Here are the six basic knots that every sailor should know:
1. The overhand or thumb knot is used to stop the end of a rope from running.
2. The square knot is useful for joining ropes together.
3. A figure eight knot prevents ropes from escaping like an overhand knot.
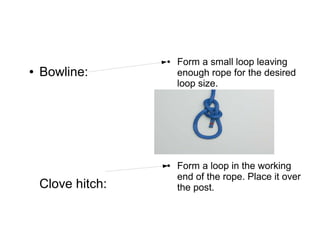
4. The bowline forms a fixed loop in the rope.
5. A clove hitch secures a rope to a post by forming loops.