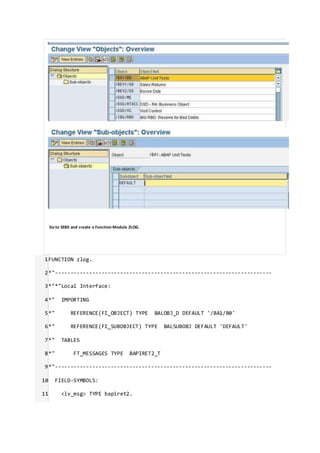
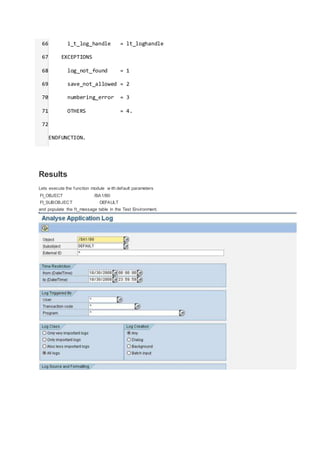
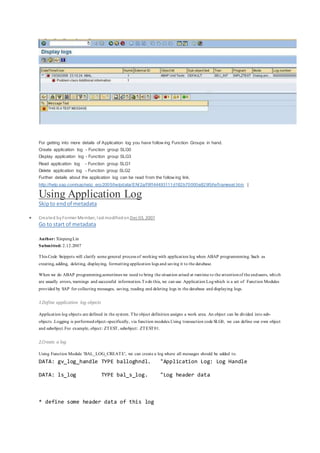
This document discusses application logging in SAP ABAP. It provides steps to create an application log object, add messages to the log, save the log to the database, and display the log. Key steps include using function modules to create a log, add messages, save logs, and display logs. Code examples are provided to demonstrate how to call the function modules to perform logging from an ABAP program.





![LOG_HEADER_INCONSISTENT
LOGGING_ERROR
Paste the code below as the source code
Error rendering macro 'code': Invalid value specified for parameter 'lang'
ZIU_MESSAGE_LOGGINGFUNCTION ZIU_MESSAGE_LOGGING.
*"----------------------------------------------------------------------
""Local interface:
*" IMPORTING
*" REFERENCE(I_LOG_OBJECT) TYPE BALOBJ_D
*" REFERENCE(I_EXTNUMBER) TYPE STRING
*" TABLES
*" T_LOG_MESSAGE STRUCTURE Z_LOG_MESSAGE
*" EXCEPTIONS
*" LOG_HEADER_INCONSISTENT
*" LOGGING_ERROR
"---------------------------------------------------------------------
"DESCRIPTION: This function module is used insert messages in the
application log
CONSTANTS: c_message TYPE syst-msgid VALUE 'ZMESSAGE',
c_999 TYPE syst-msgno VALUE '999'.
DATA:
l_log_handle TYPE balloghndl,
l_s_log TYPE bal_s_log,
l_dummy TYPE string,
l_ext_no TYPE bal_s_log-extnumber,
l_s_mdef TYPE bal_s_mdef.
IF t_log_message[] IS NOT INITIAL.
l_s_log-object = i_log_object.
l_ext_no = i_extnumber.
l_s_log-extnumber = l_ext_no.
"Create the log with header data
CALL FUNCTION 'BAL_LOG_CREATE'
EXPORTING
i_s_log = l_s_log
IMPORTING](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sapapplicationlog-180621023711/85/Sap-application-log-7-320.jpg)