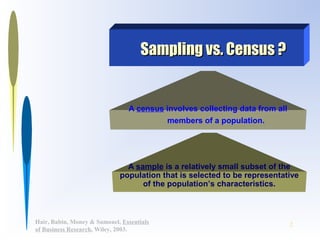
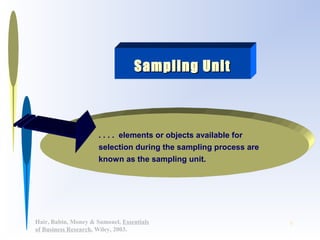
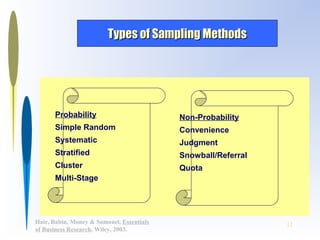
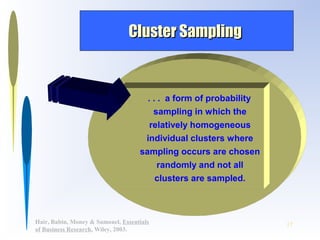
This document discusses sampling methods for business research. It defines key terms like target population, sampling frame, and sampling unit. It explains the difference between probability and non-probability sampling. Several sampling methods are described, including simple random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and convenience sampling. The document also covers determining appropriate sample size based on factors like population variability, required precision, and confidence level.