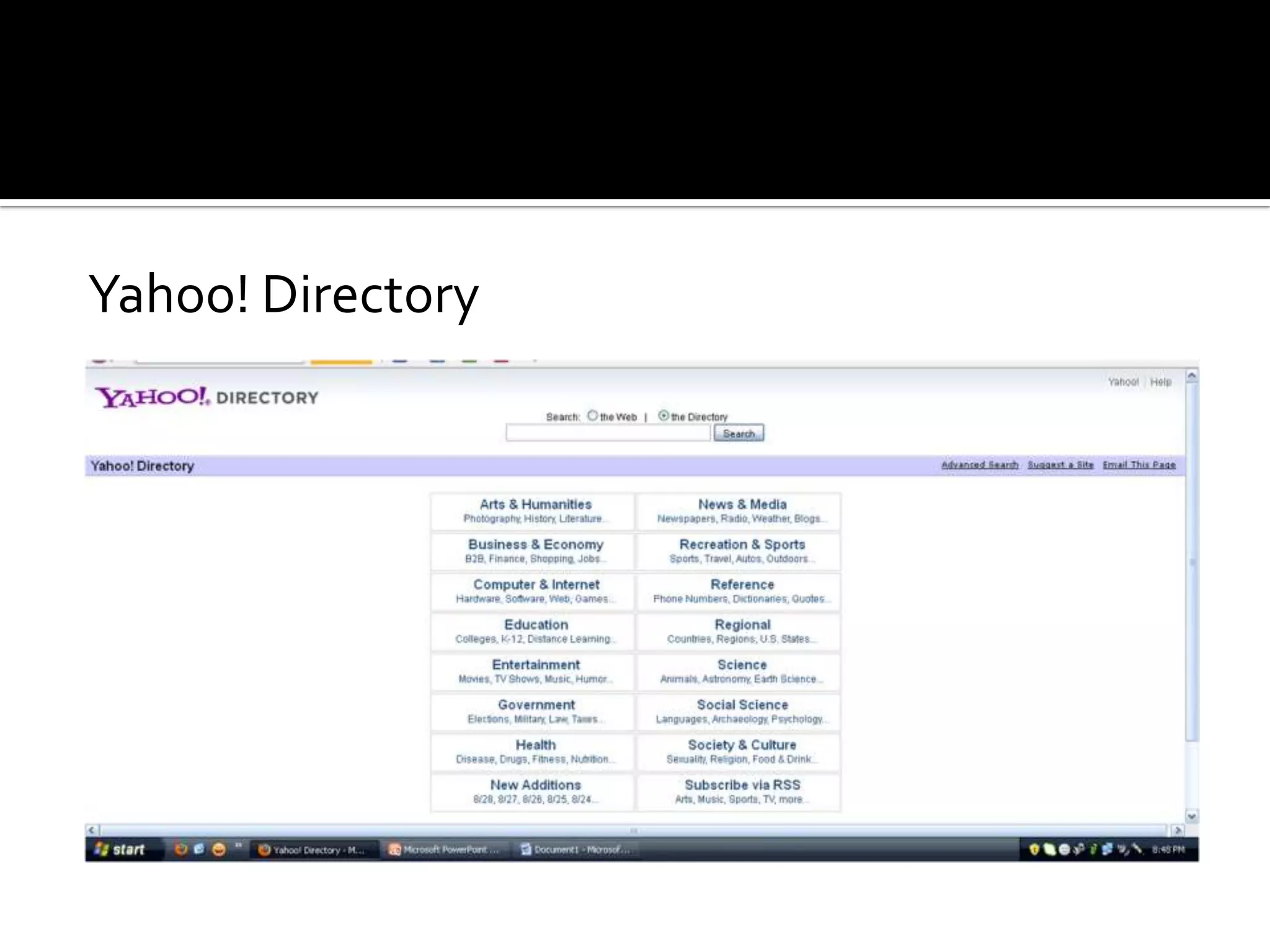
The document discusses search engines and web directories. It explains that search engines use web crawlers to discover and index web pages in their database so that users can search for keywords. When a user searches, the search engine returns a ranked list of relevant documents. Popular search engines include Google, Bing, and Yahoo. In contrast, web directories organize websites into categories edited by humans rather than searching keywords. Some criteria for evaluating information on websites are accuracy, authority, objectivity, currency, and coverage.