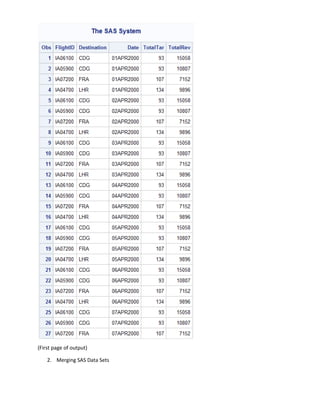
The goal is to combine data from three monthly SAS data sets (April, May, June) into a single quarterly data set for analysis. The document provides code to:
1) Examine the monthly data sets and identify variable names.
2) Write a data step to concatenate the monthly data sets into a new quarterly data set, renaming variables as needed.
3) Add two new variables (TotalTar and TotalRev) calculating totals and print the new data set.
The second part of the document merges two data sets to compare targeted vs actual cargo revenue for flights from Birmingham on December 15, 1999, calculating any lost revenue.