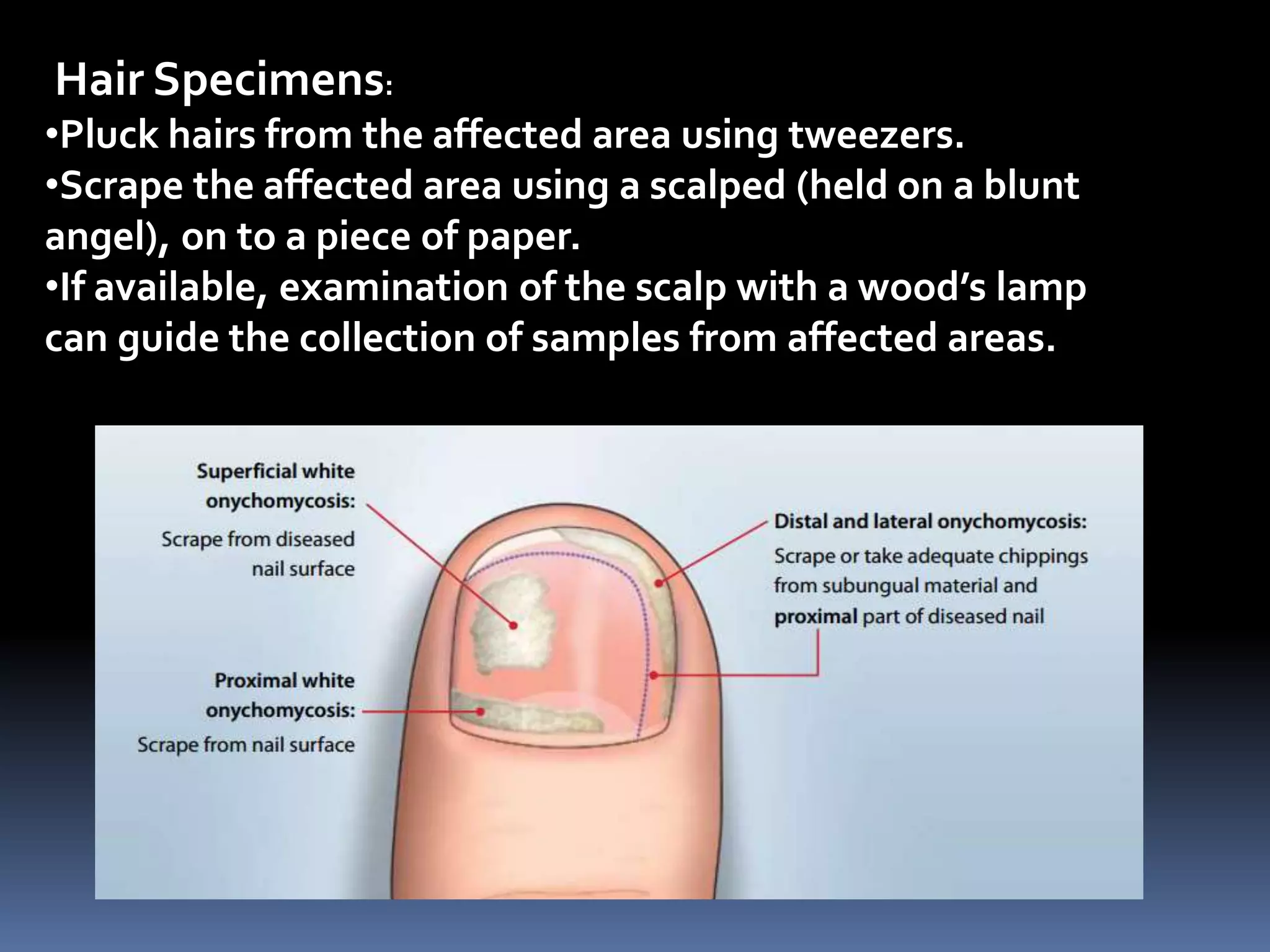
This document provides guidelines for collecting samples from patients to test for various types of infections, including bacterial, viral, fungal and protozoan. It describes collecting blood, urine, stool and cerebral spinal fluid samples for testing white blood cell counts, bacteria, viruses and parasites. Specific instructions are given for collecting skin, nail, hair and mucous membrane samples for fungal testing. The document stresses using sterile containers and transporting samples at the proper temperature range.