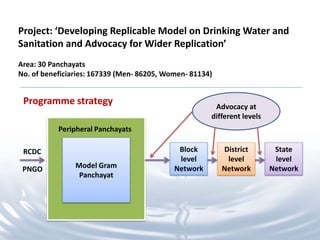
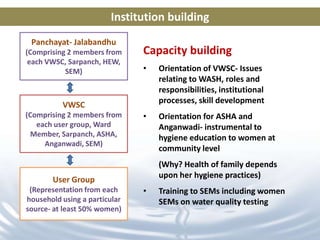
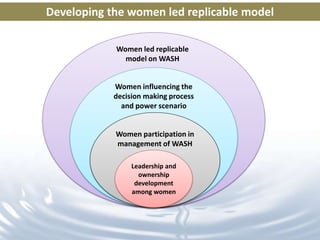
This document discusses the development of a women-led replicable model for water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) in Odisha, India. It notes that many rural households in Odisha lack access to water or sanitation. The program aims to develop and demonstrate a model across 30 panchayats benefiting over 167,000 people. Key aspects of the model include situational analysis, awareness building, institution building like water and sanitation committees, capacity building, participatory planning, and developing women's leadership and decision-making roles. Qualitative outcomes observed include greater women's participation in various WASH activities and decision making processes.