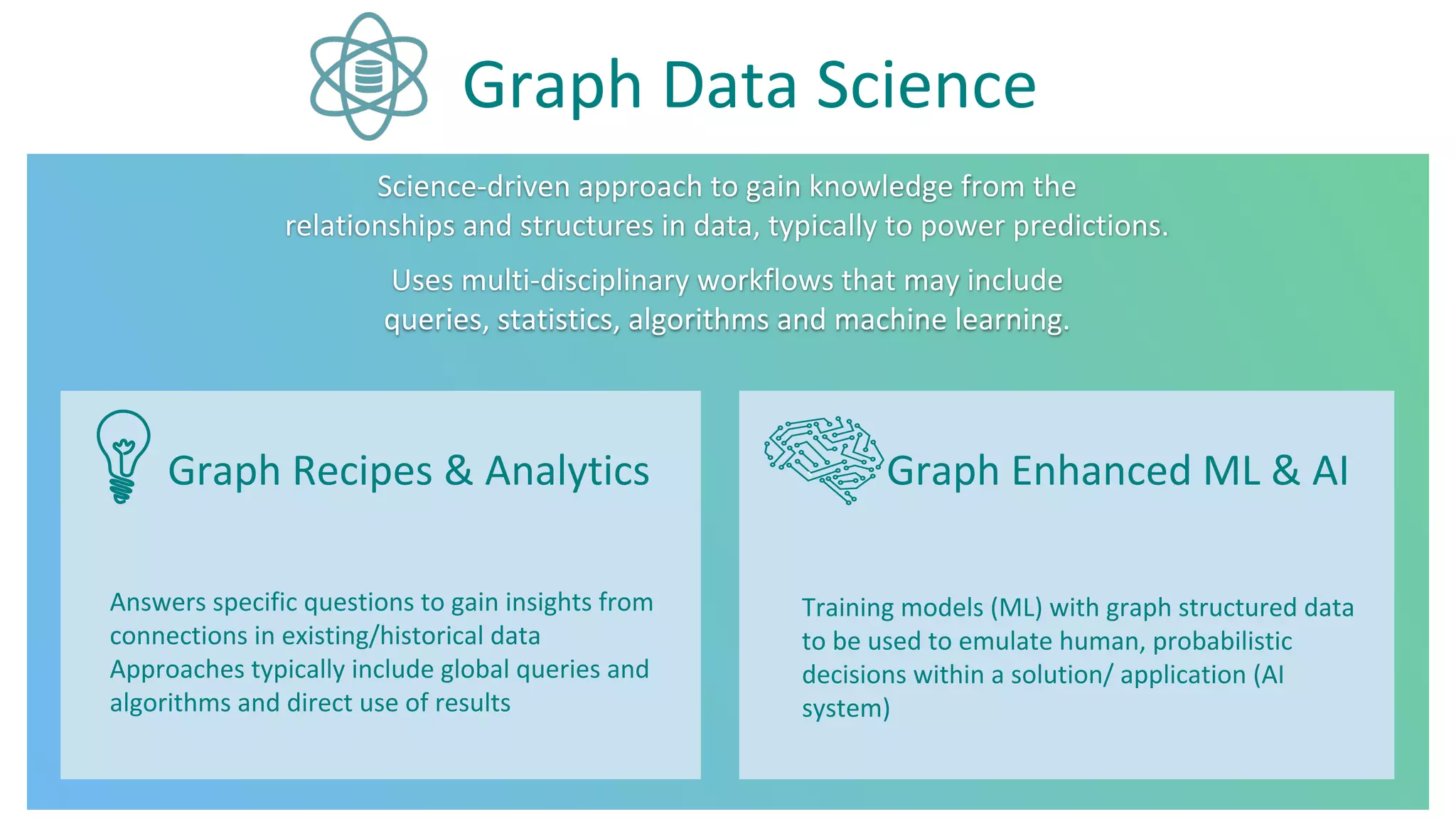
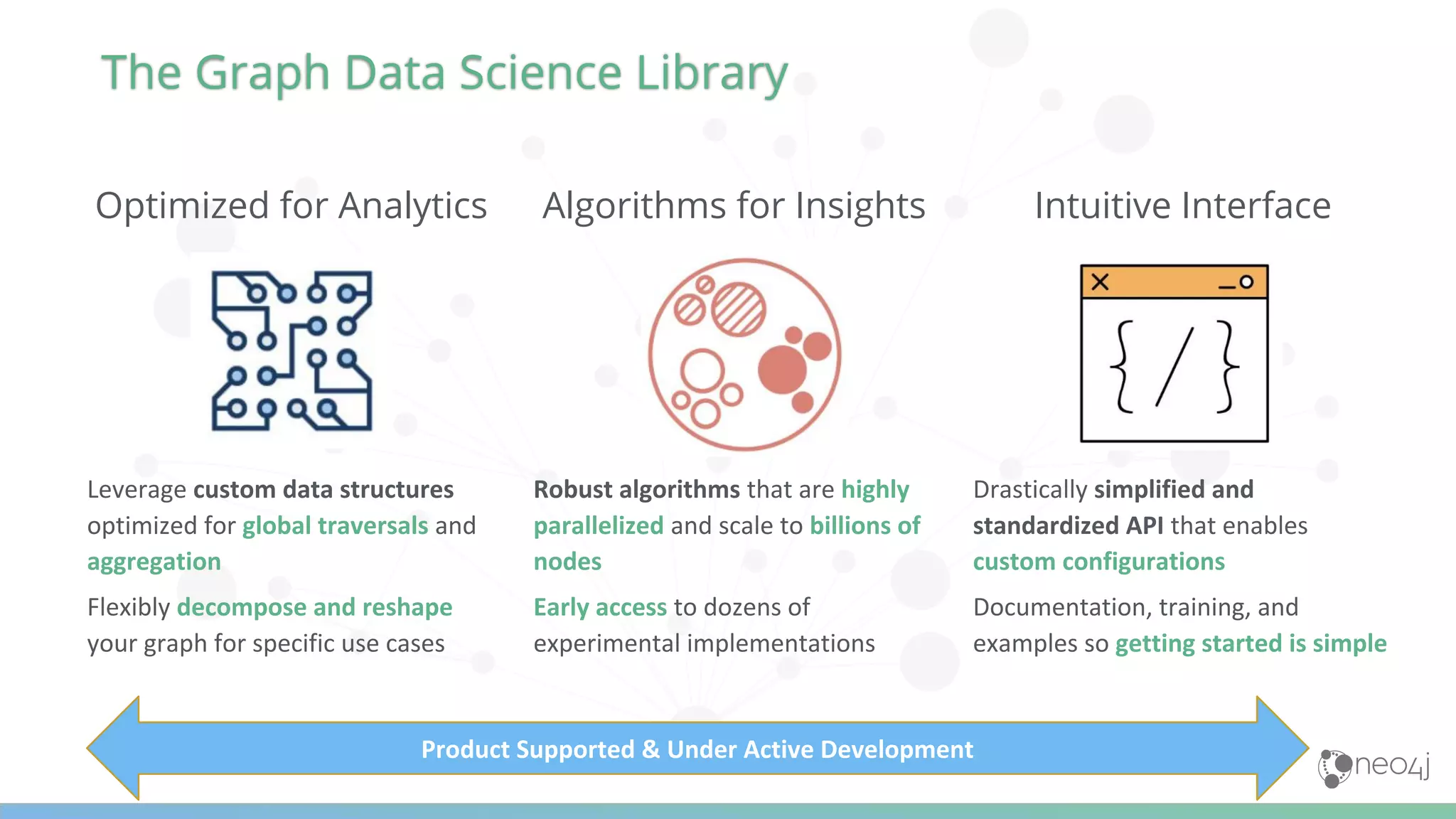
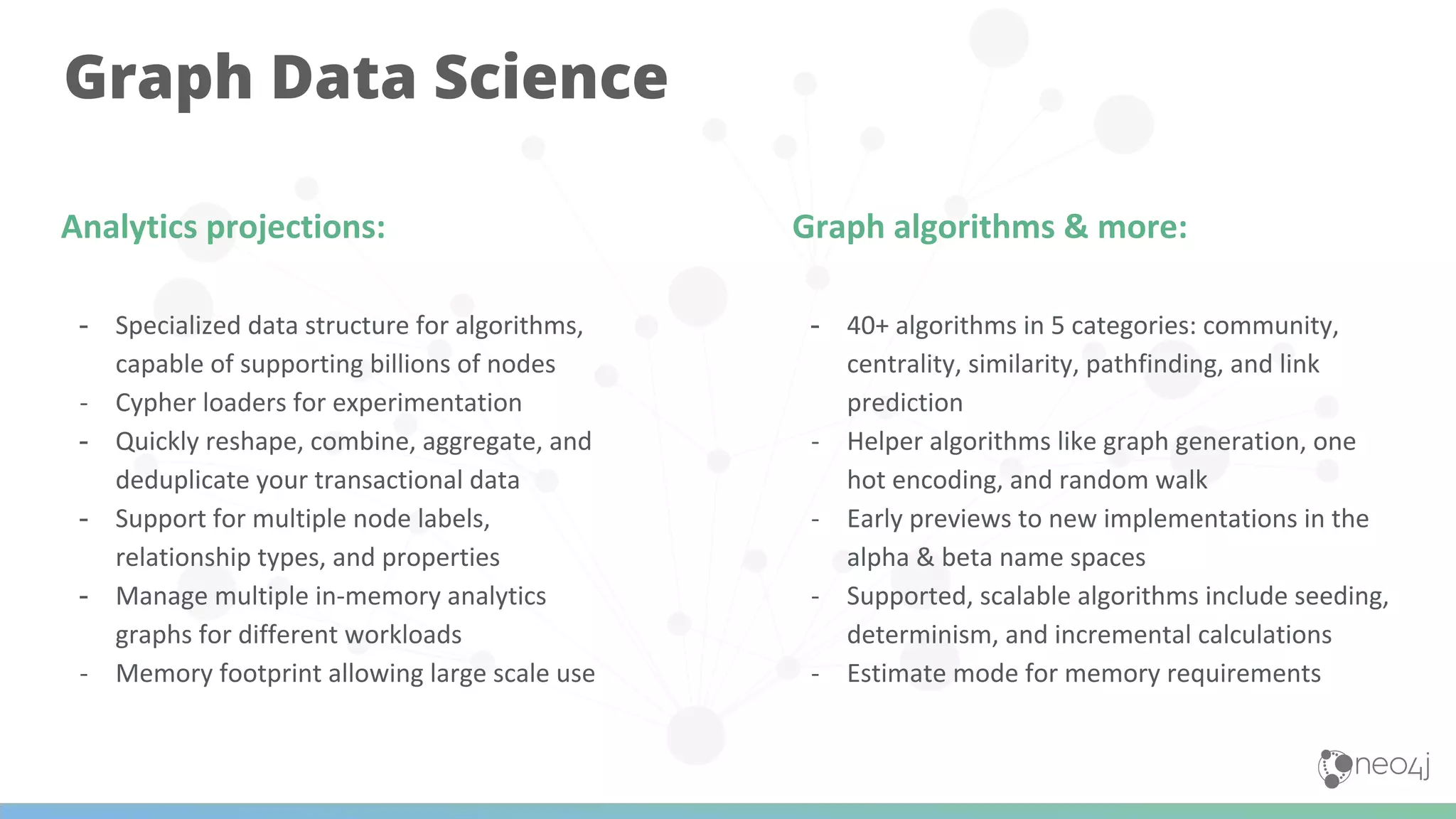
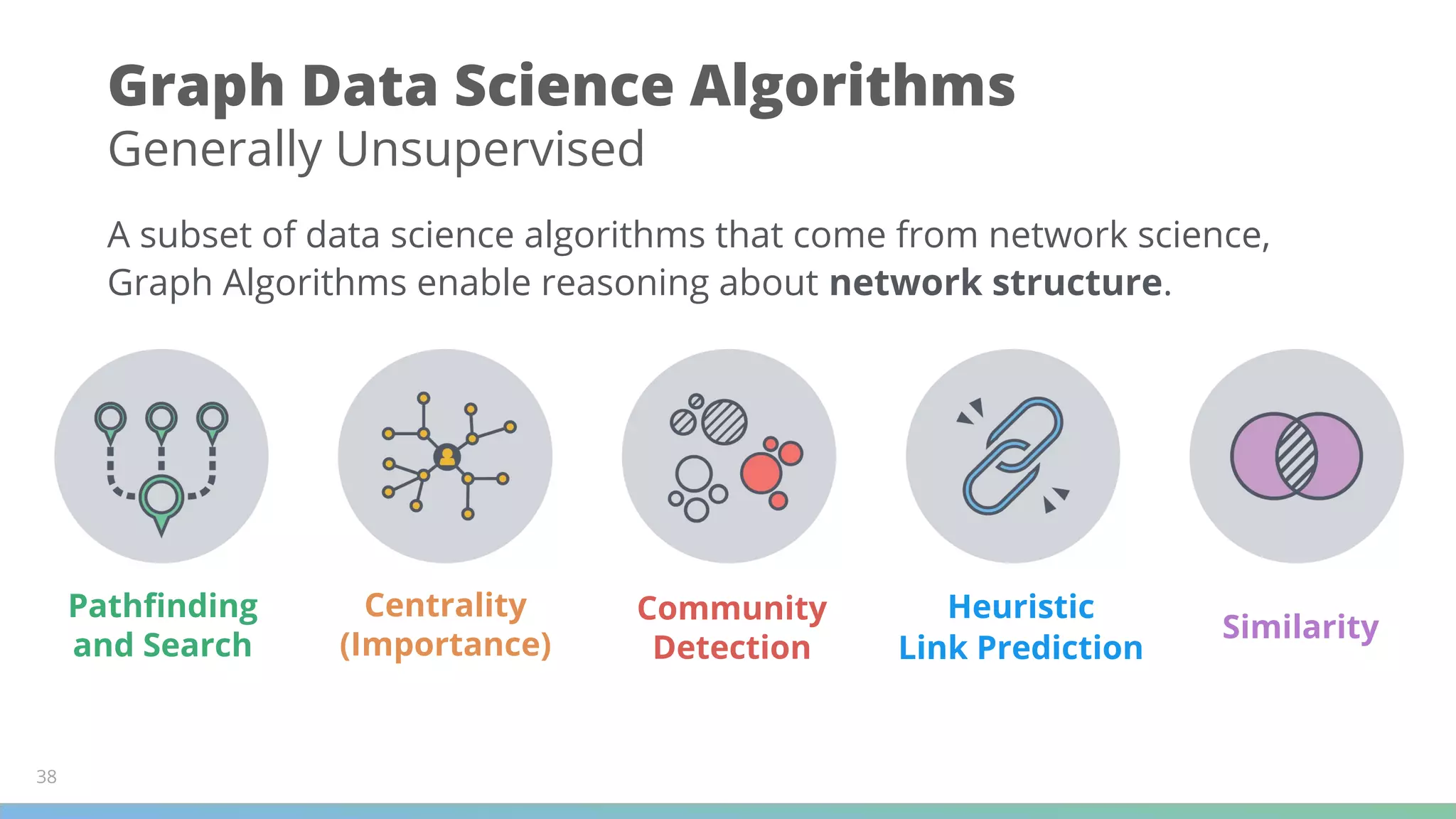
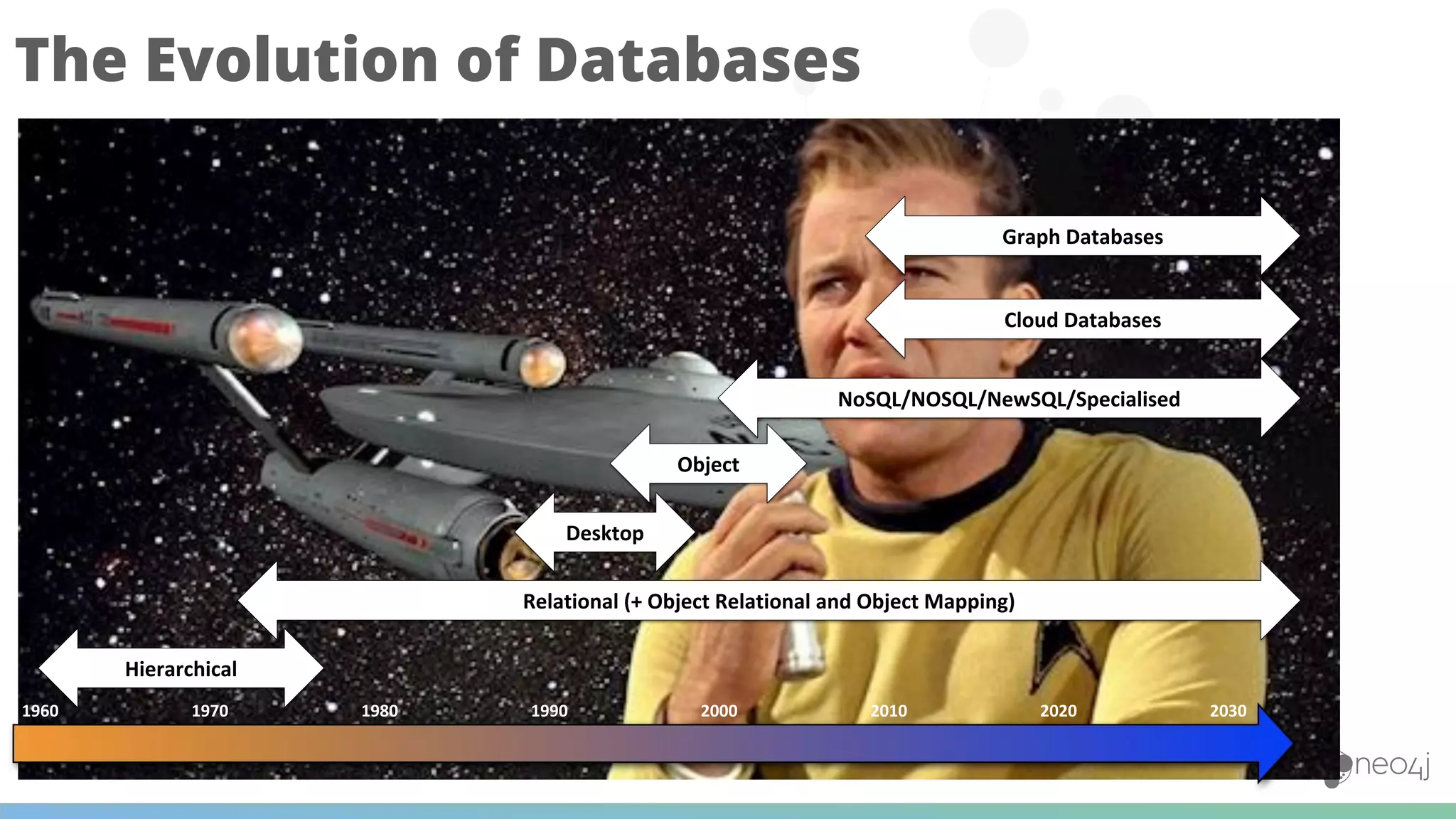
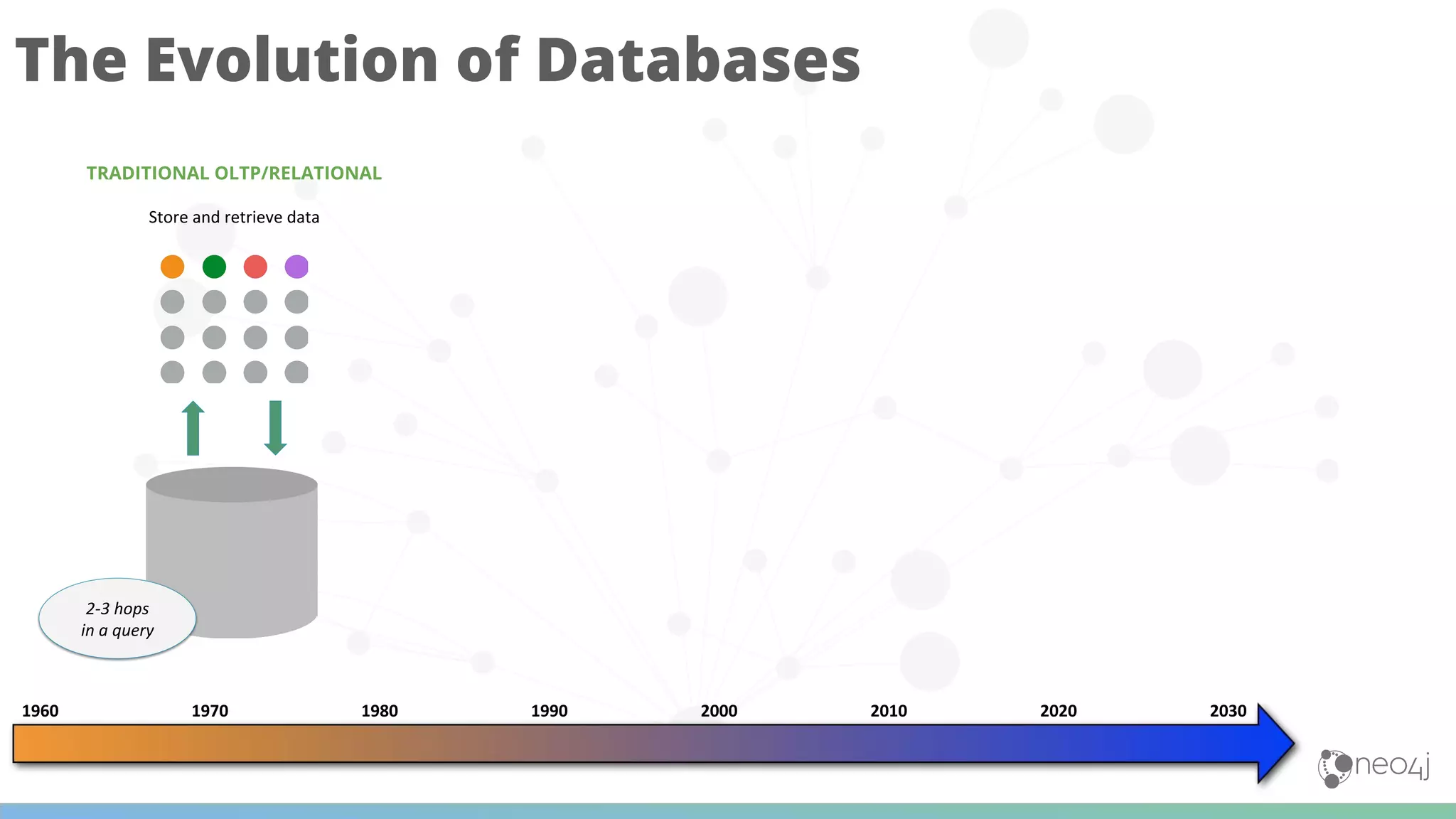
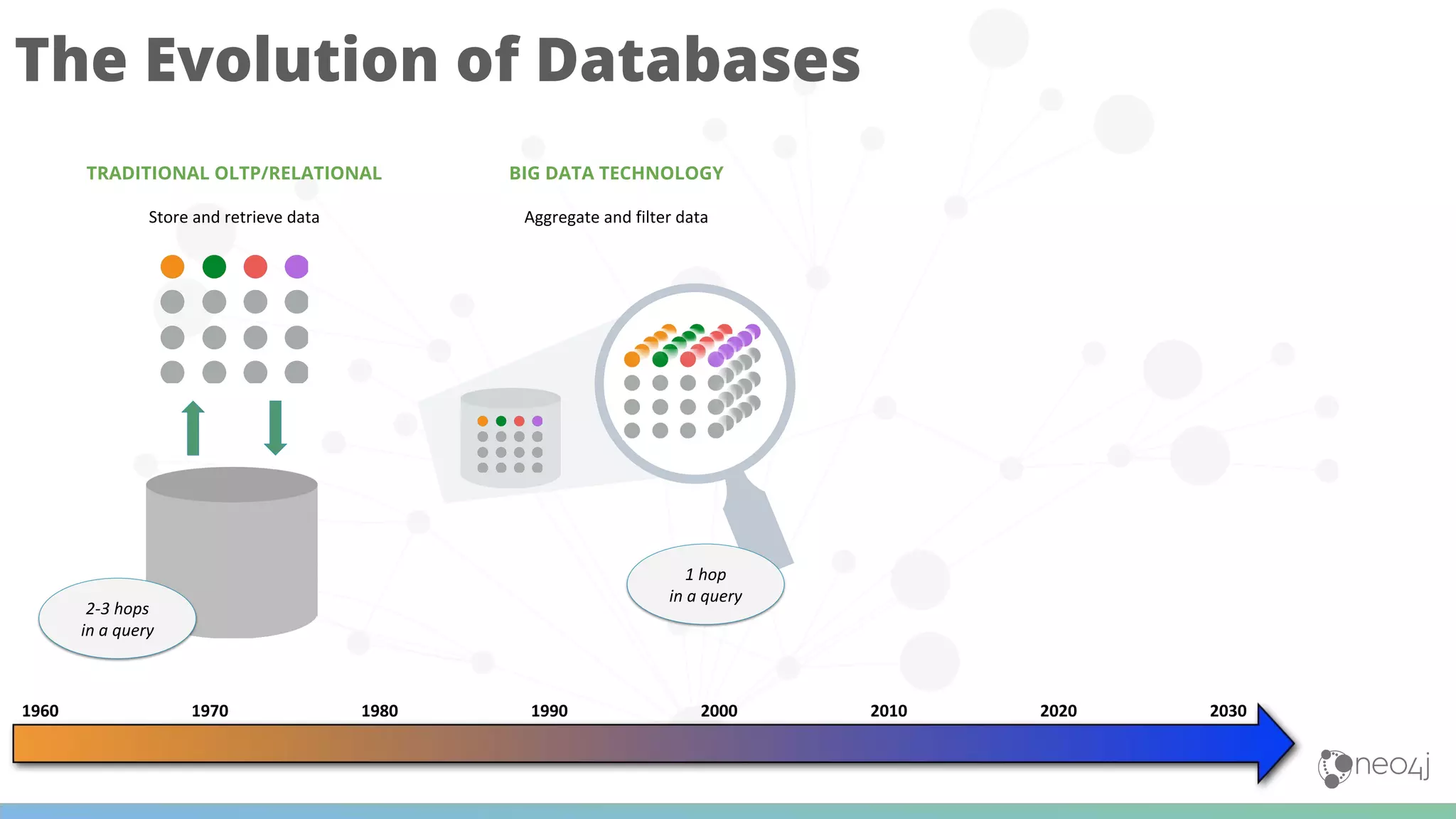
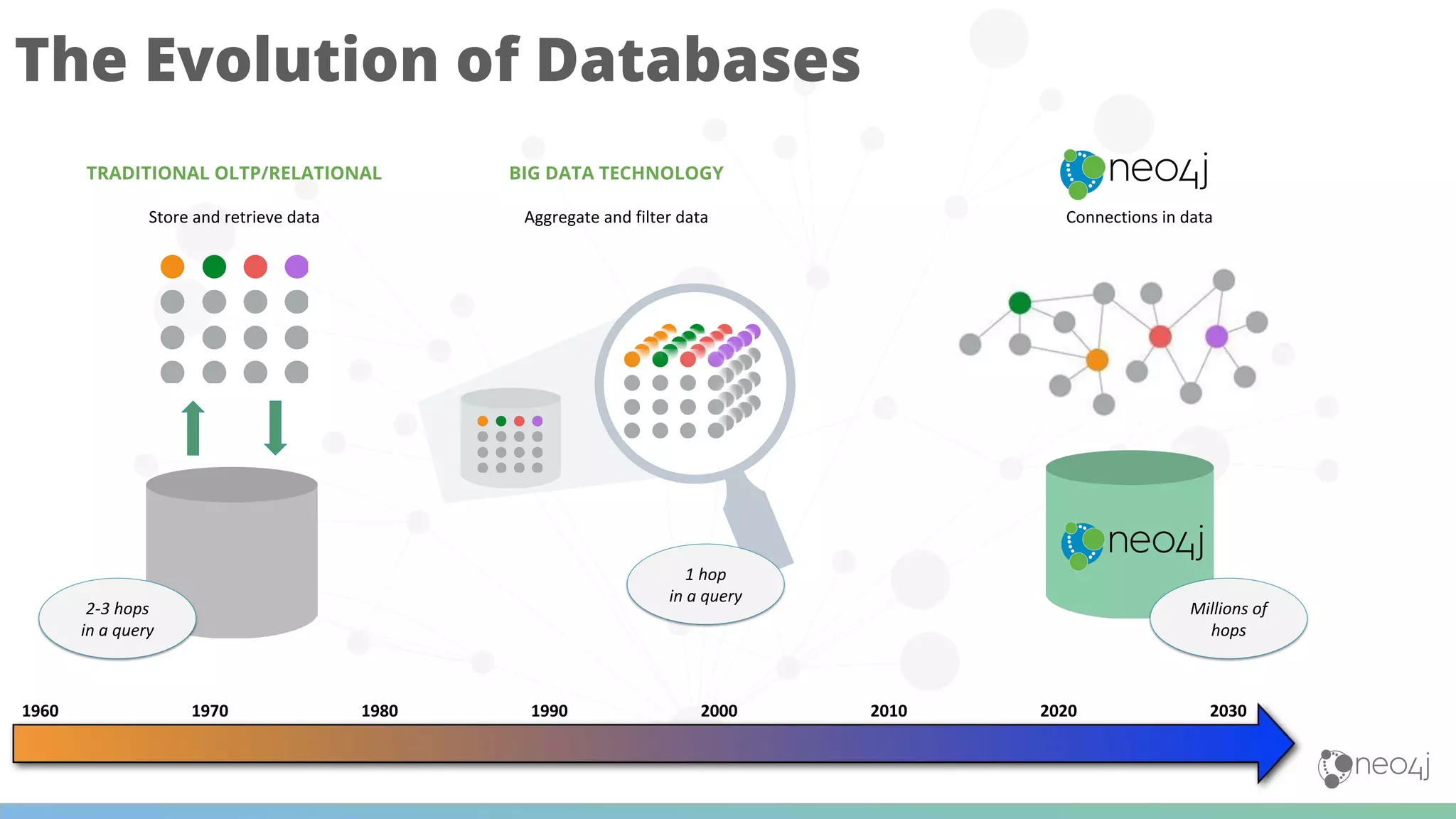
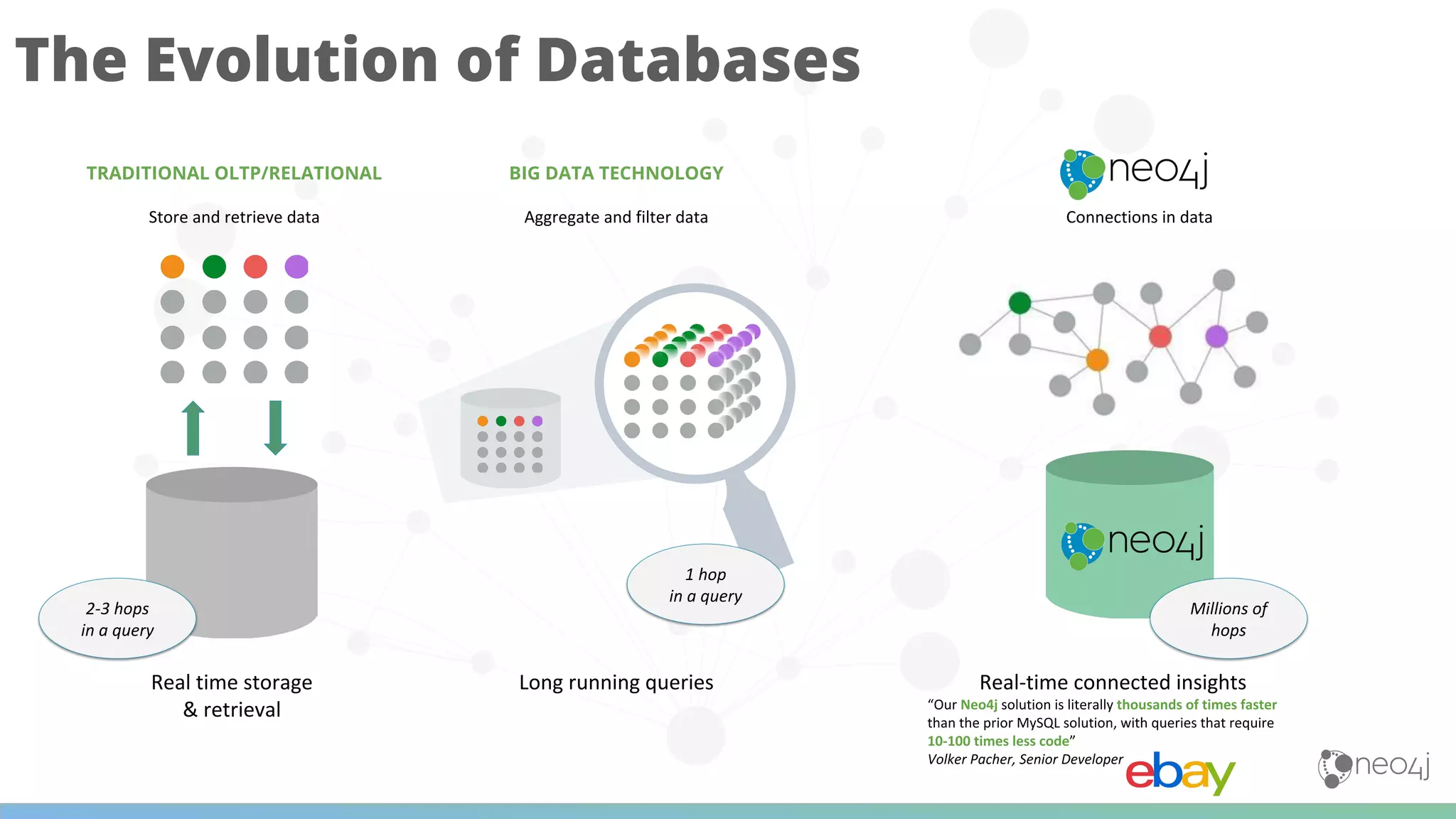
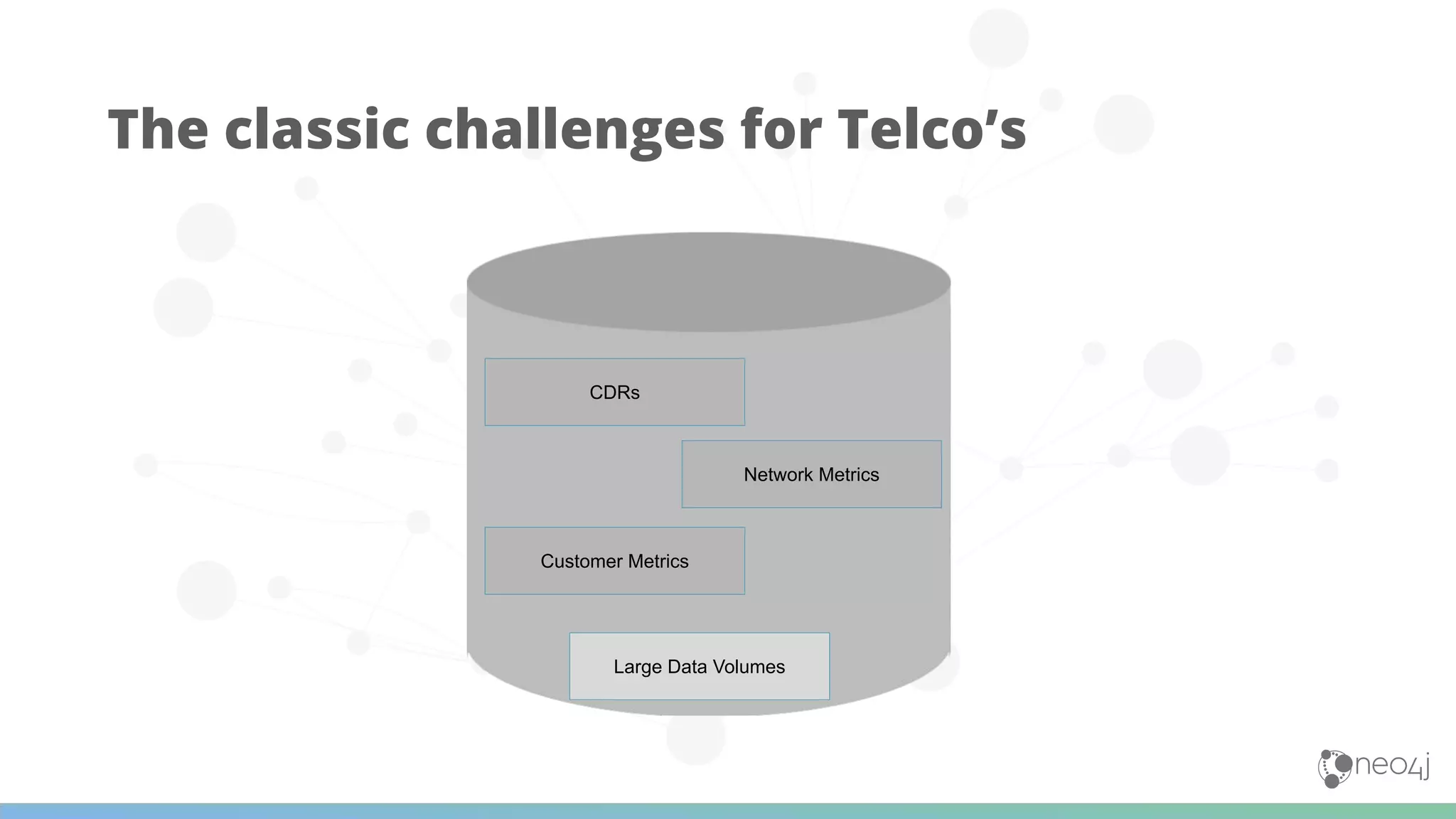
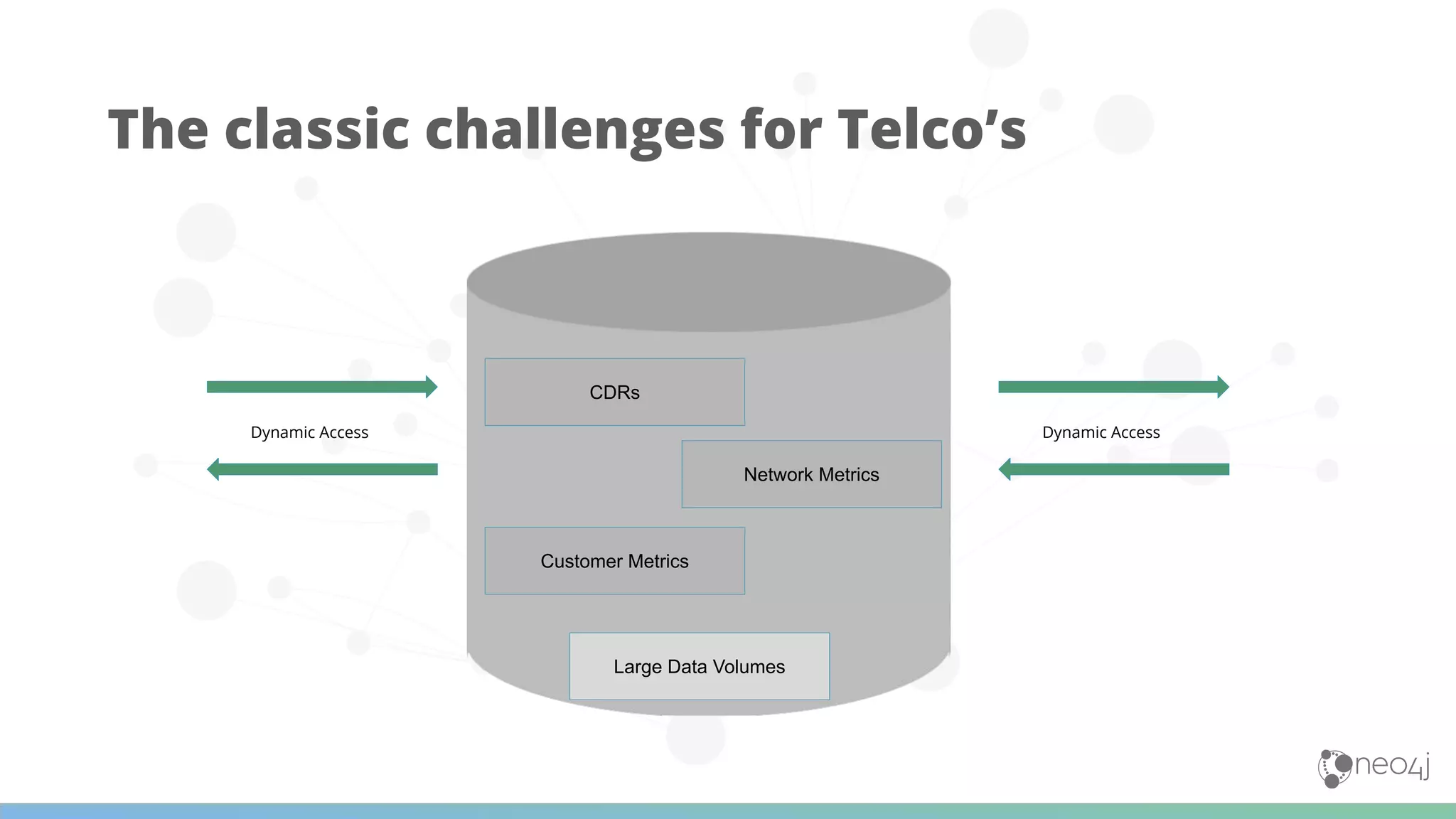
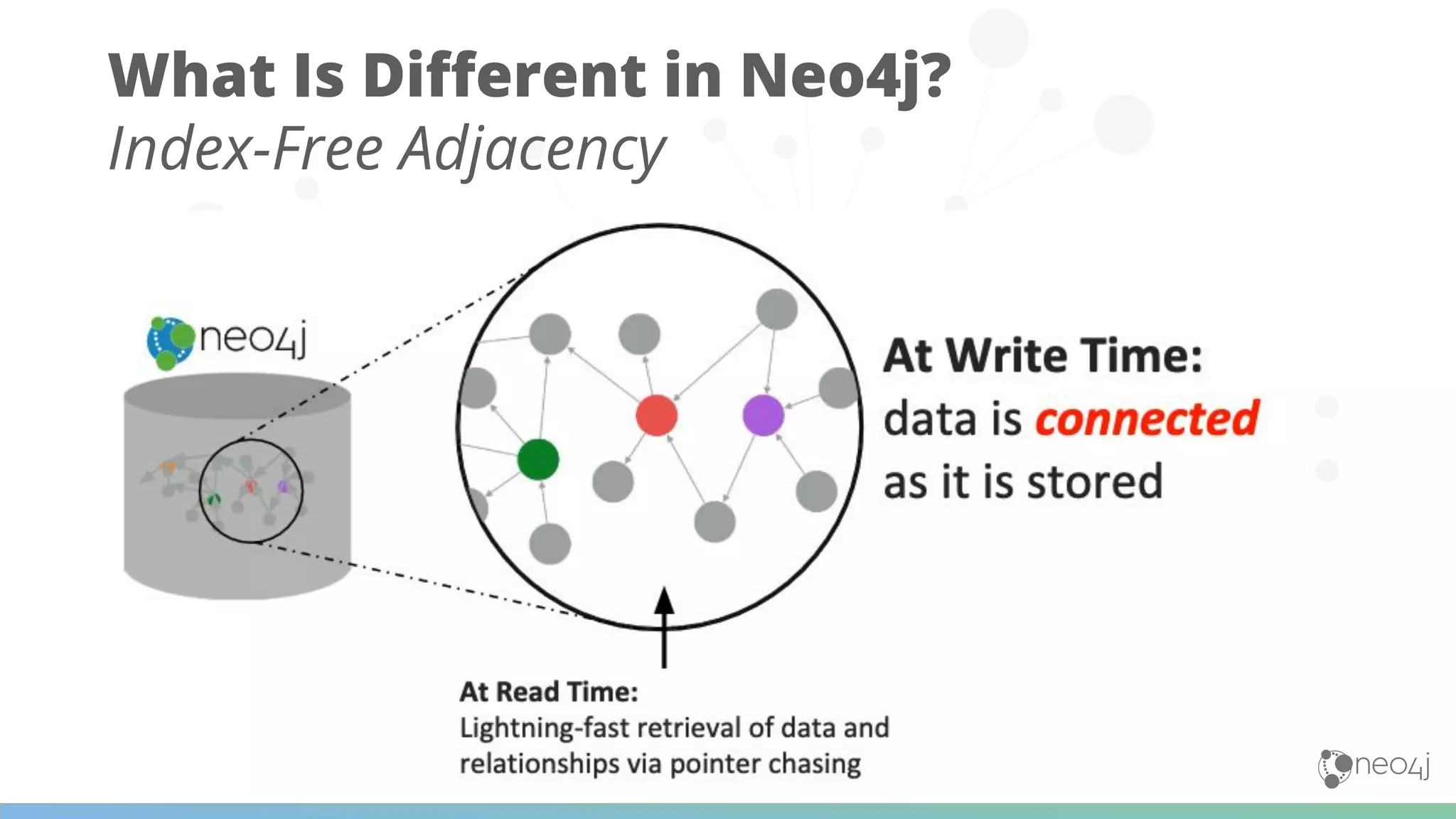
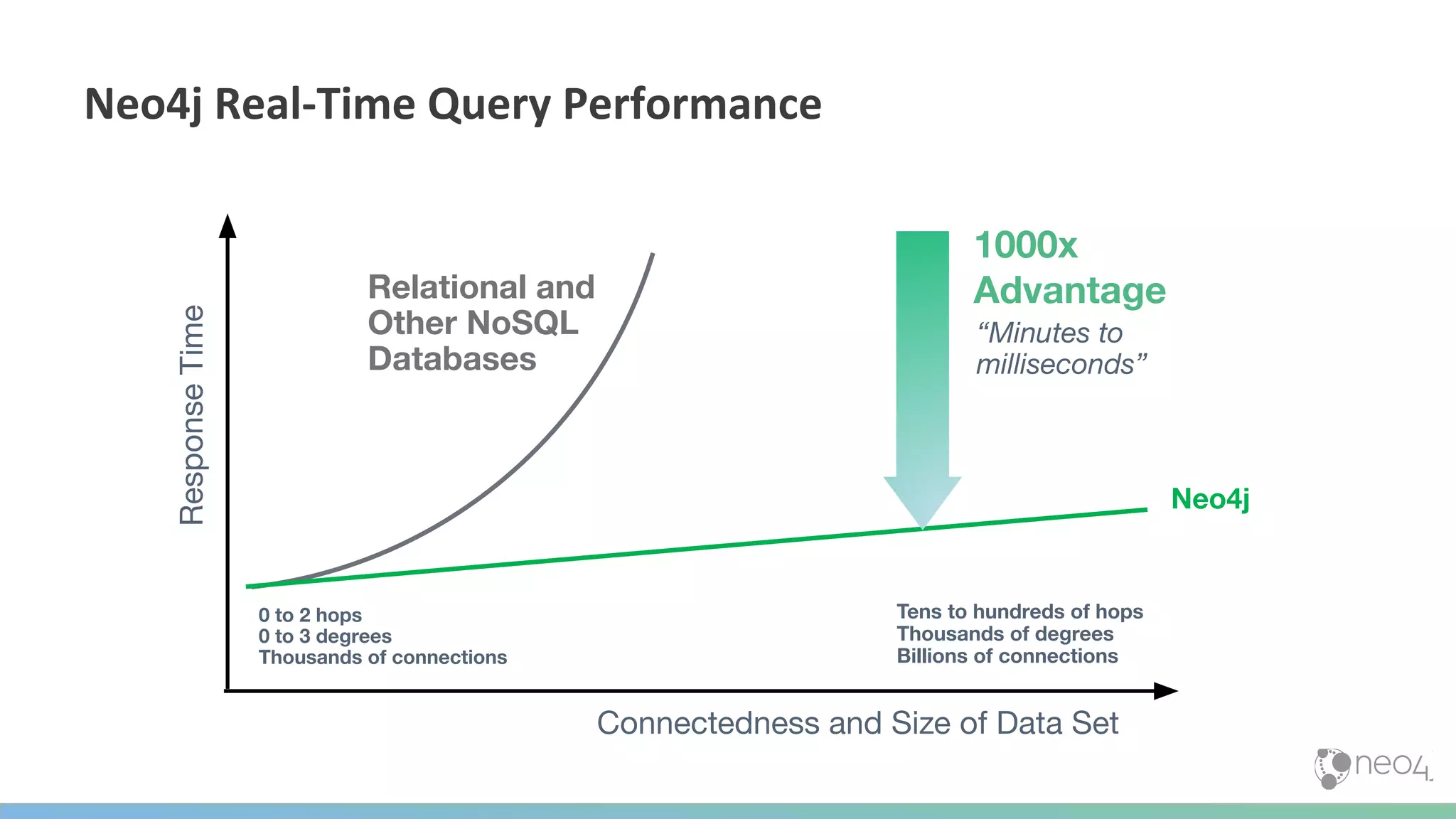
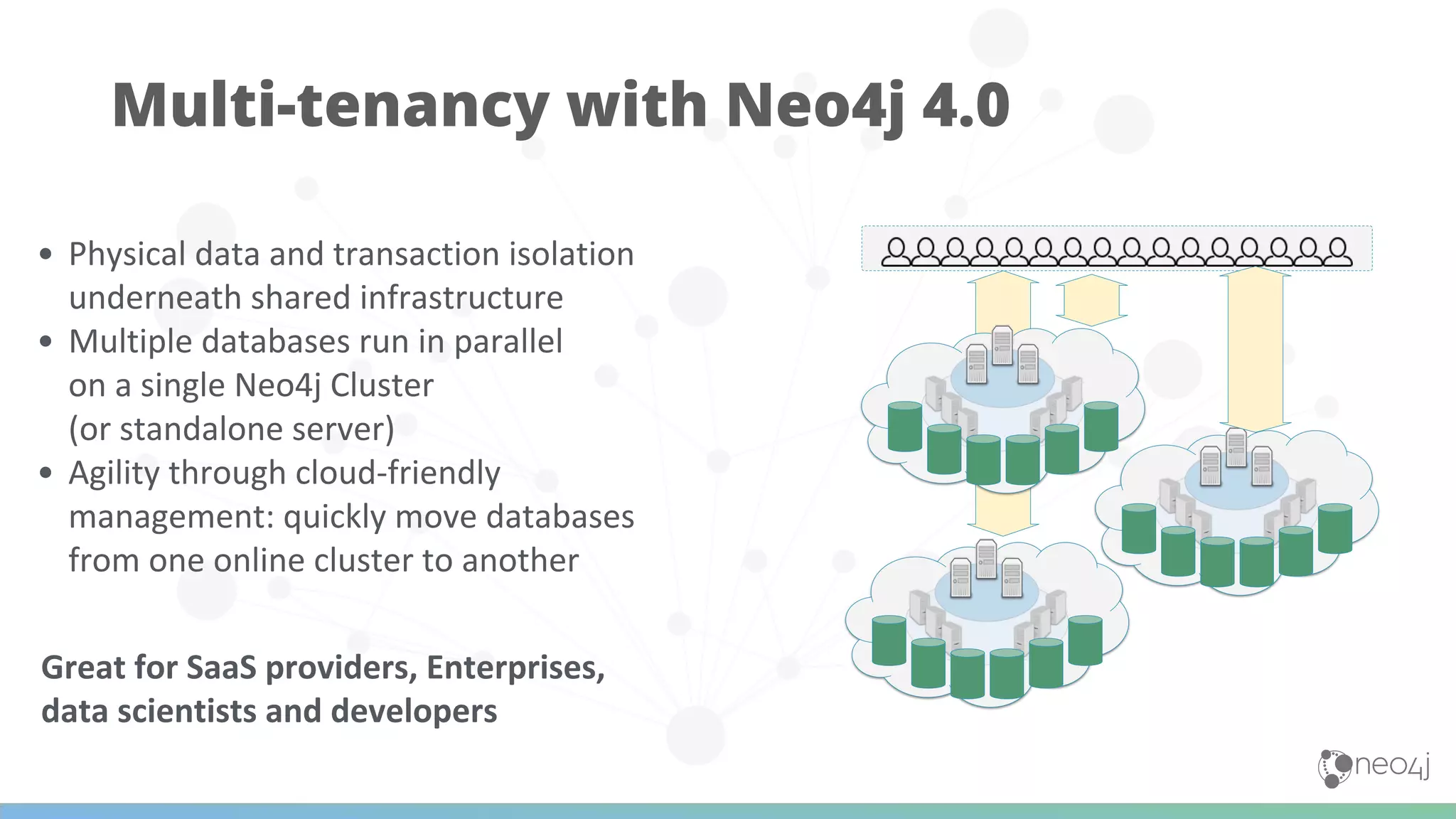
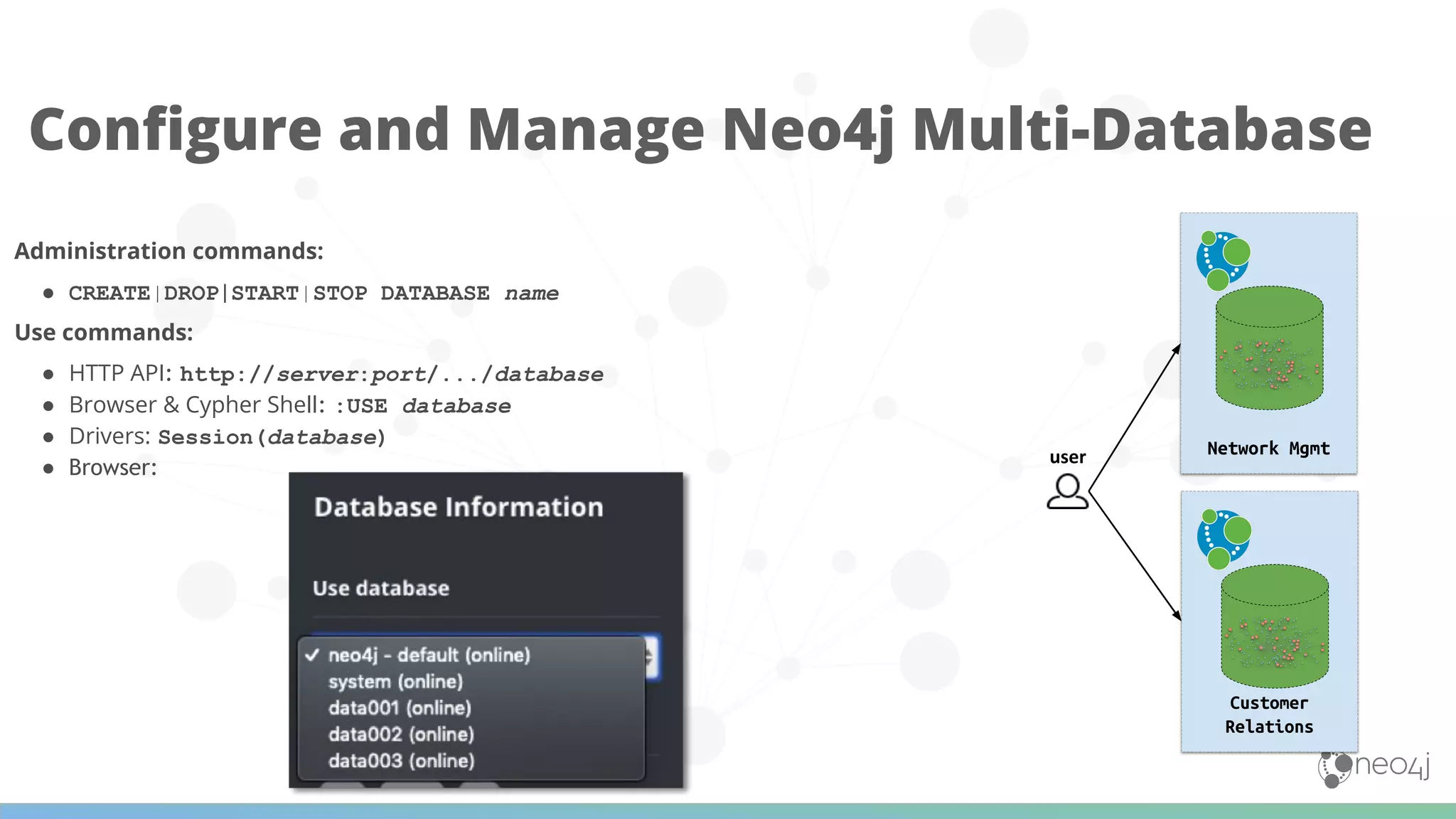
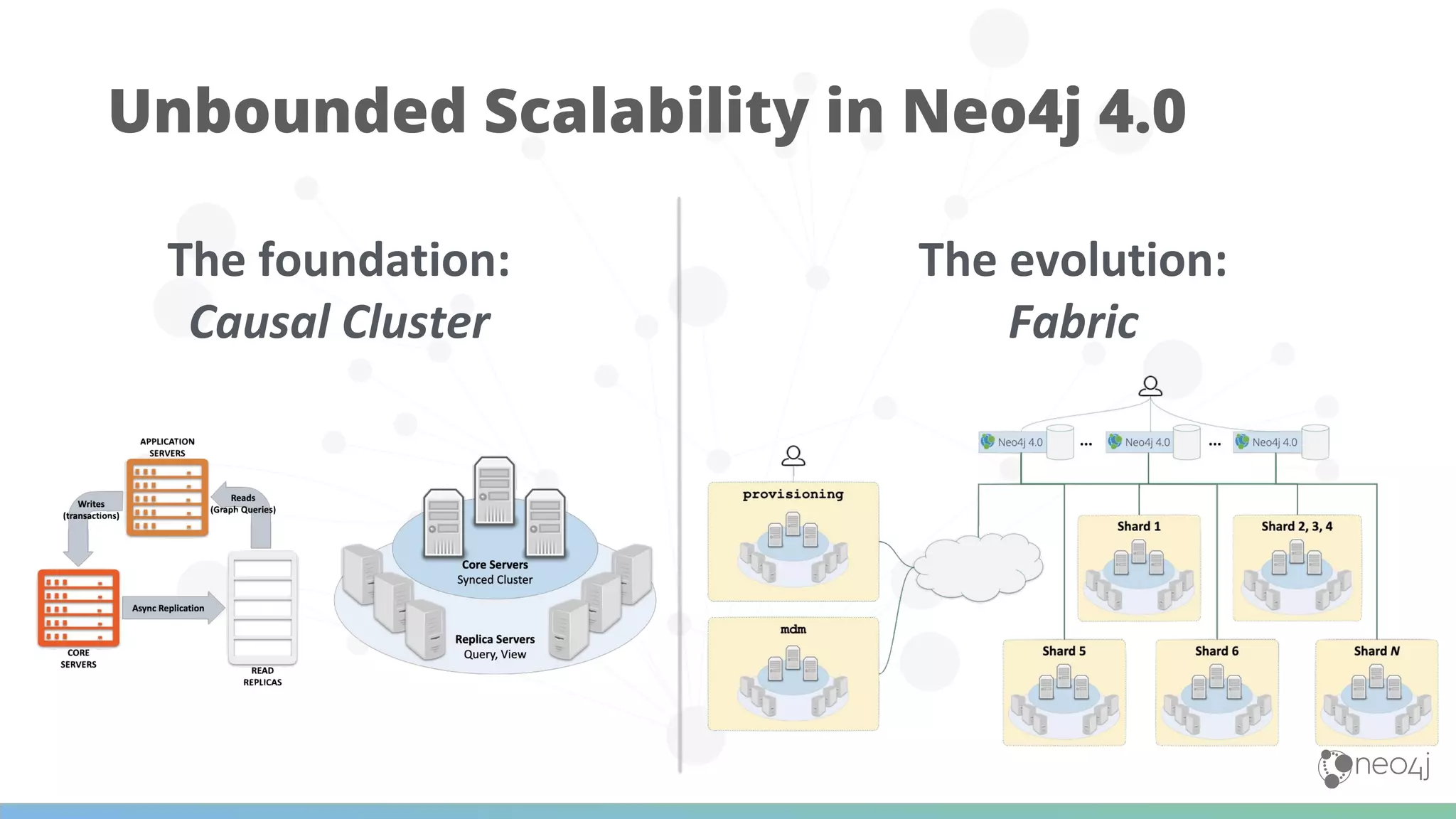
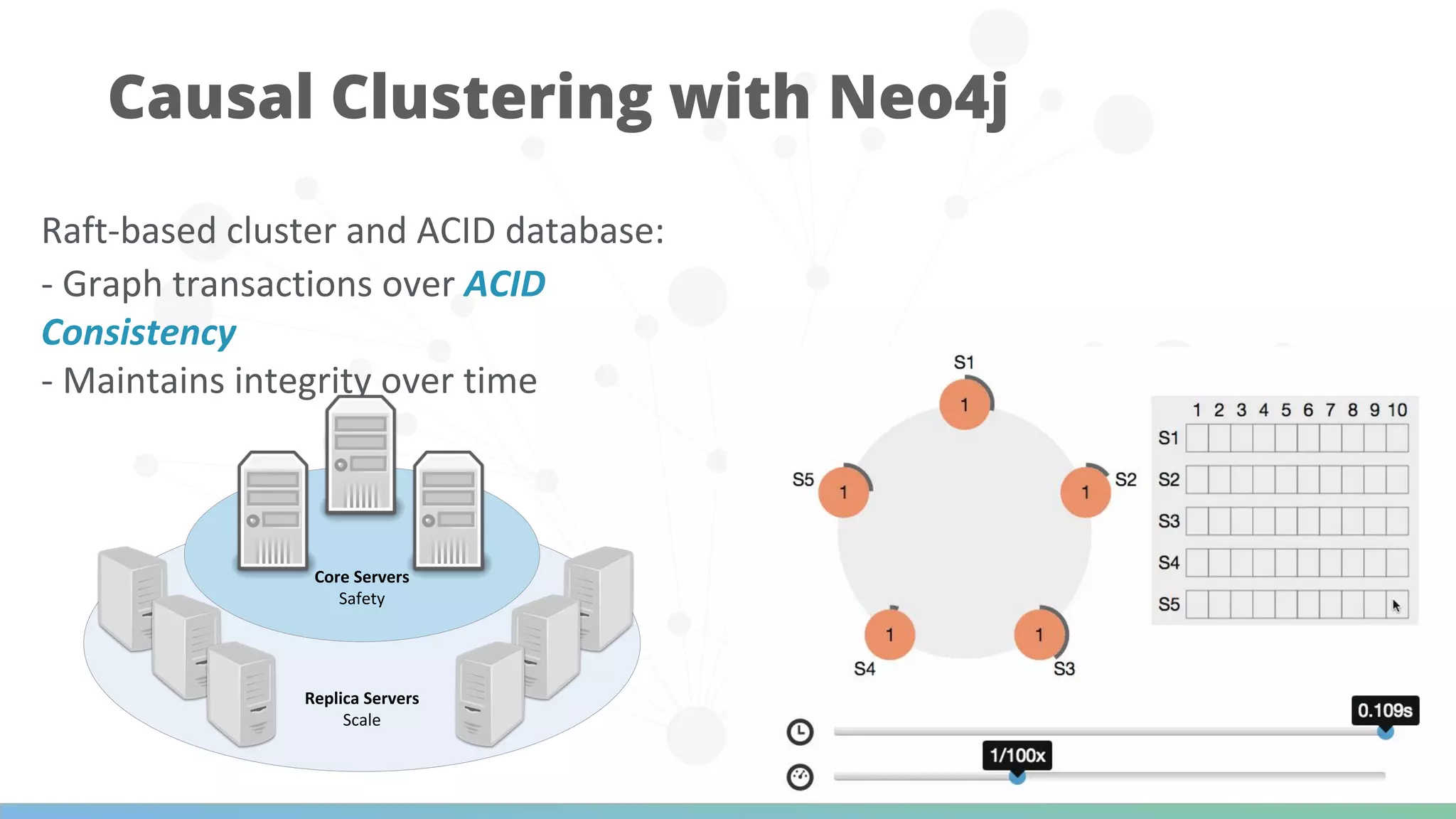
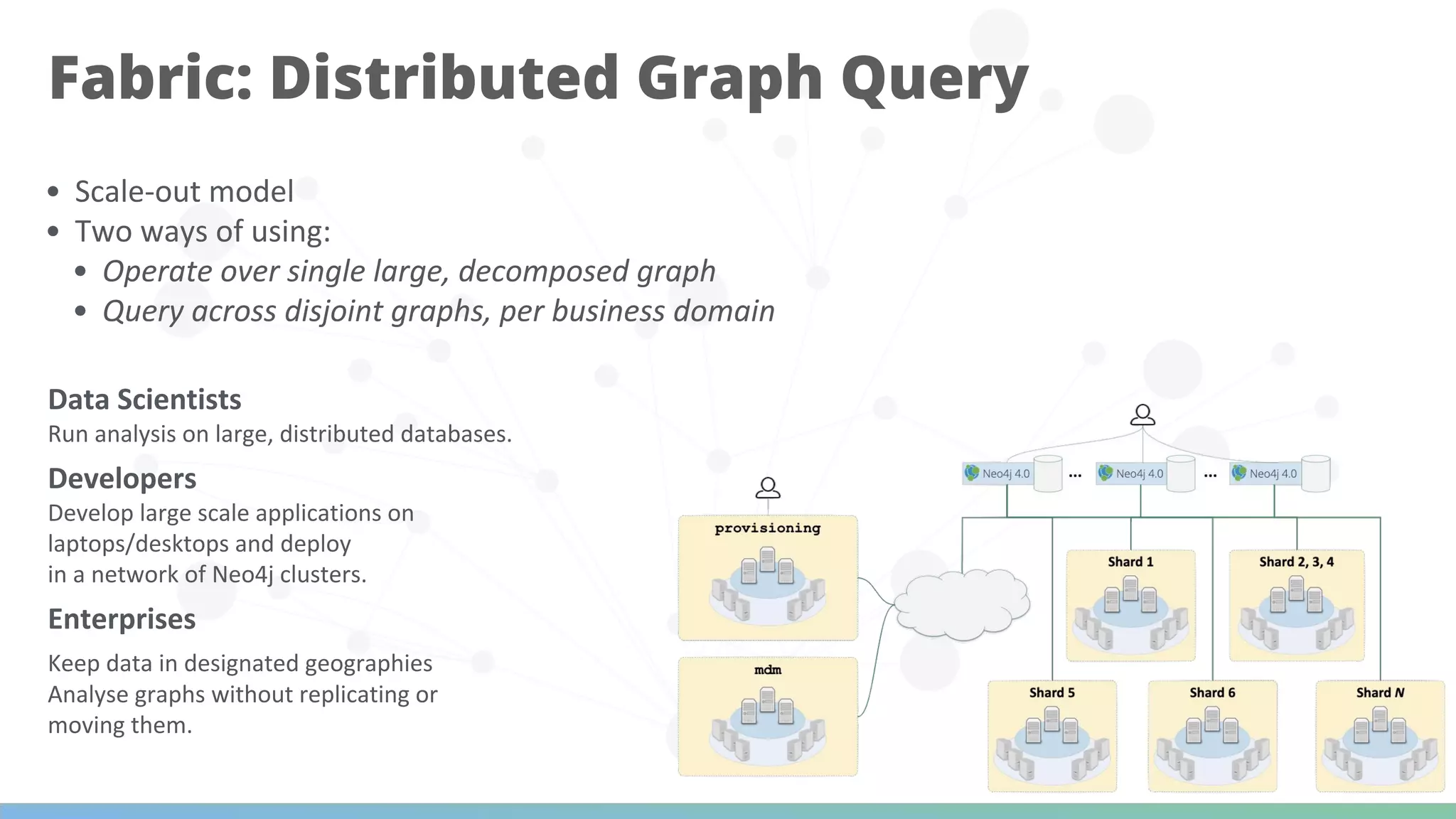
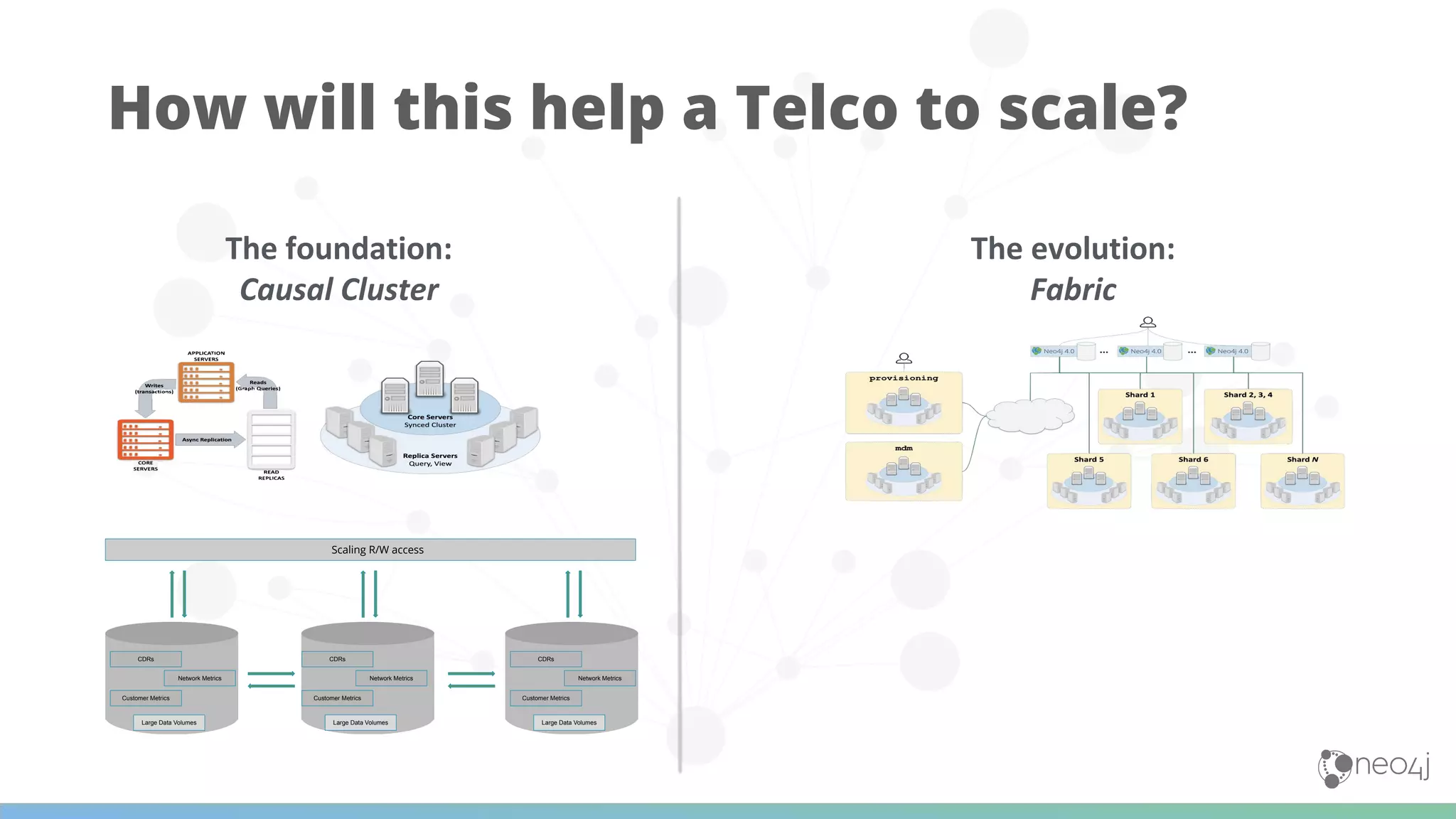
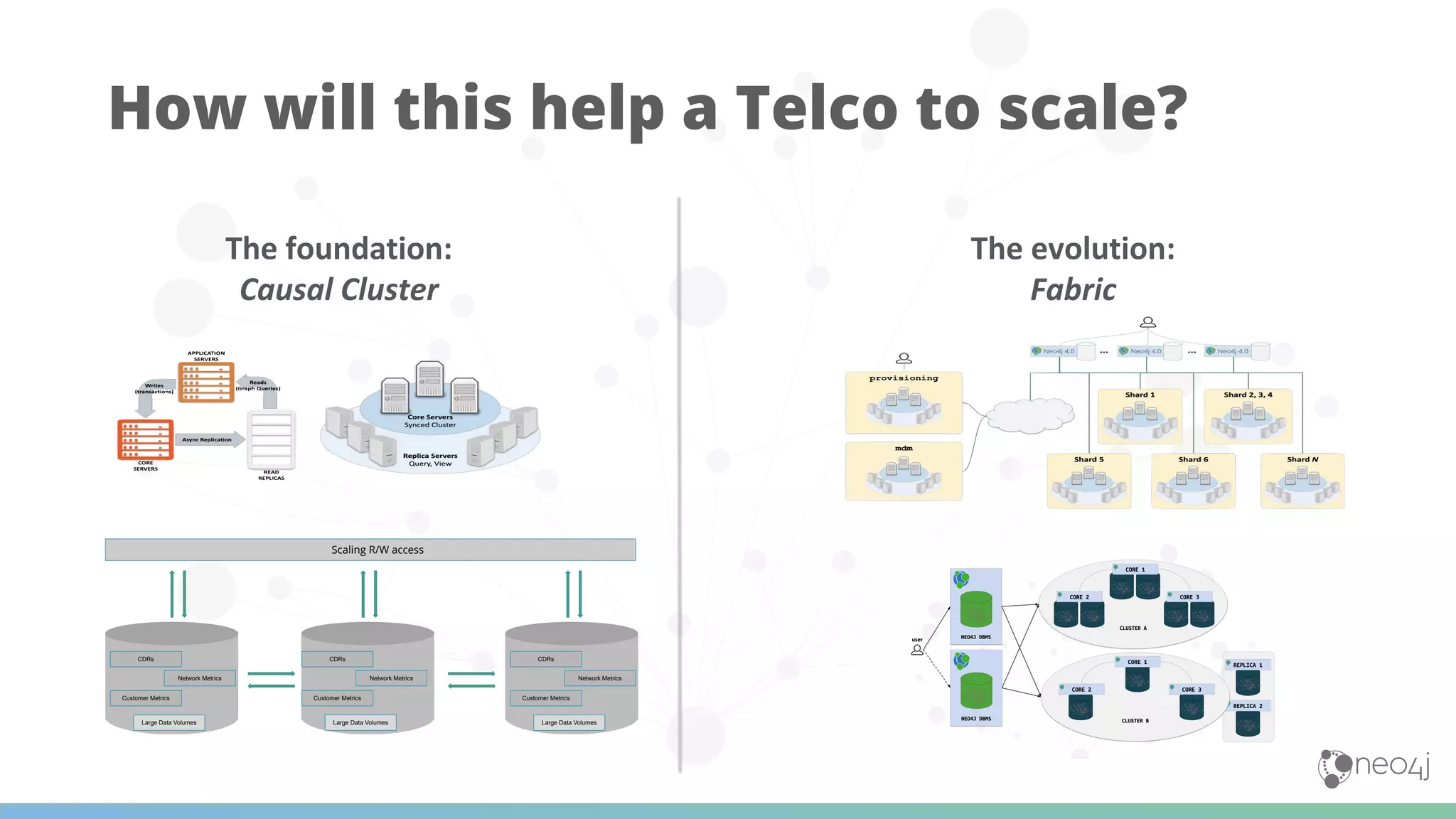
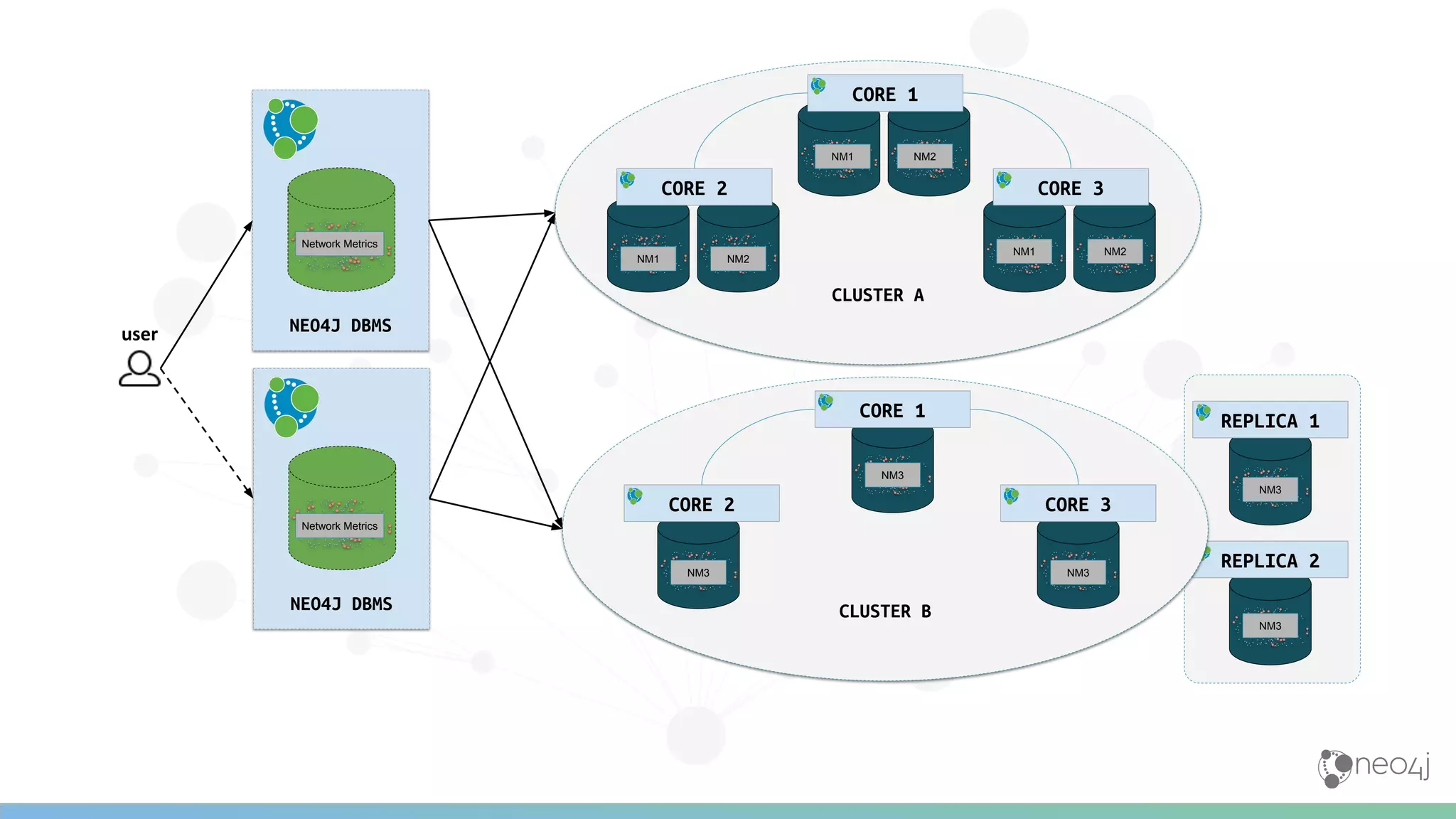
The document discusses Neo4j's capabilities for scalability and graph analytics. It describes how Neo4j provides unbounded scalability through features like causal clustering and multi-tenancy. This allows large datasets to be queried efficiently across distributed databases. Neo4j also includes tools for graph analytics and data science through its graph data science library, which supports algorithms and analytics on graphs with billions of nodes. These capabilities enable use cases for telecommunications companies to perform scalable analytics on large, connected datasets.

![Cypher Queries
SQL
Cypher in Neo4j
MATCH (boss)-[:MANAGES*0..3]->(sub),
(sub)-[:MANAGES*1..3]->(report)
RETURN boss.name AS Boss,
sub.name AS Subordinate,
count(report) AS Total](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jfortelco-scalability-stefankolmar-200616141253/75/Scalability-and-Graph-Analytics-with-Neo4j-Stefan-Kolmar-Neo4j-19-2048.jpg)
![Multi-graph Cypher Queries
SQL
UNWIND corporate.graphIds() AS gid
CALL {
USE corporate.graph( gid )
MATCH (boss)-[:MANAGES*0..3]->(sub),
(sub)-[:MANAGES*1..3]->(report)
RETURN boss.name AS Boss,
sub.name AS Subordinate,
count(report) AS Total
}
RETURN Boss, Subordinate, Total ORDER BY Total
Cypher in Neo4j 4.0
• Executes queries in parallel on multiple databases, combining or aggregating results.
• Chains queries together from multiple databases for sophisticated real-time analyses.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jfortelco-scalability-stefankolmar-200616141253/75/Scalability-and-Graph-Analytics-with-Neo4j-Stefan-Kolmar-Neo4j-20-2048.jpg)

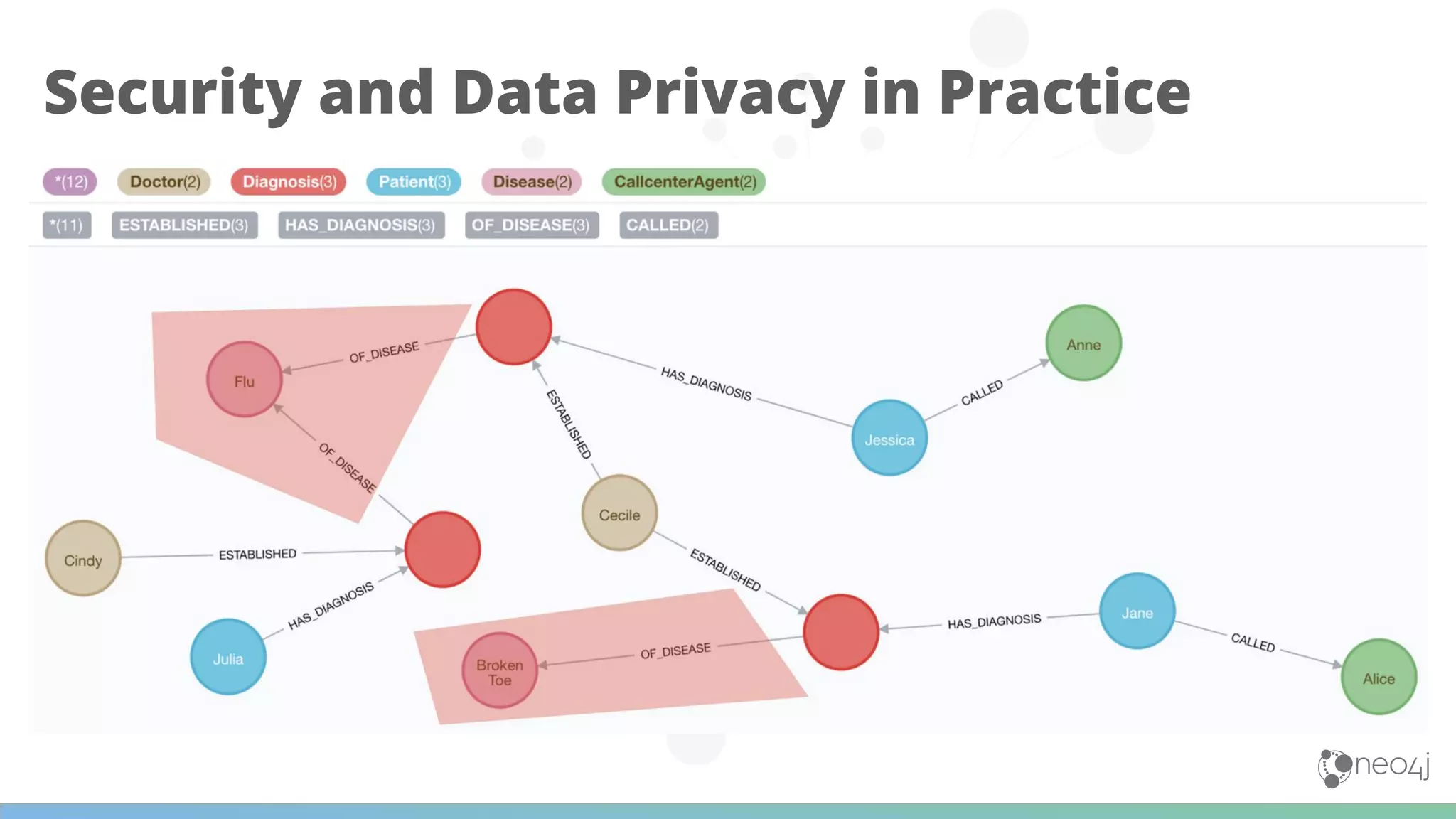


![Call Centre Agent
MATCH (:CallcenterAgent {name: 'Alice'})
<-[:CALLED]-(p:Patient)-[:HAS_DIAGNOSIS]-(dia)
<-[:ESTABLISHED]-(d:Doctor)
RETURN p.name, d.name, dia.name;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jfortelco-scalability-stefankolmar-200616141253/75/Scalability-and-Graph-Analytics-with-Neo4j-Stefan-Kolmar-Neo4j-32-2048.jpg)