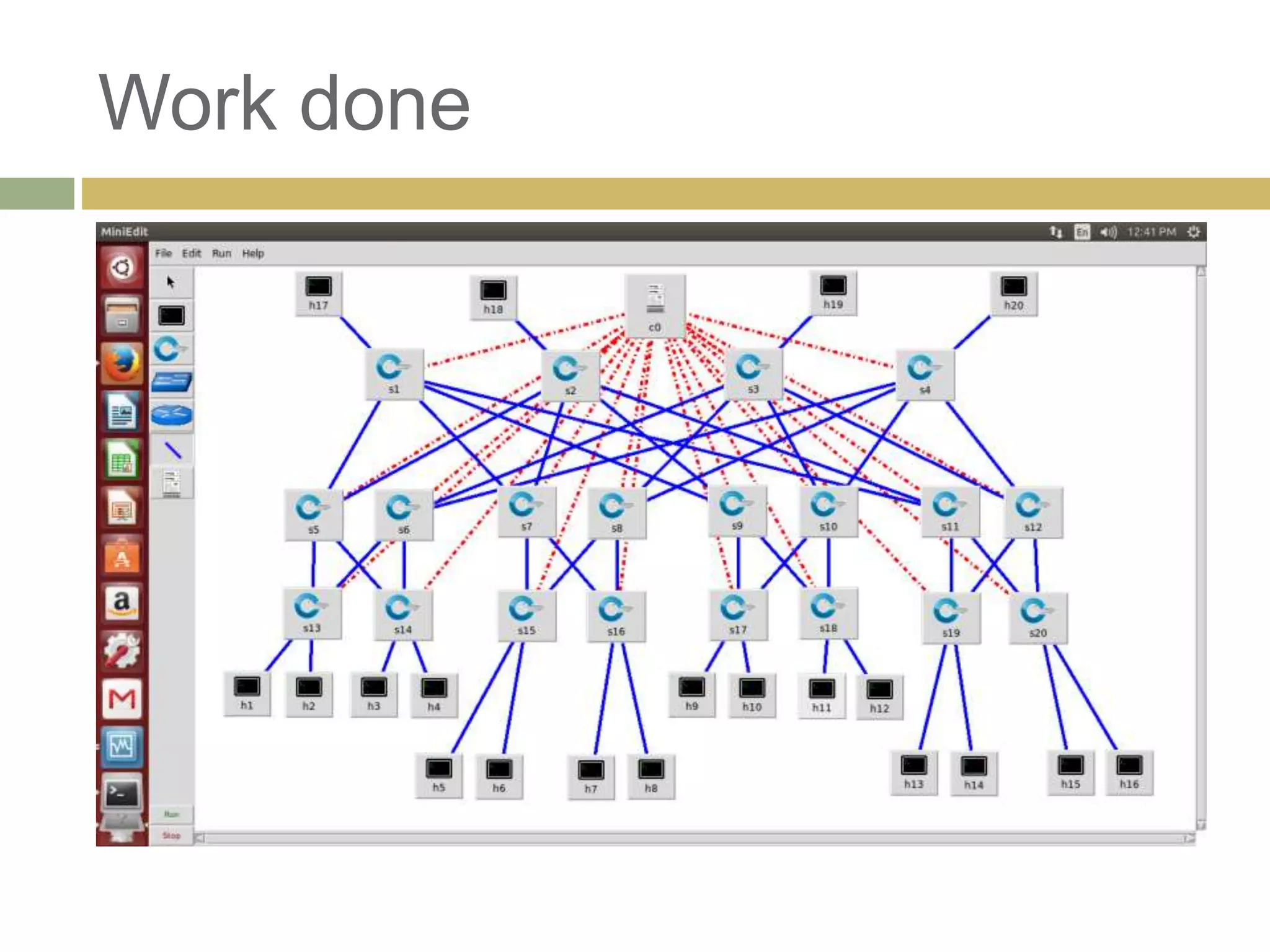
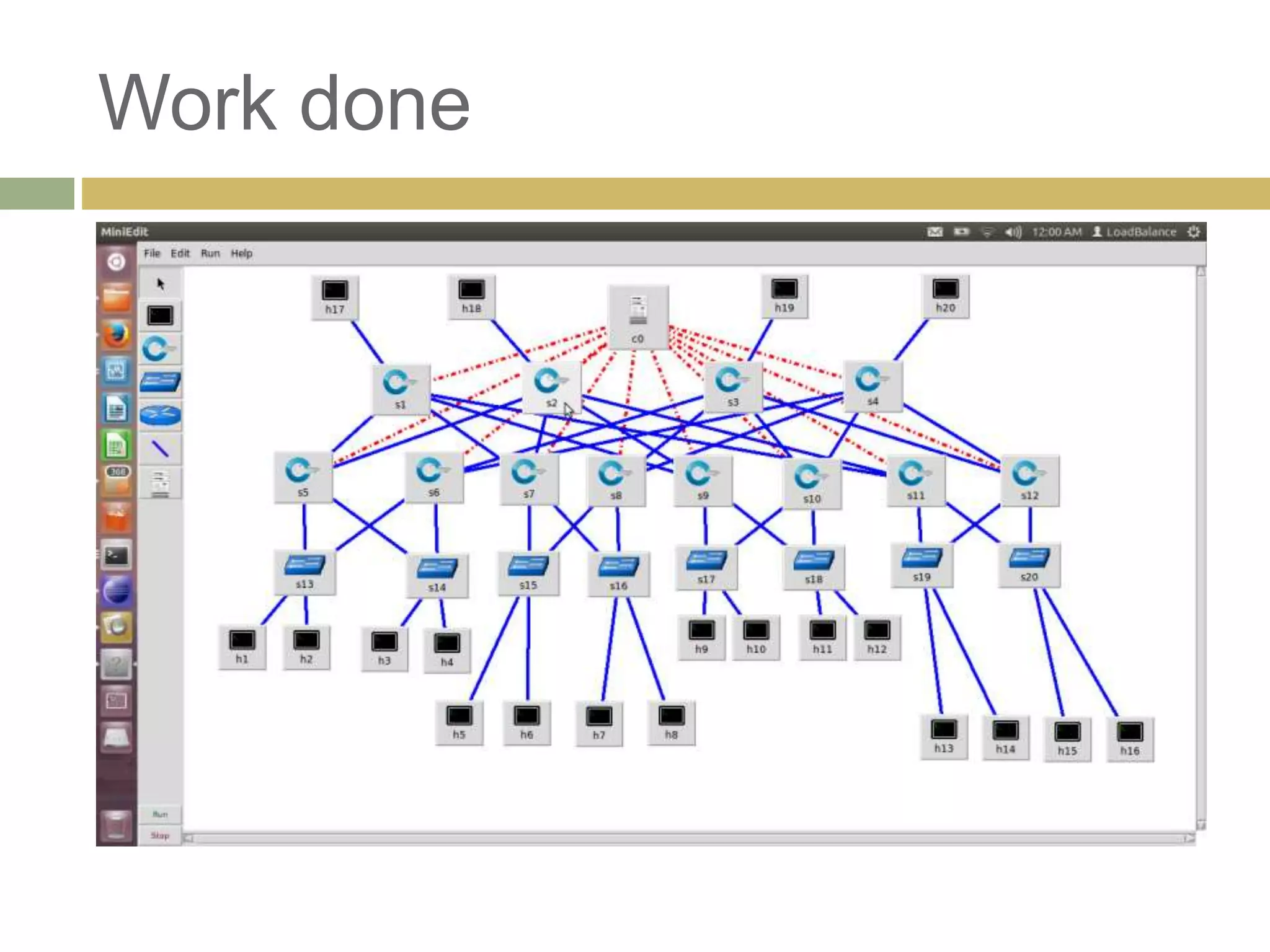
This progress report summarizes work on a final year project focusing on load balancing in data center networks using software defined networking. The report outlines the need for new networking paradigms to handle changing traffic patterns. It discusses SDN and how it separates the control plane from the forwarding plane. The work done so far includes experimenting with SDN controllers and traffic patterns in a virtualized fat tree network topology. Next steps are to develop an automated traffic generation tool and evaluate different controller options.