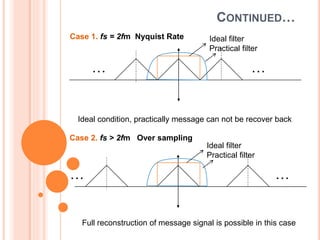
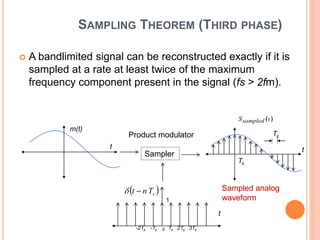
The document discusses the sampling theorem, highlighting that a bandlimited signal can be accurately reconstructed if sampled at a rate at least twice the maximum frequency component present. It outlines different scenarios based on guard bands and sampling rates, including cases of ideal and practical filters. Applications of this theorem include audio and video sampling, communication systems, and digital signal processing.


![CONTINUED…
)
(2
cos
2
)
(
cos
2
1
.
.
.
t
T
t
T
T
T
n
t s
s
s
s
s
n
s
)
(2
cos
)
(
2
)
(
cos
)
(
2
)
(
1
.
.
.
t
t
m
t
t
m
t
m
T
s
s
s
t
sampled
S
Spectrum
m(t)
fm
-fm
Modulation by
cos(s t)
Modulation by cos(2 s t)
]
)[
(
n
s
T
n
t
t
m
t
sampled
S](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-samplingtheorem-240728173456-db0947ae/85/Sampling-Theorem-A-Comprehensive-Overview-Introduction-4-320.jpg)
![CONTINUED…
Spectrum
ws
-ws
]
[
cos s
s
s w
w
w
w
t
nw
FT
)
(2
cos
)
(
2
)
(
cos
)
(
2
)
(
1
.
.
.
t
t
m
t
t
m
t
m
T
s
s
s
t
sampled
S
Spectrum
fm
-fm fs-fm fs
-fs fs+fm
-fs+fm
-fs+fm
…
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-samplingtheorem-240728173456-db0947ae/85/Sampling-Theorem-A-Comprehensive-Overview-Introduction-5-320.jpg)