The document discusses various AWS services including Elastic Load Balancing, Auto Scaling, AWS CloudFormation, and Amazon CloudFront. It provides information on:
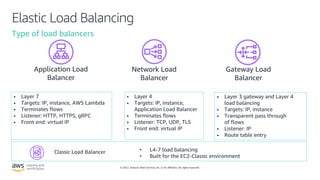
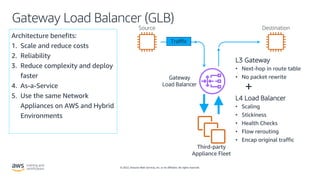
- How Elastic Load Balancing distributes traffic across multiple targets to improve scalability. It describes different types of load balancers.
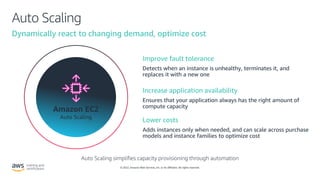
- How Auto Scaling automatically launches or terminates EC2 instances based on user-defined policies to dynamically scale capacity as needed.
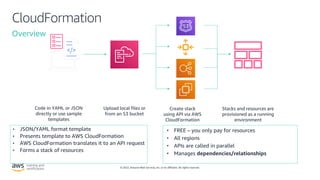
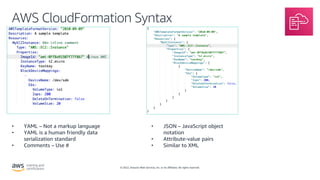
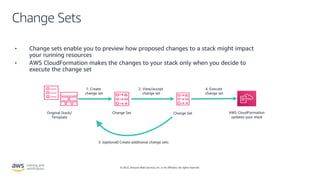
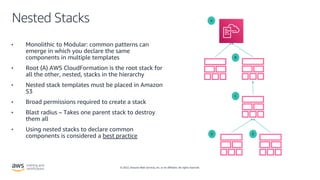
- How AWS CloudFormation allows defining infrastructure as code using templates to deploy and manage AWS resources in a reproducible and predictable manner.
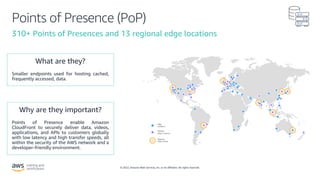
- How Amazon CloudFront is a global content delivery network (CDN) that securely delivers data, videos, applications, and APIs to customers with low latency and high transfer