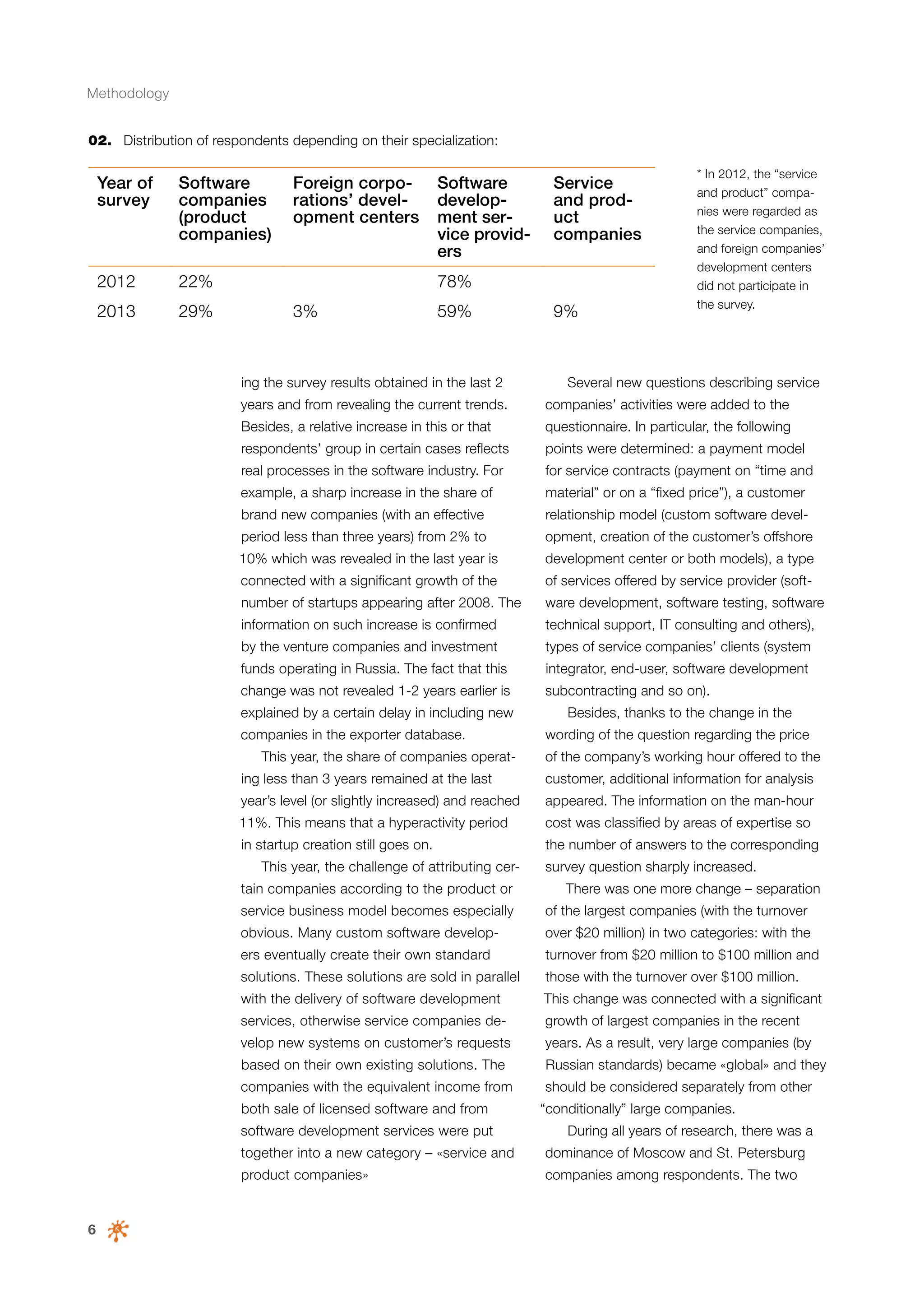
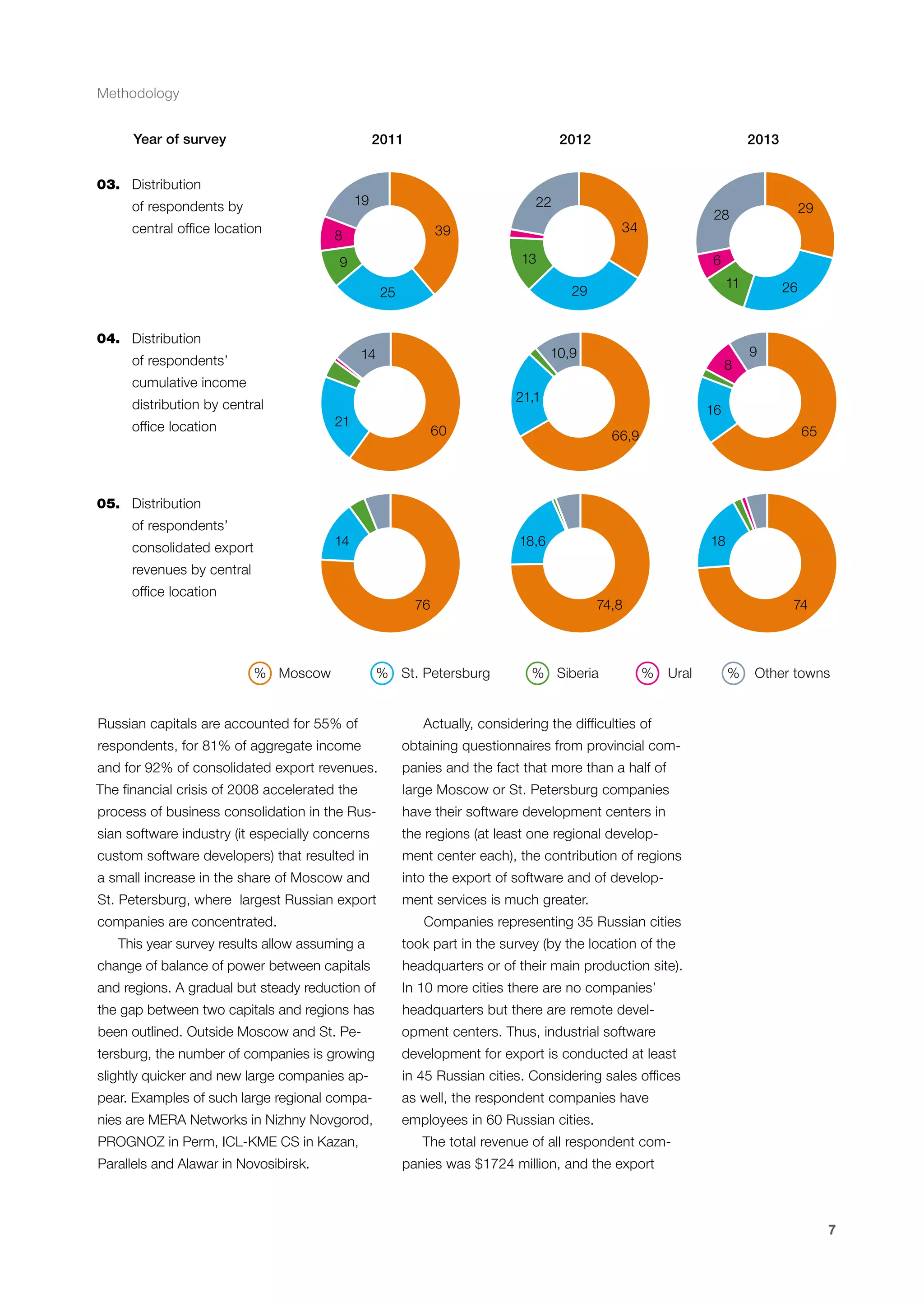
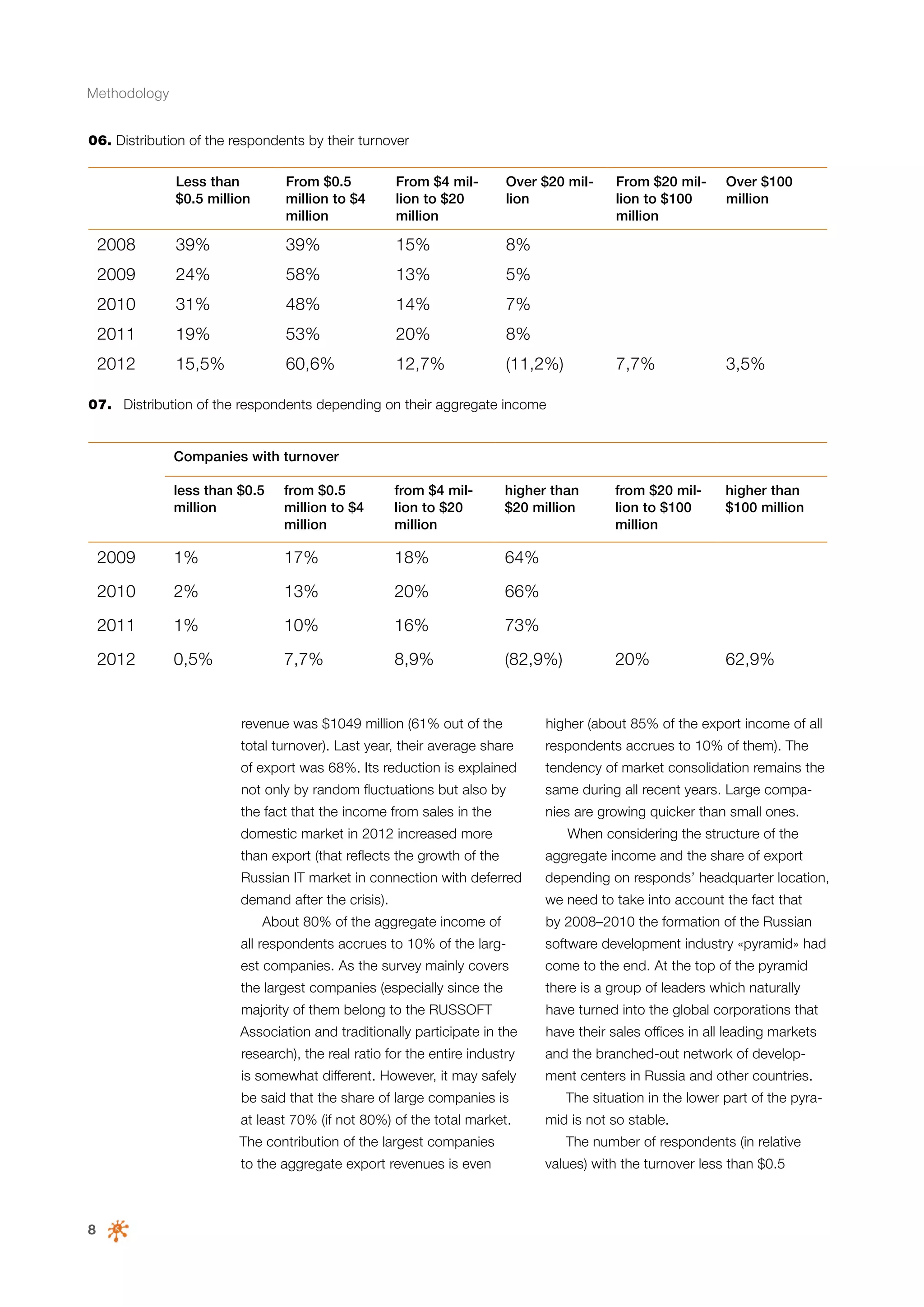
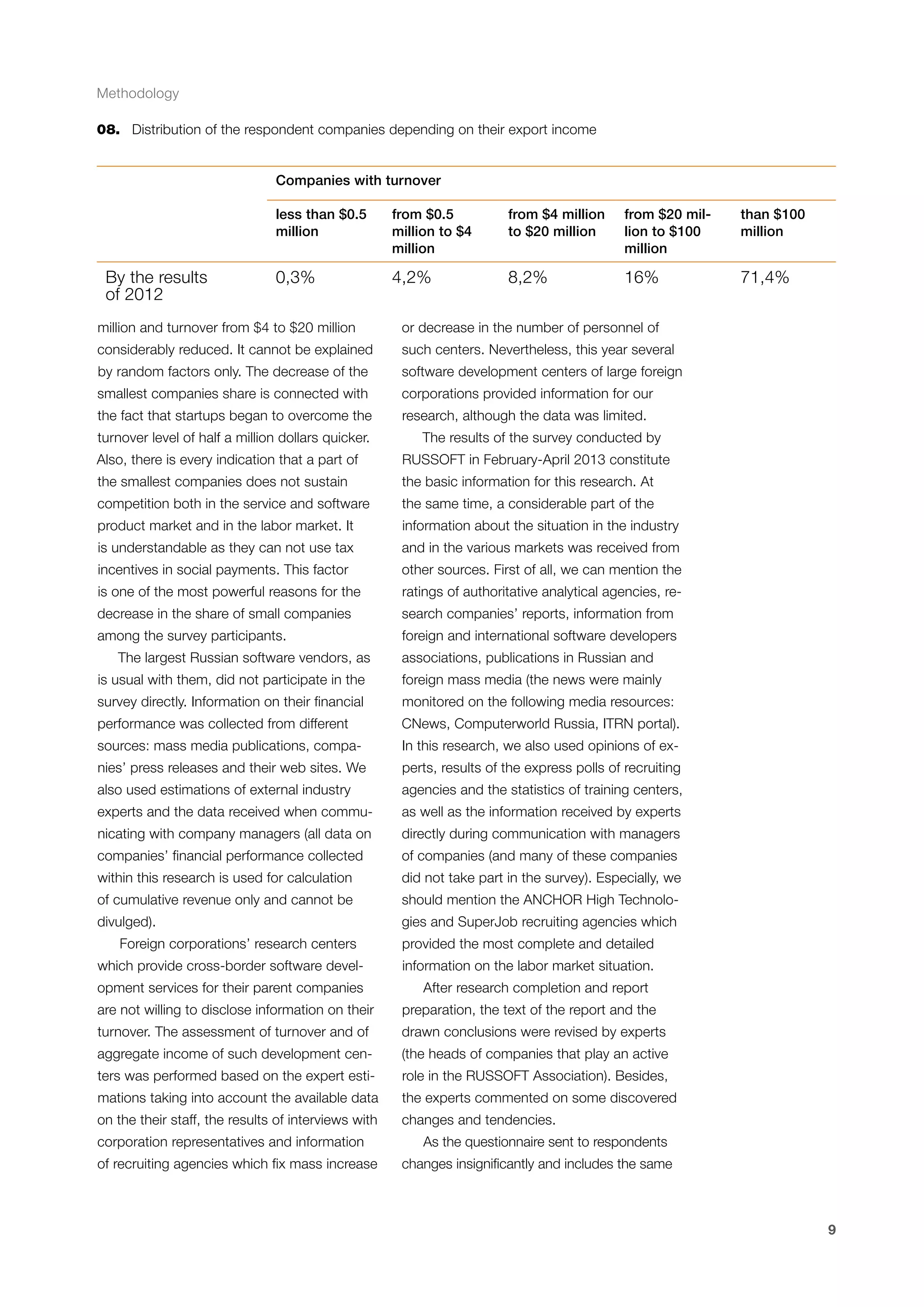
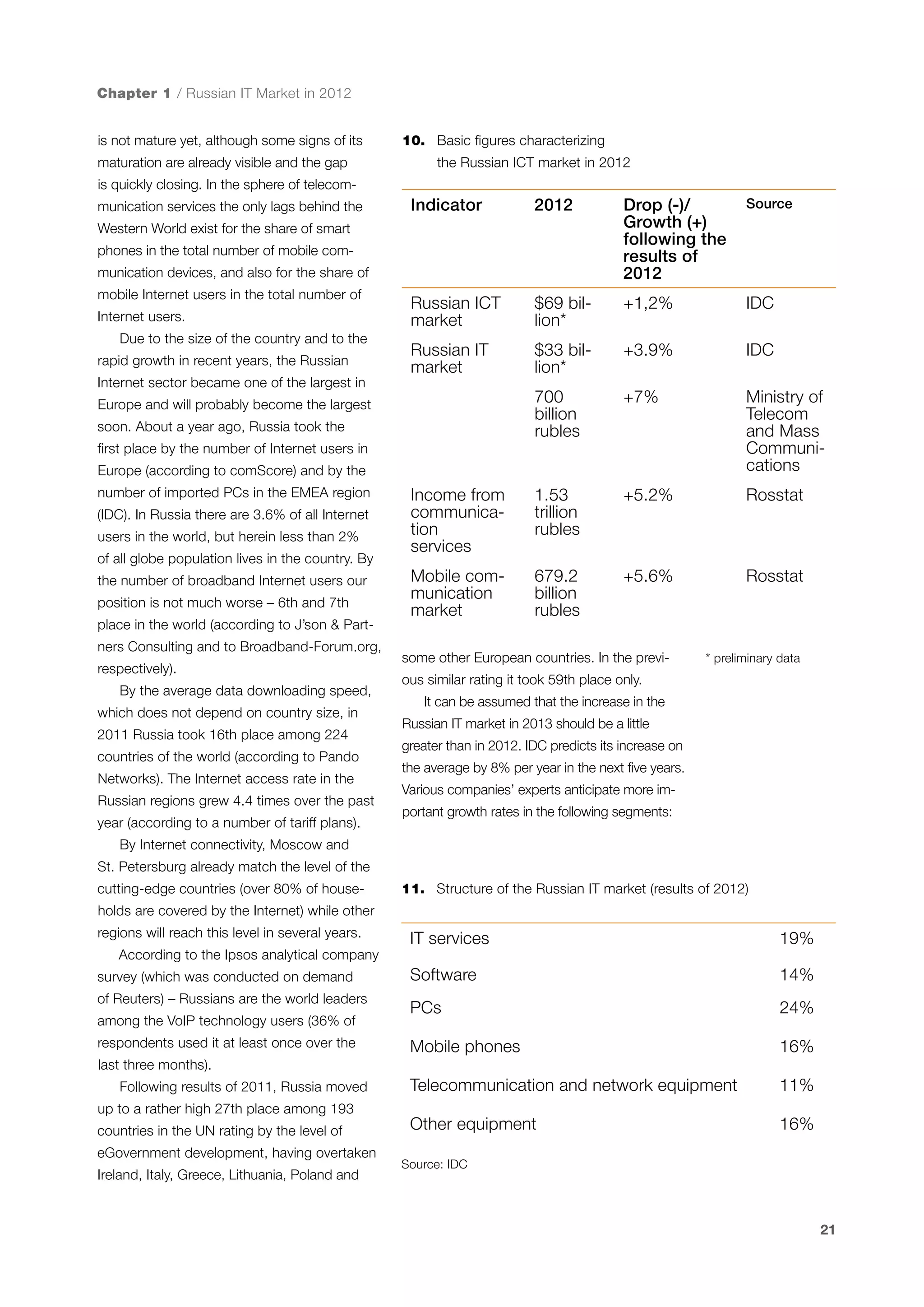
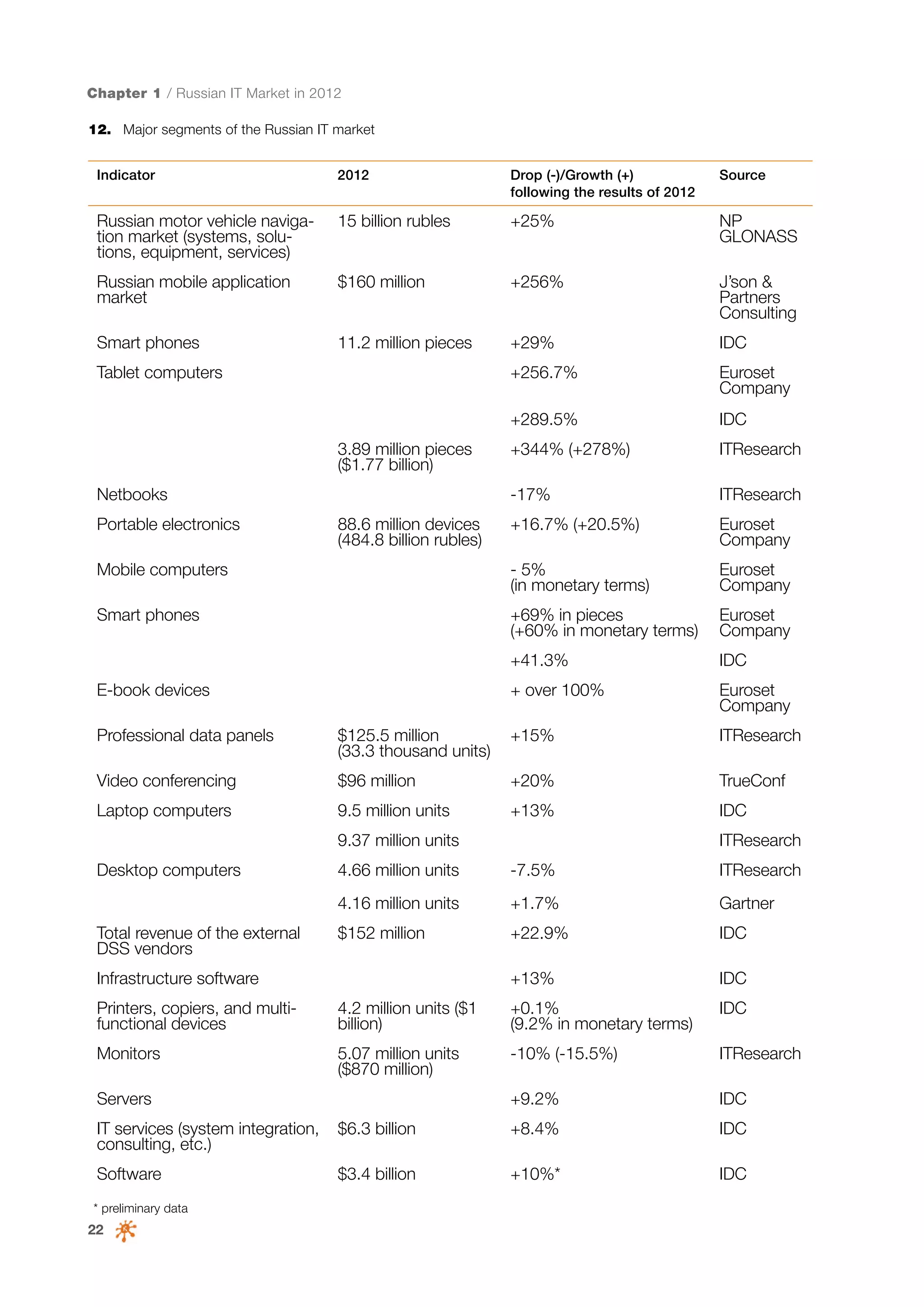
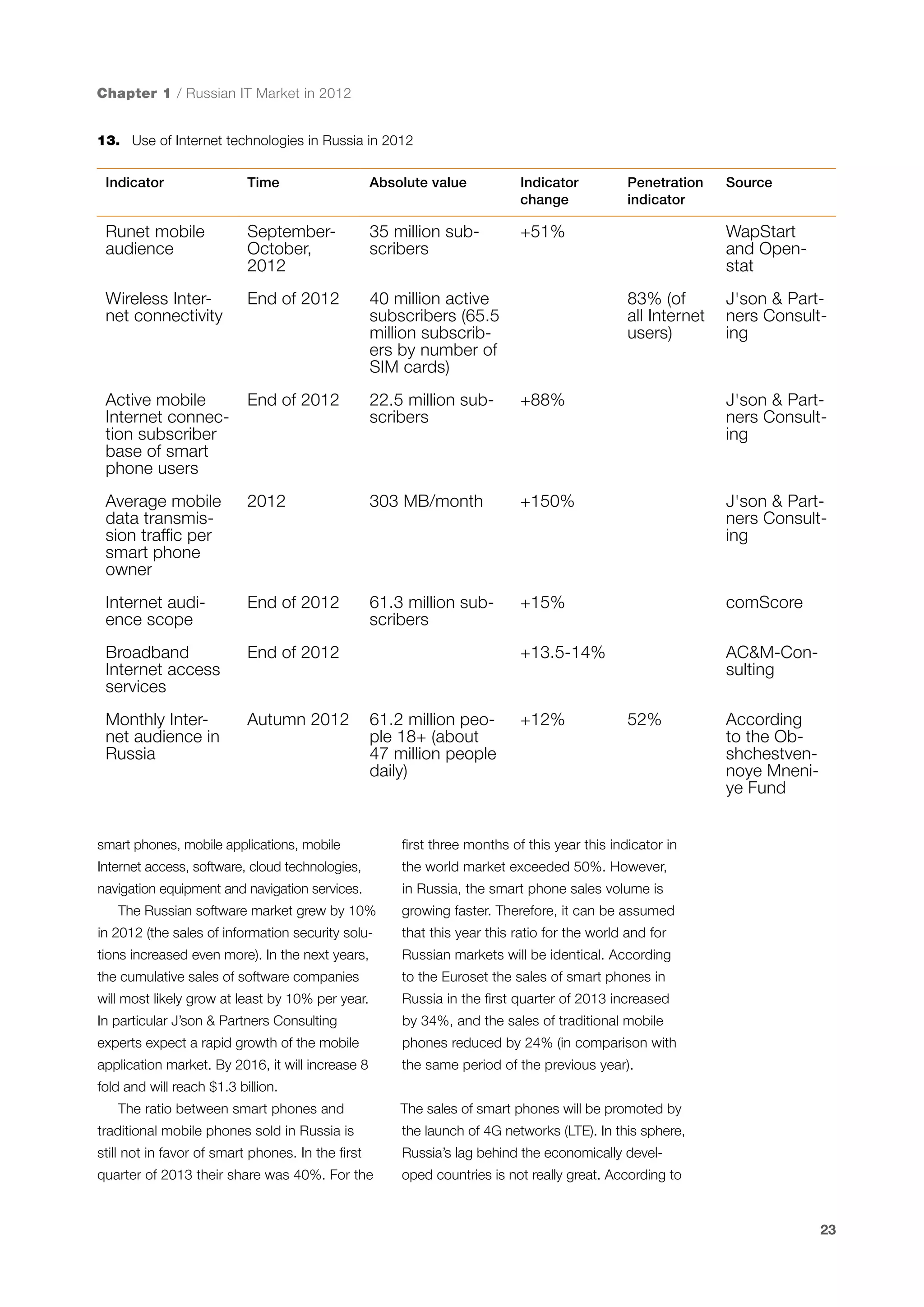
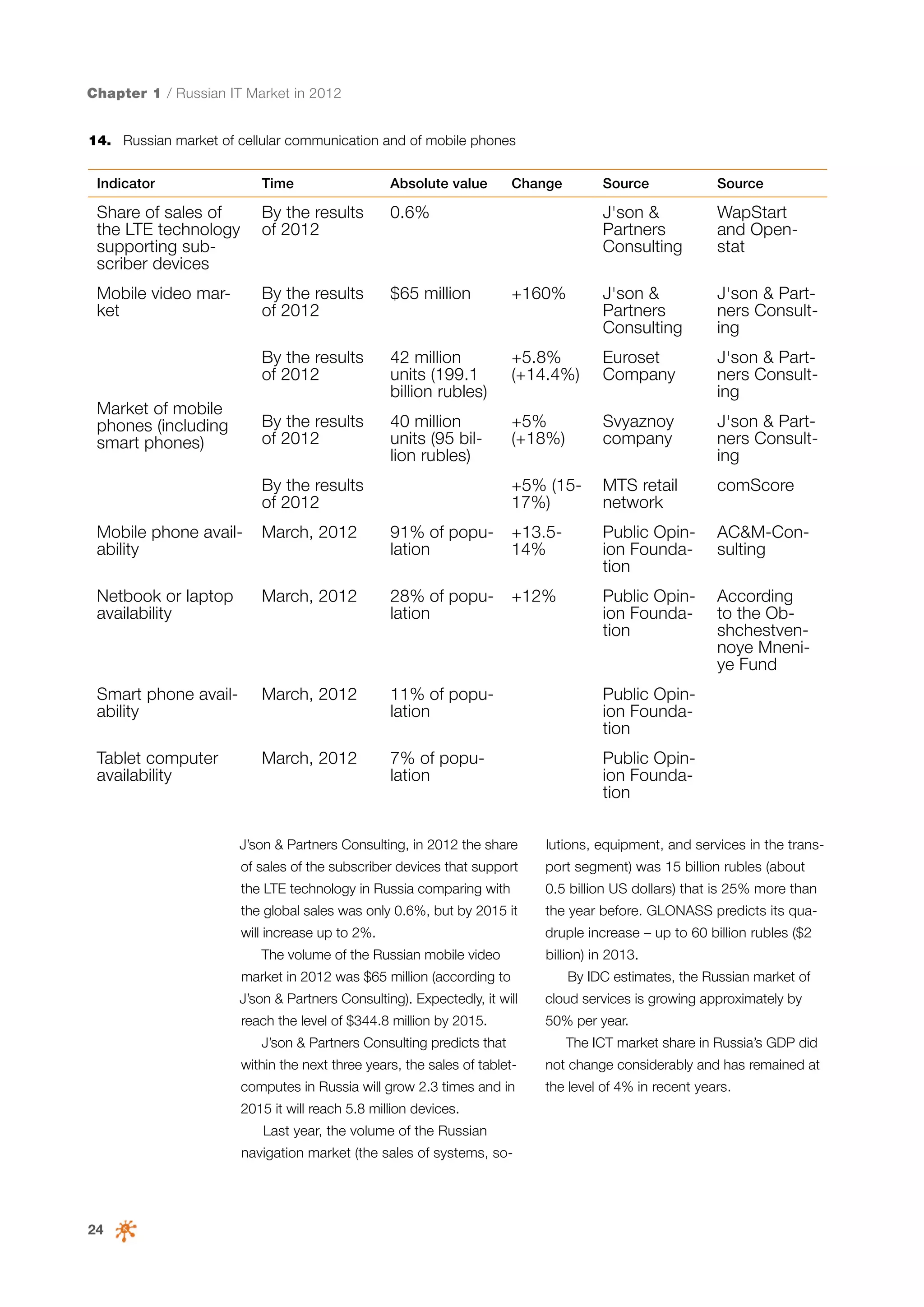
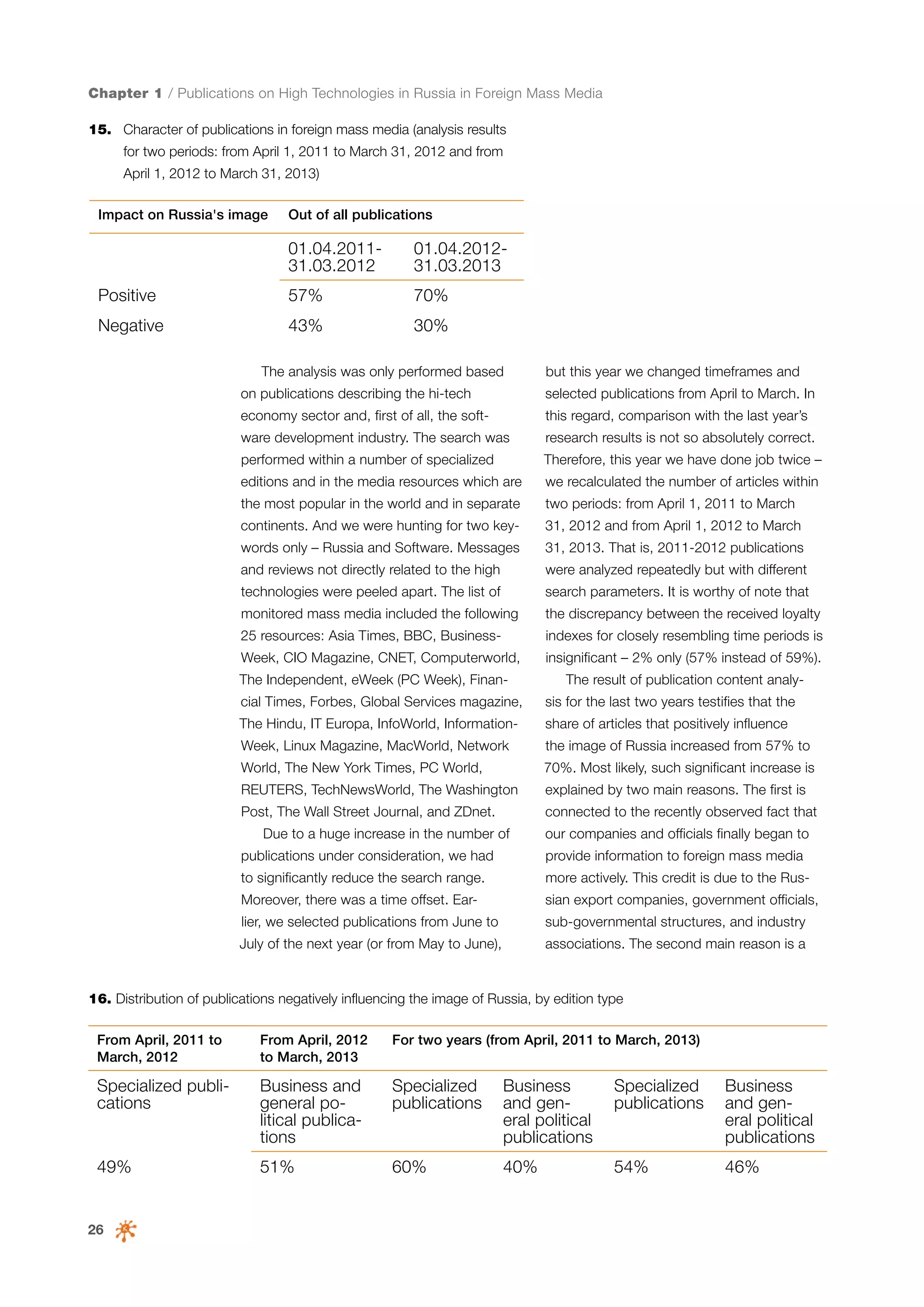
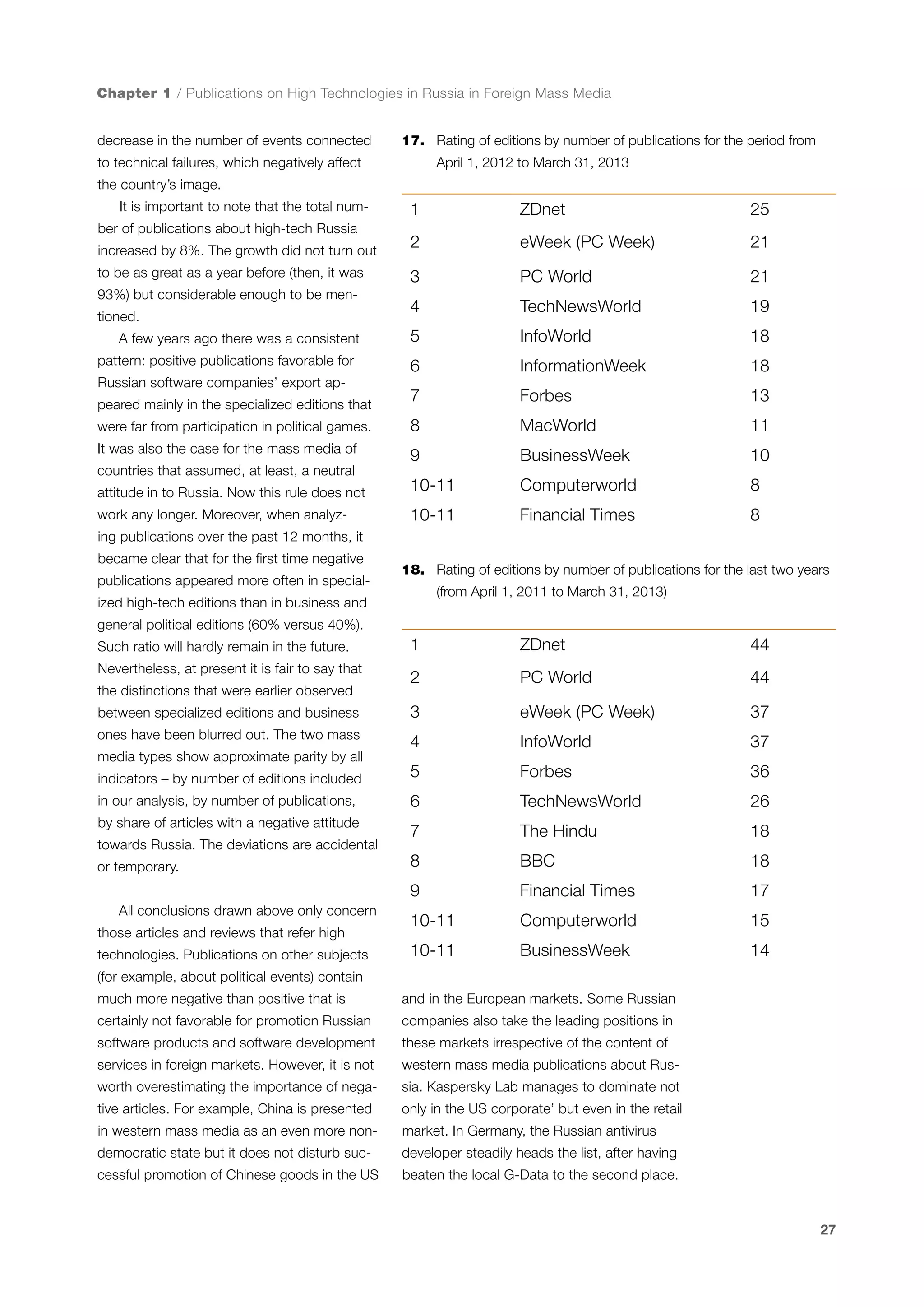
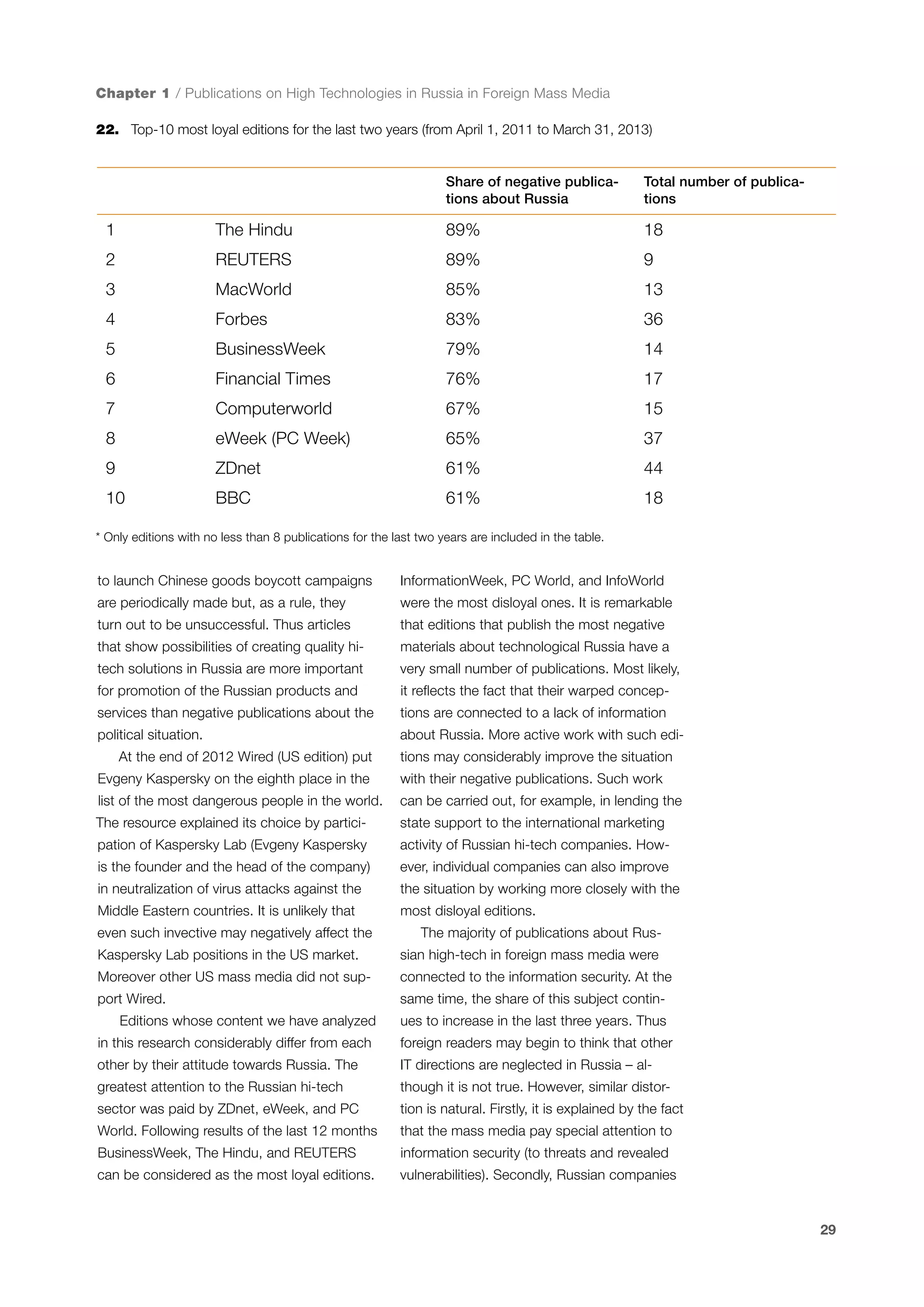
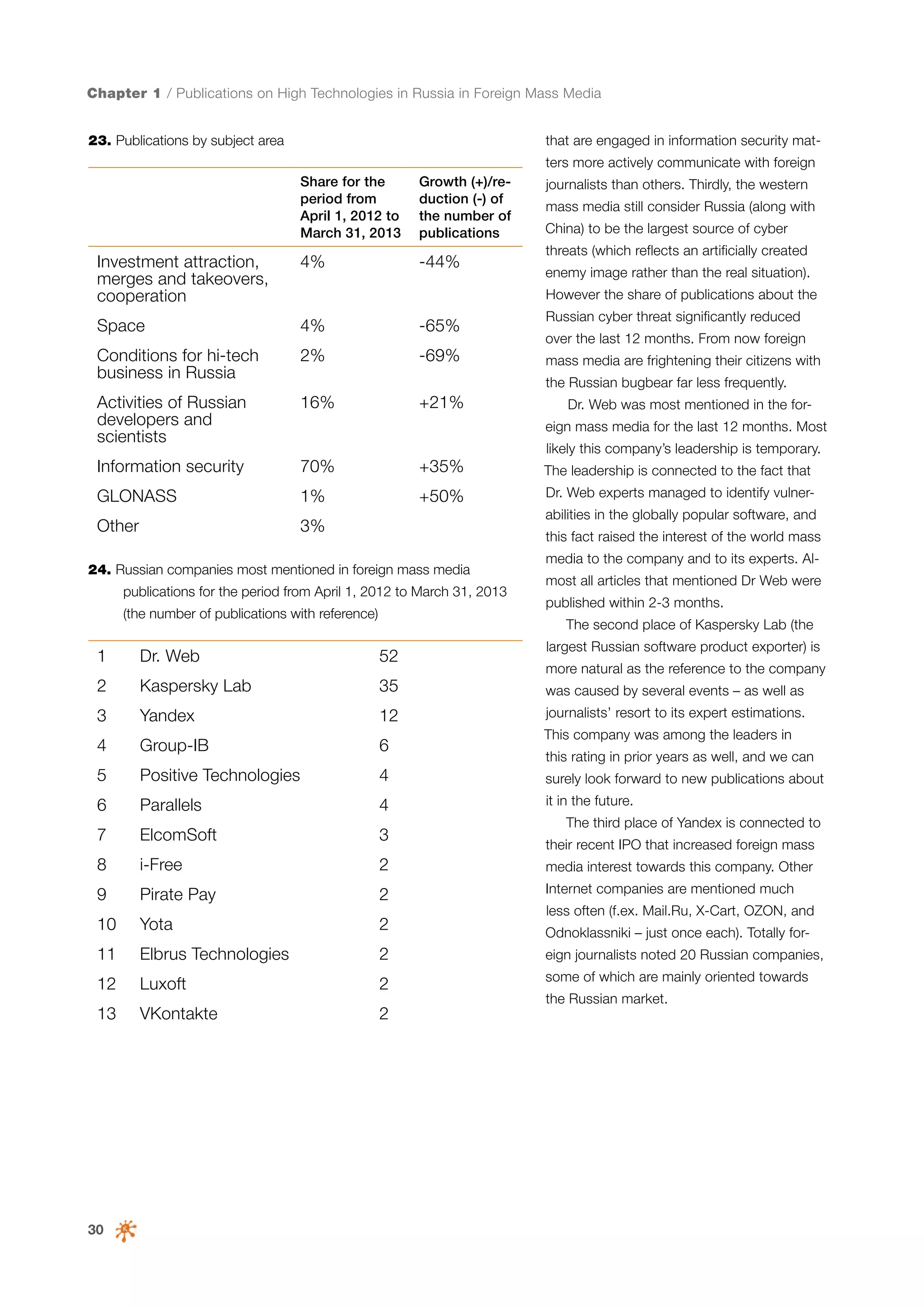
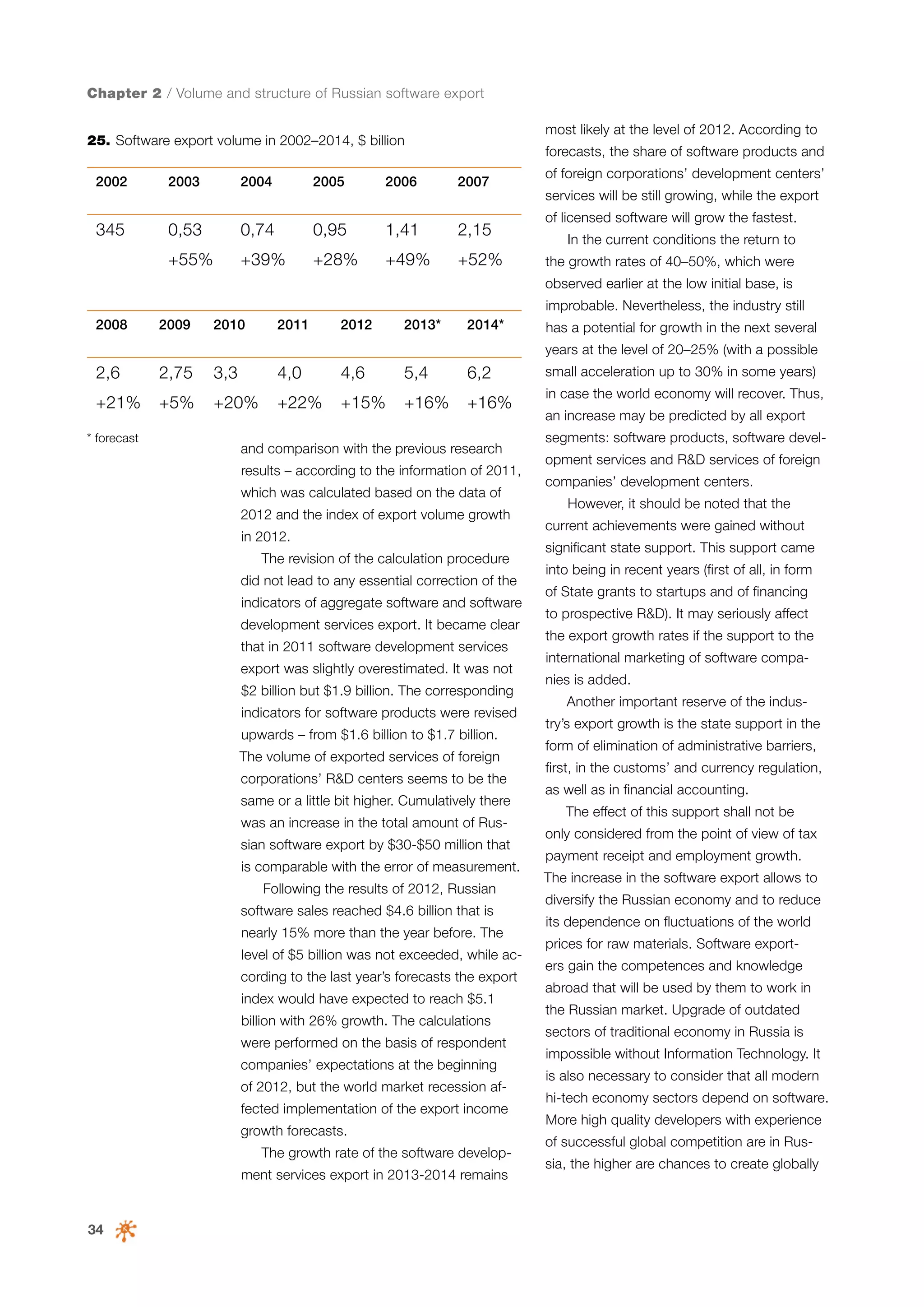
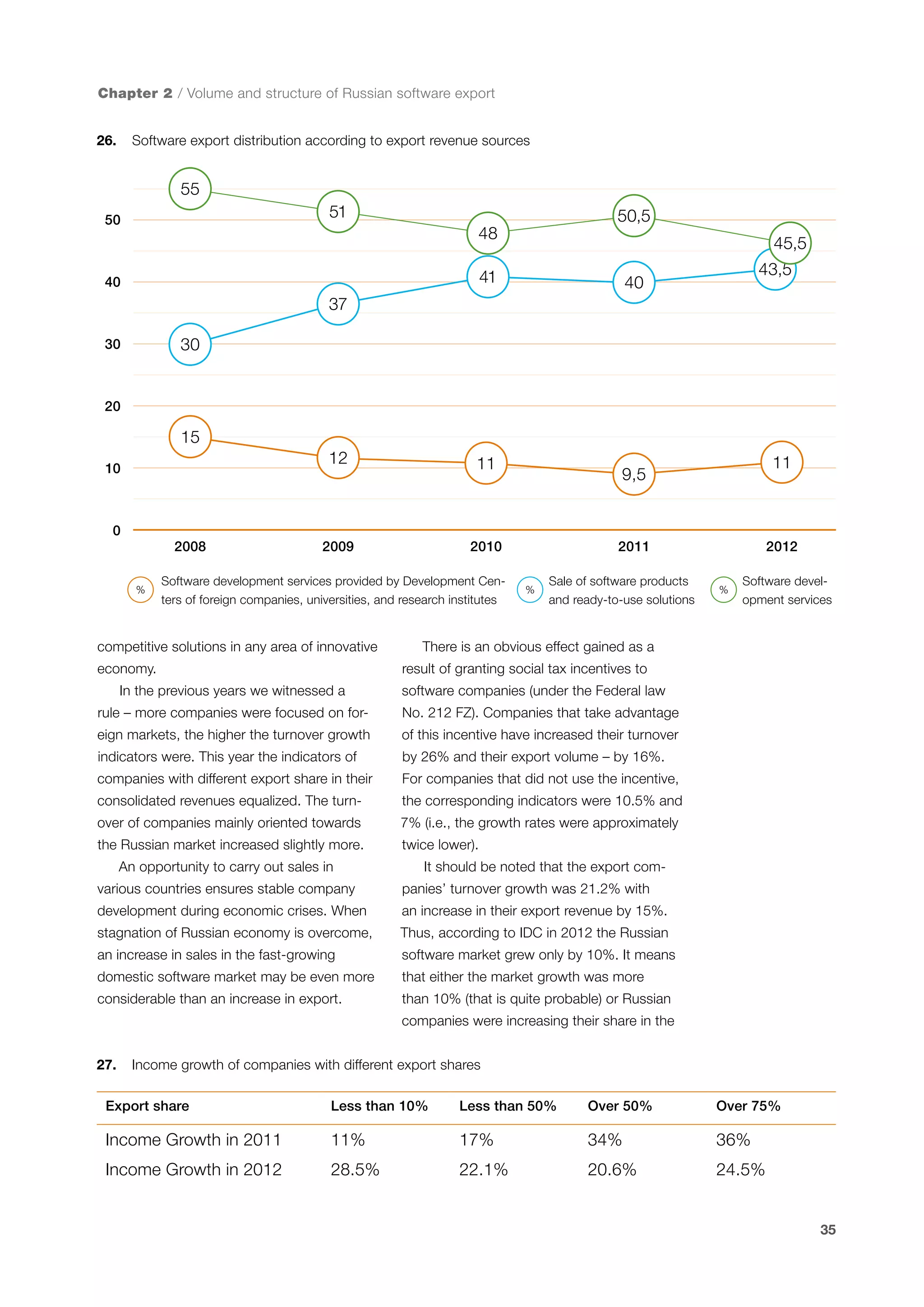
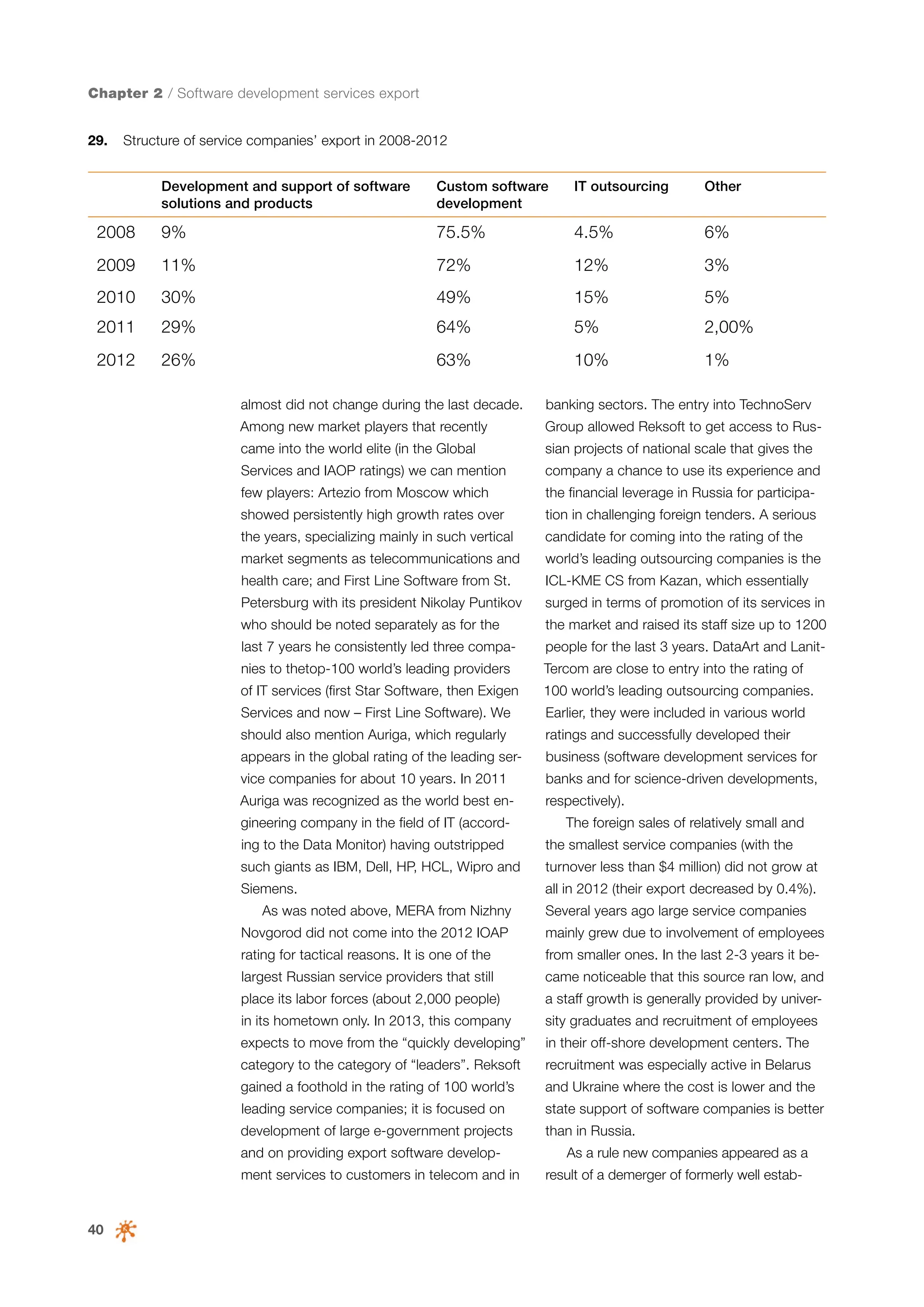
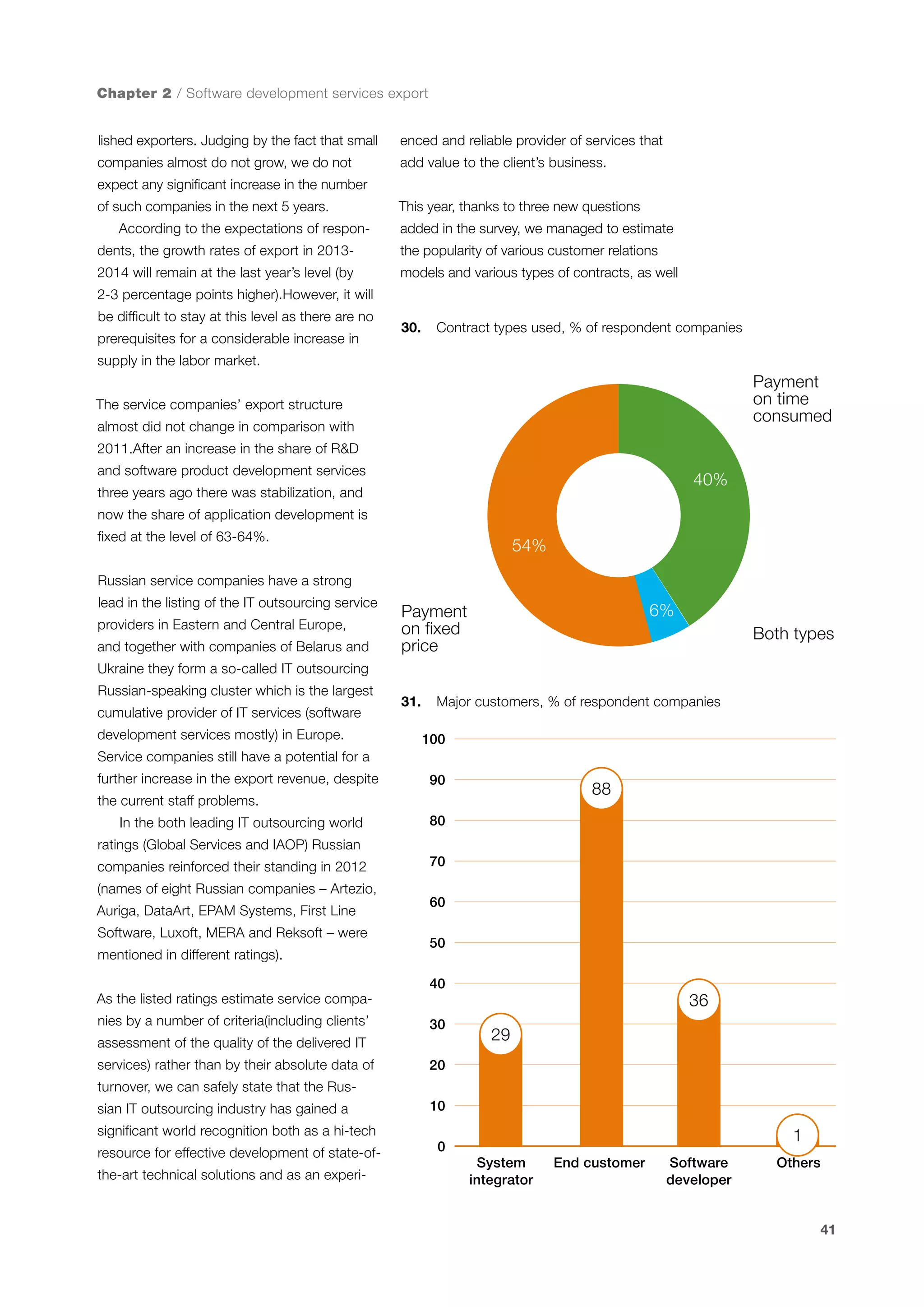
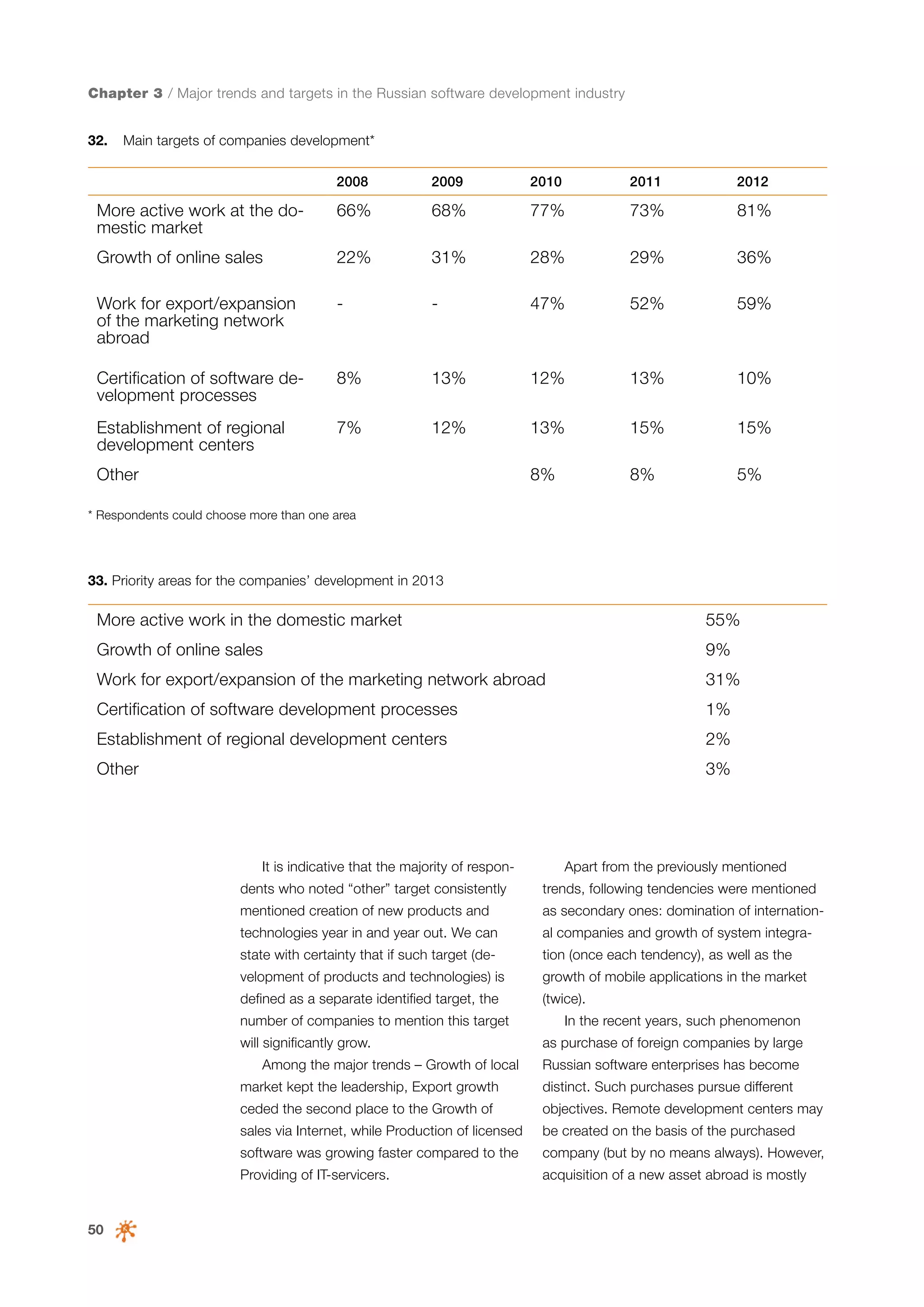
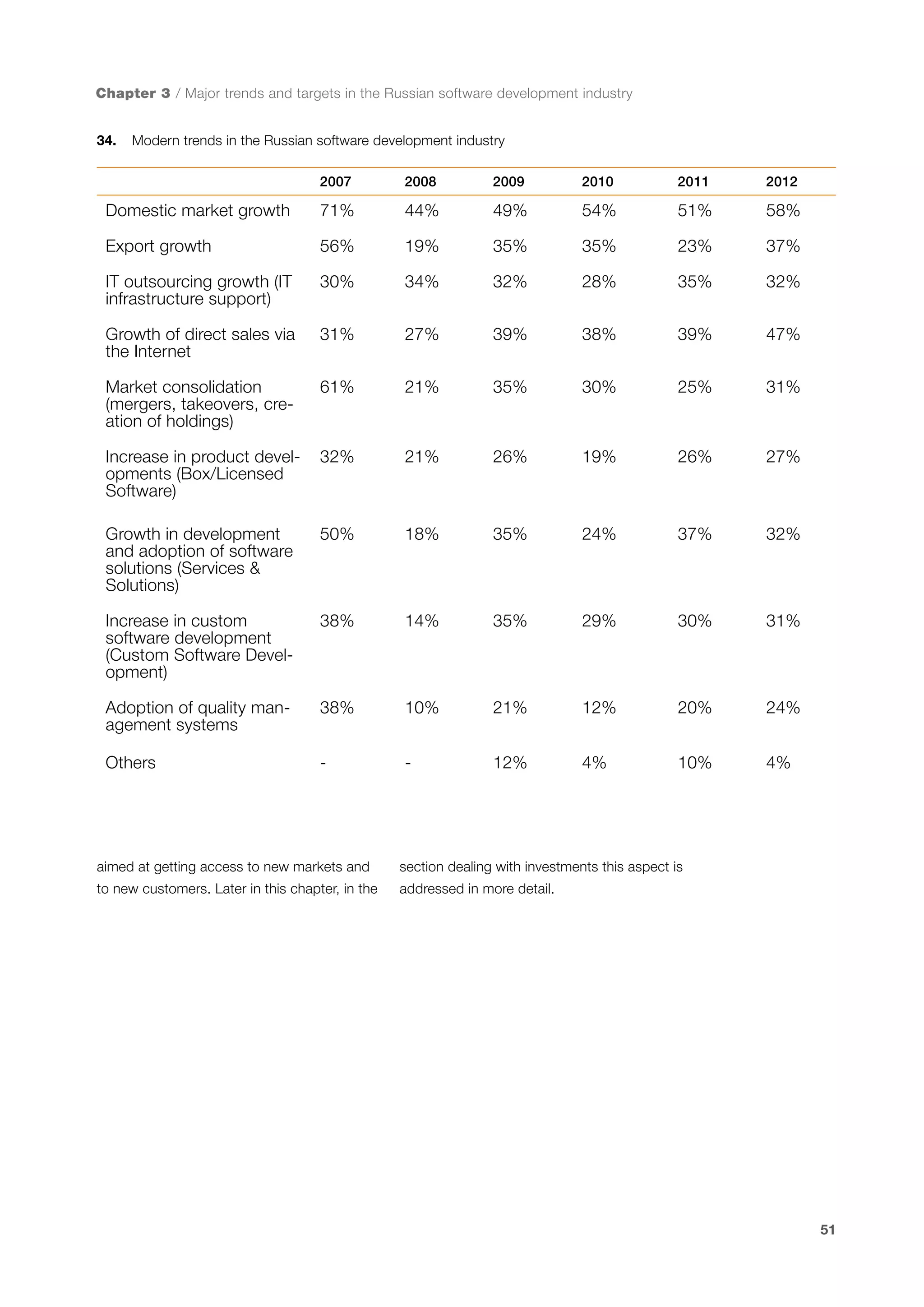
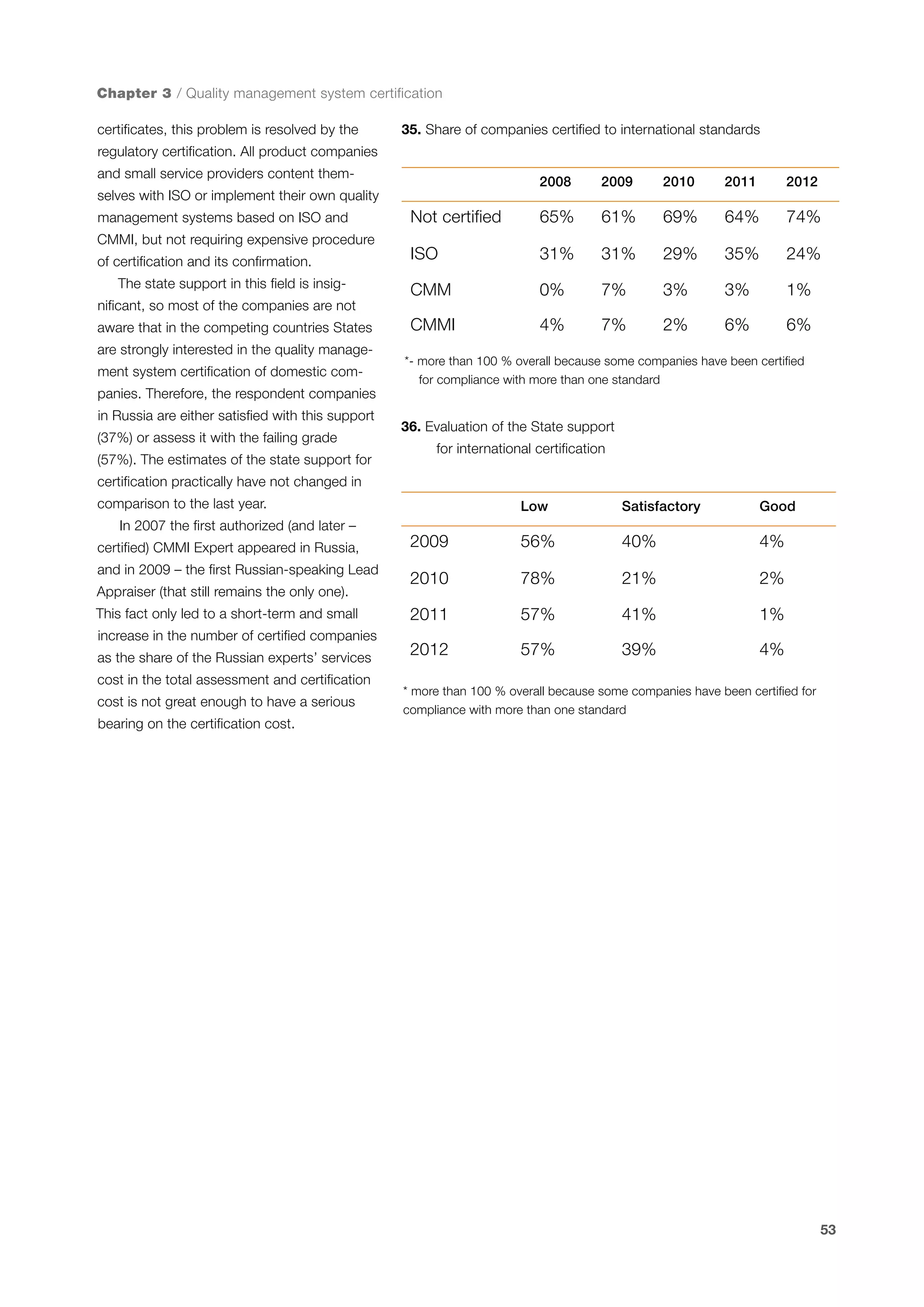
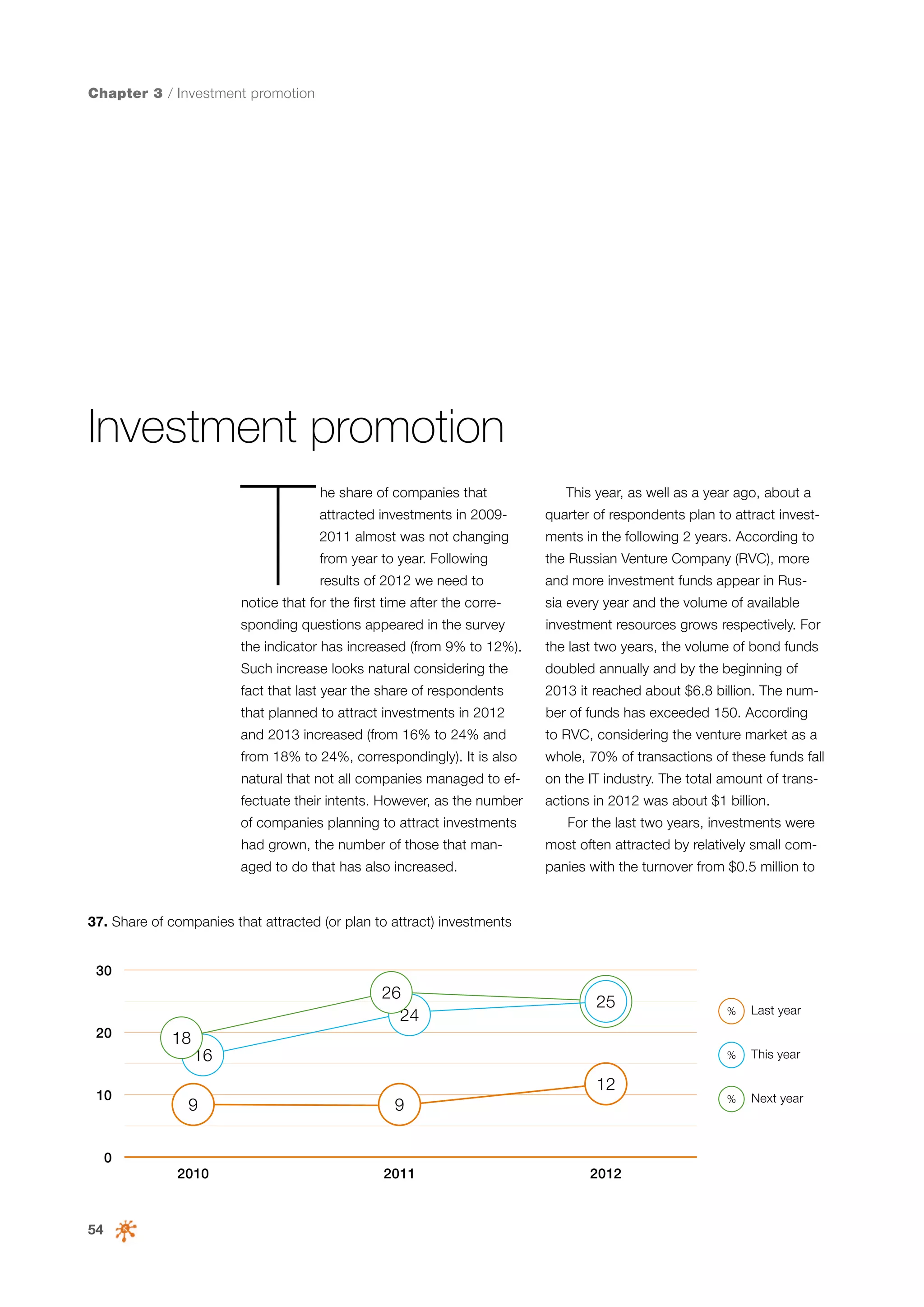
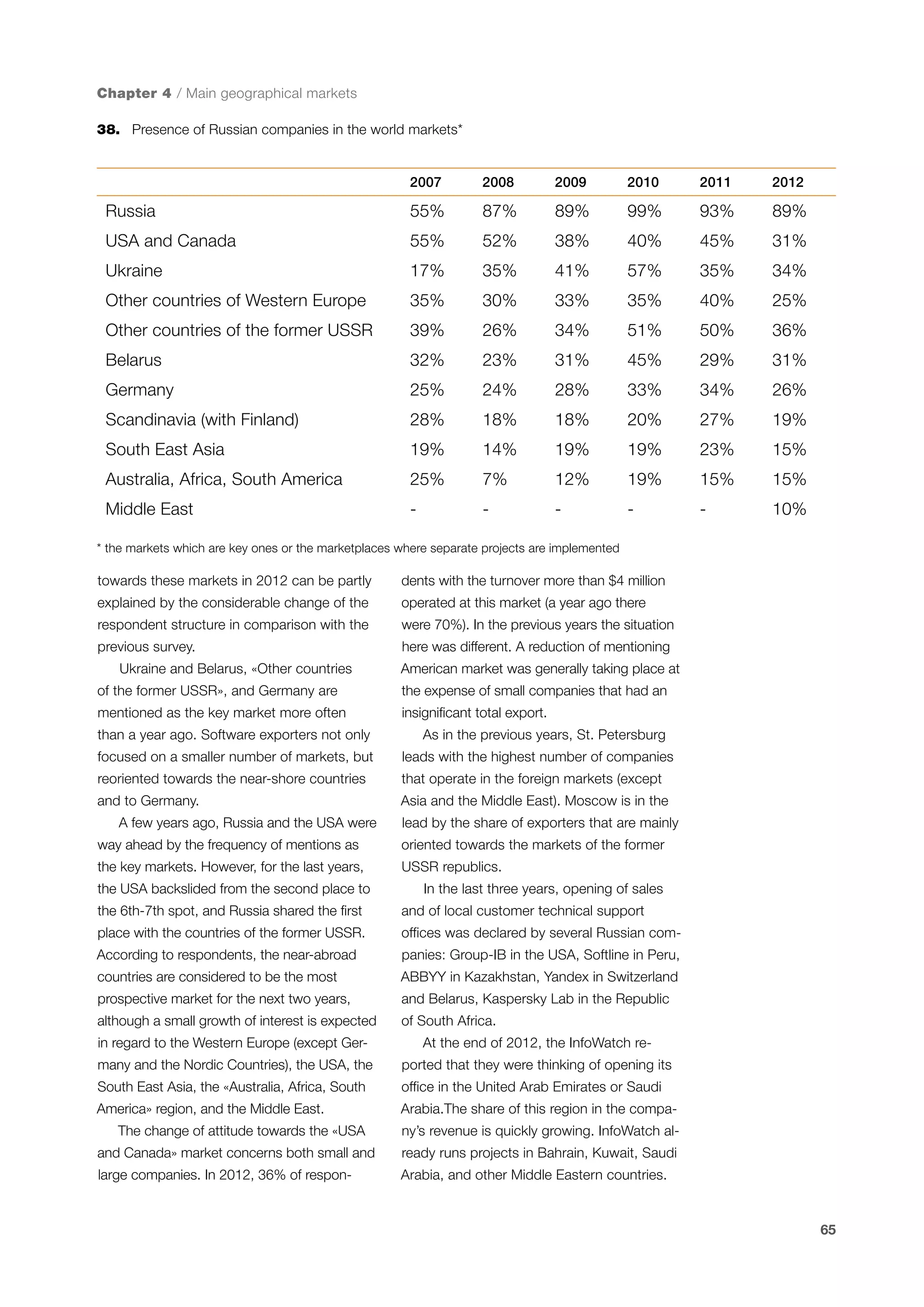
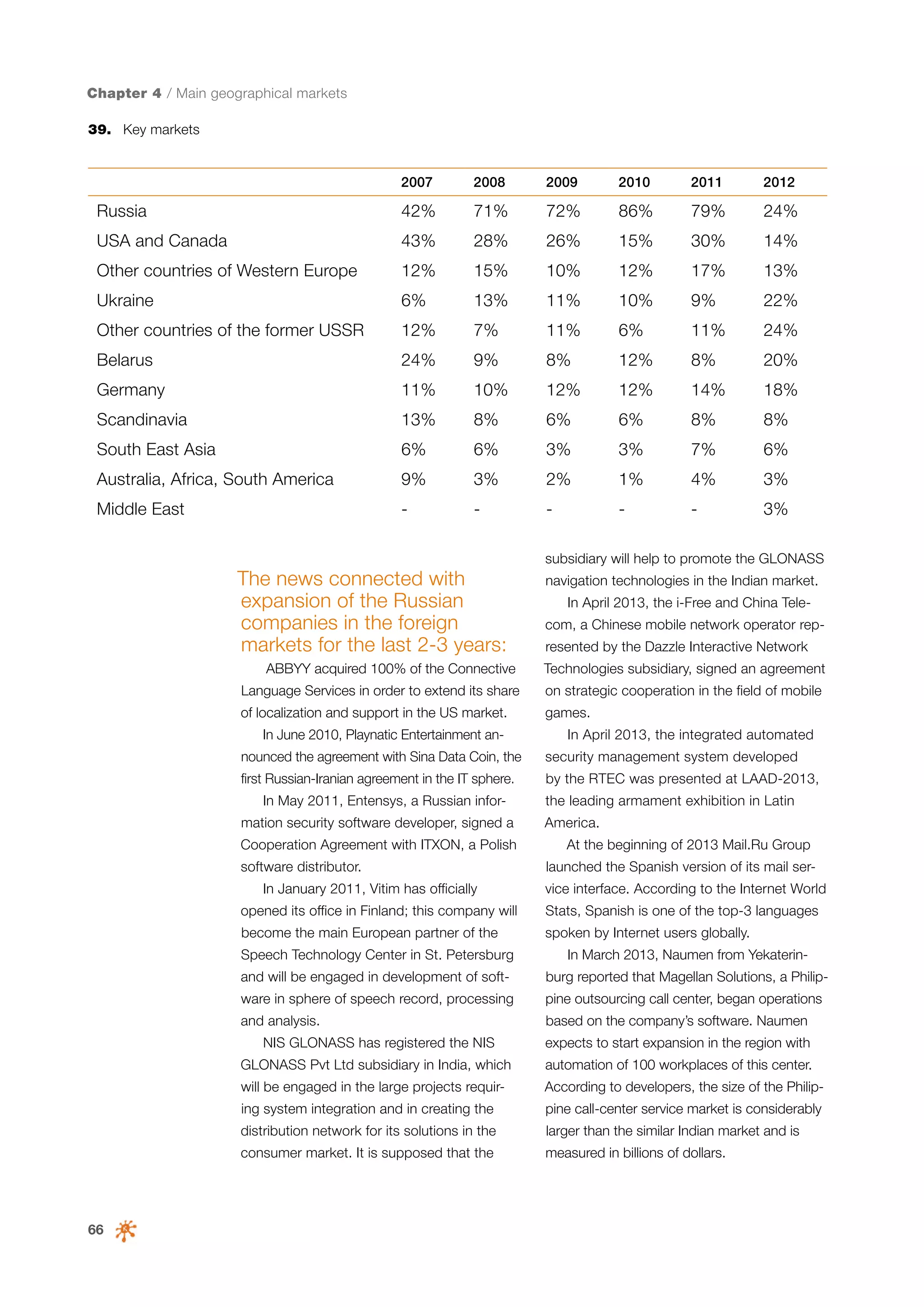
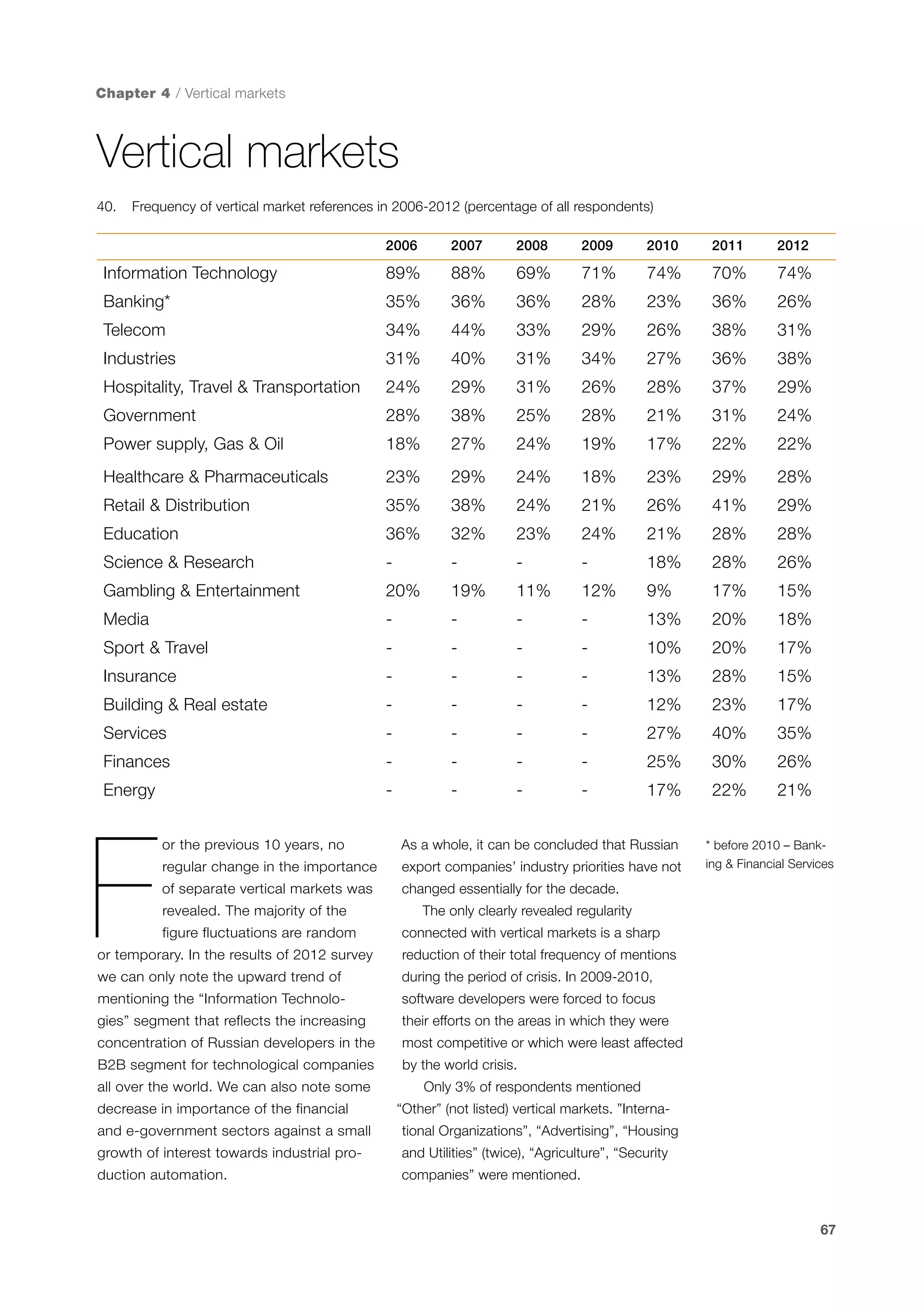
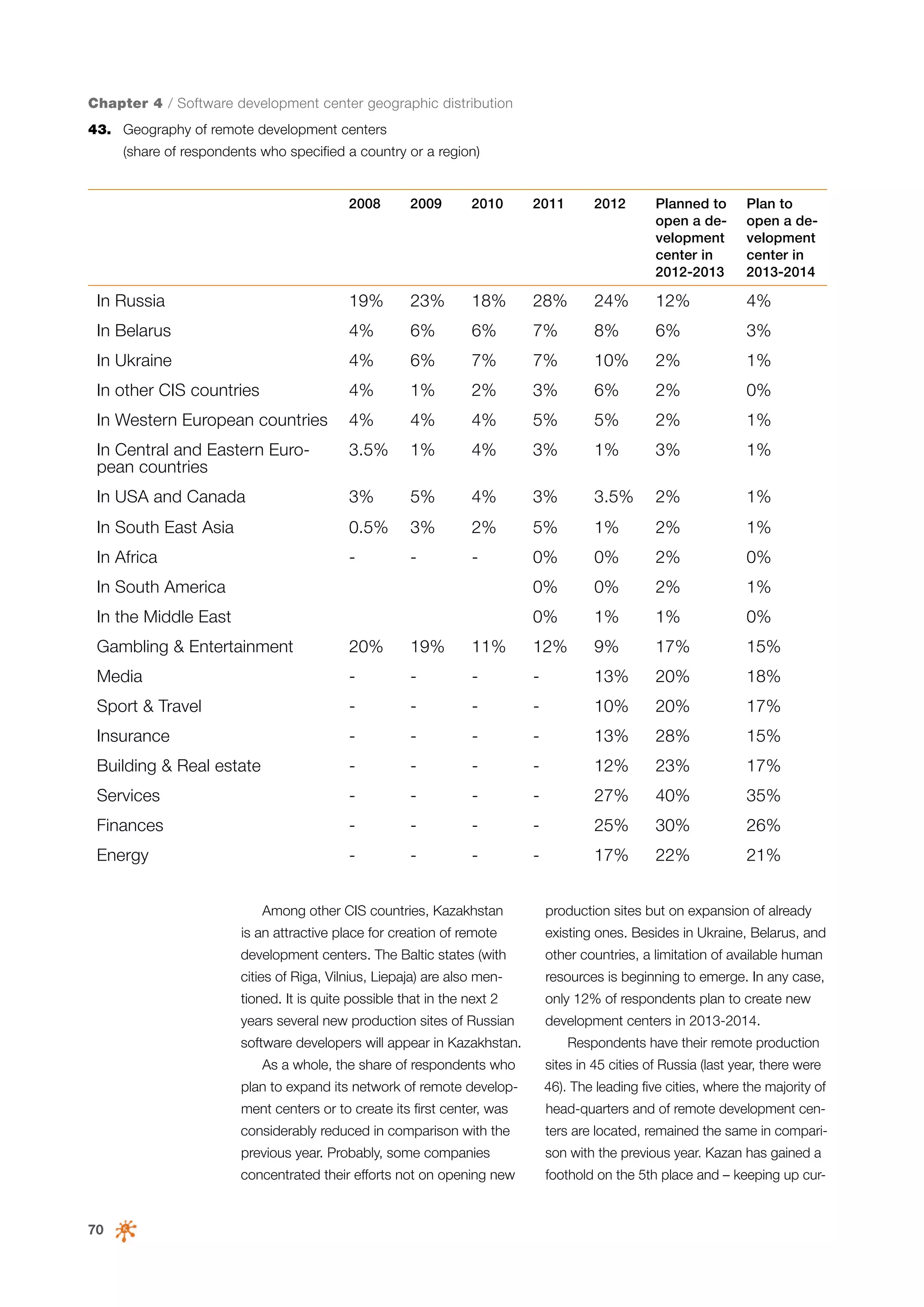
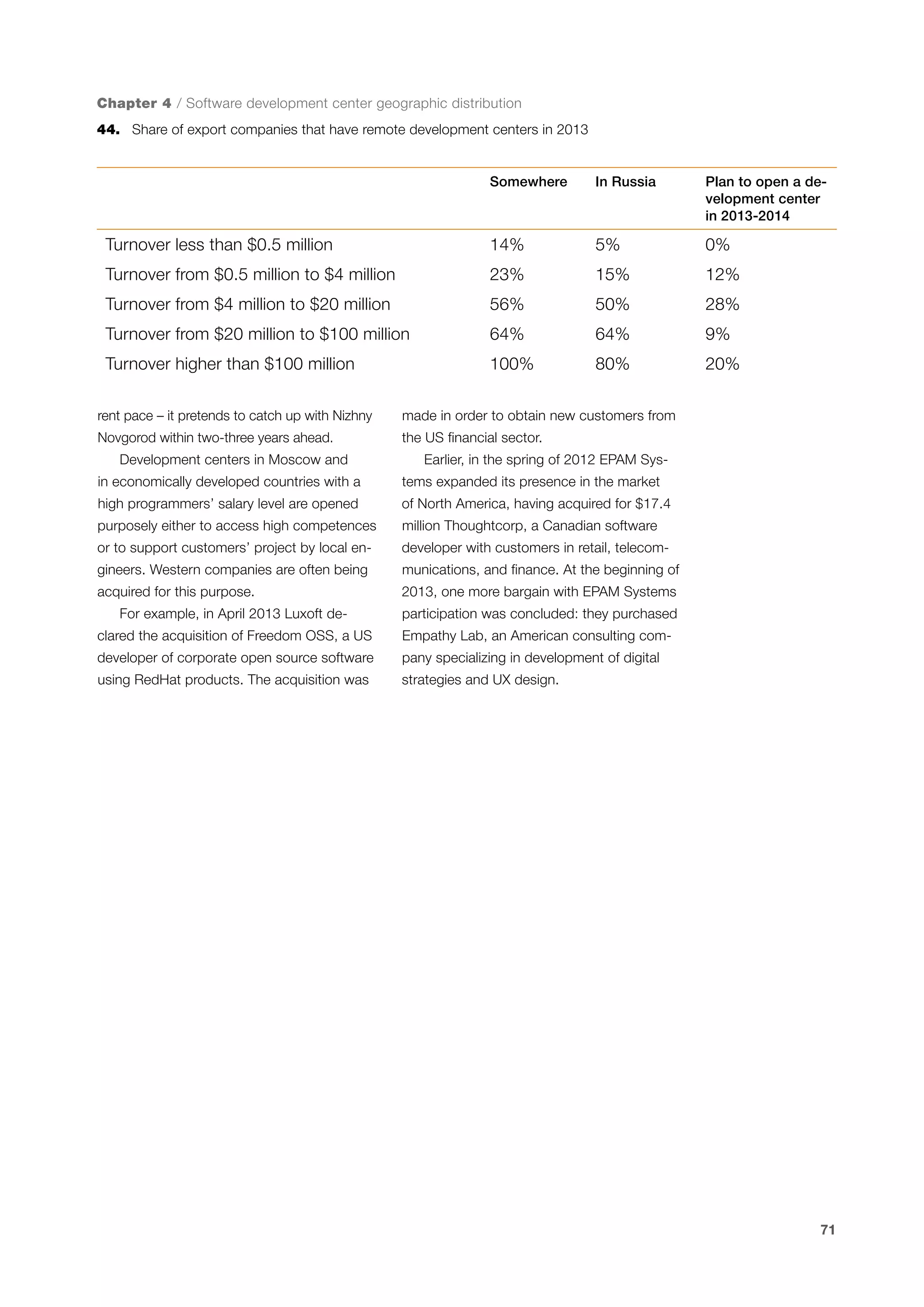
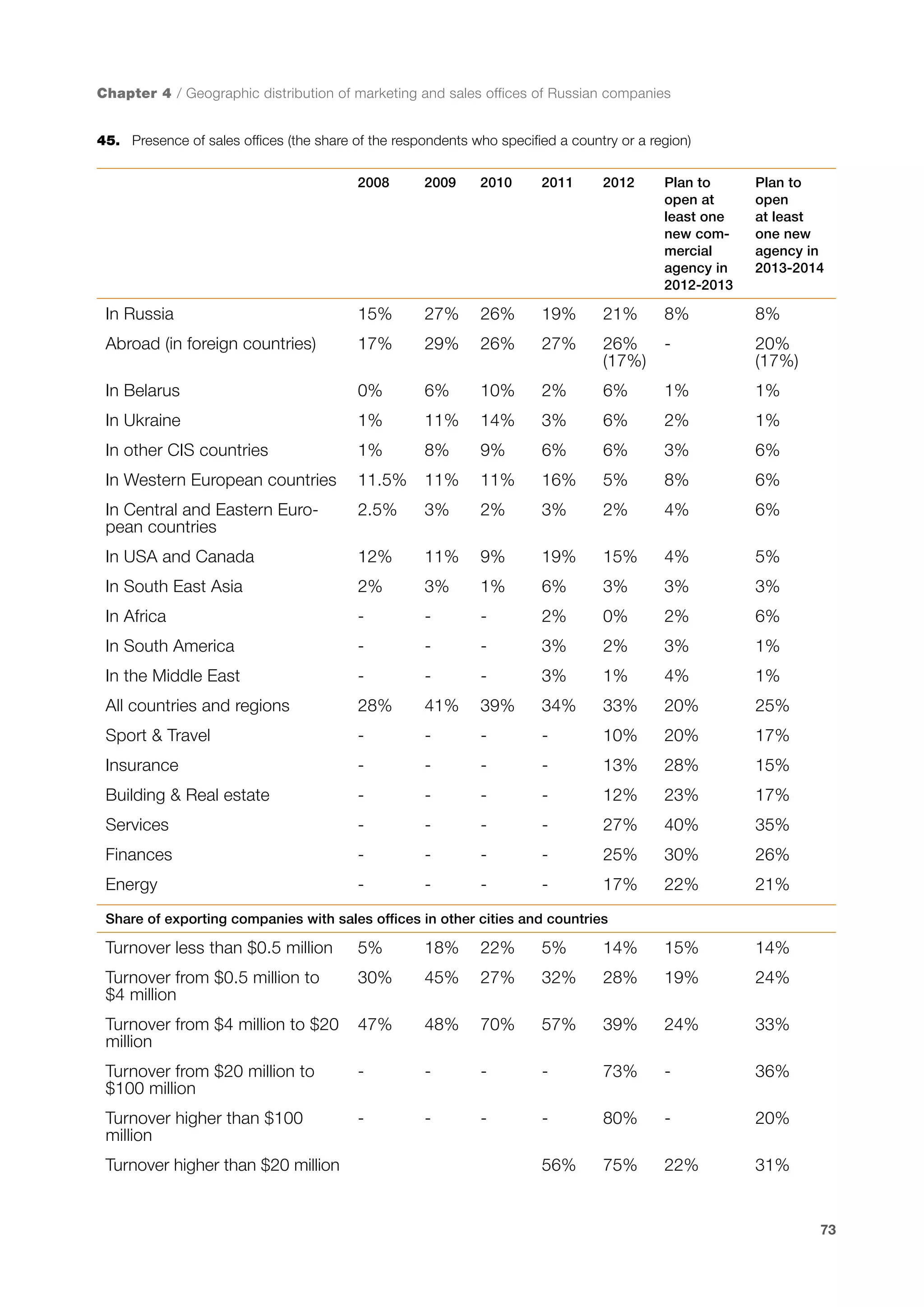
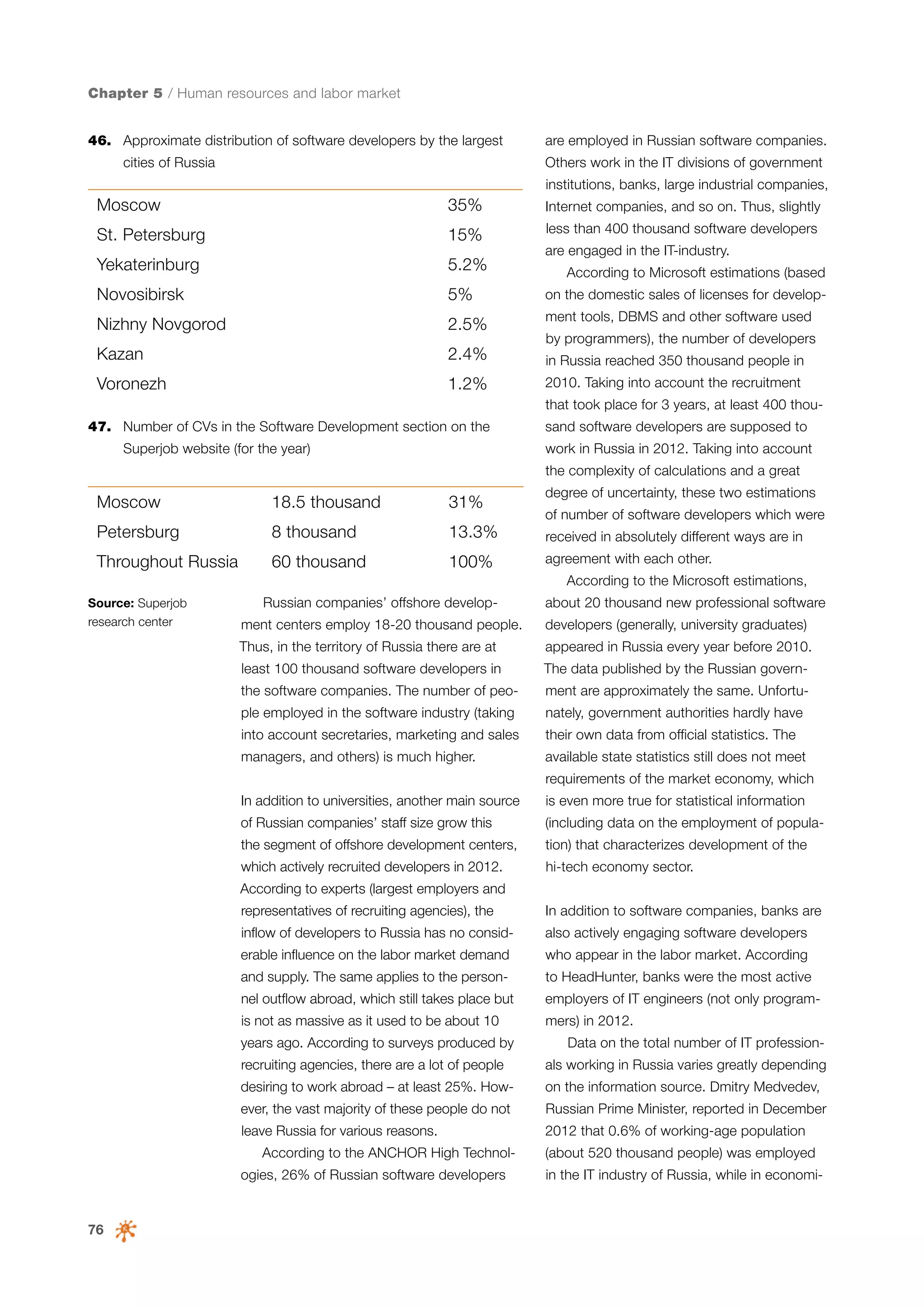
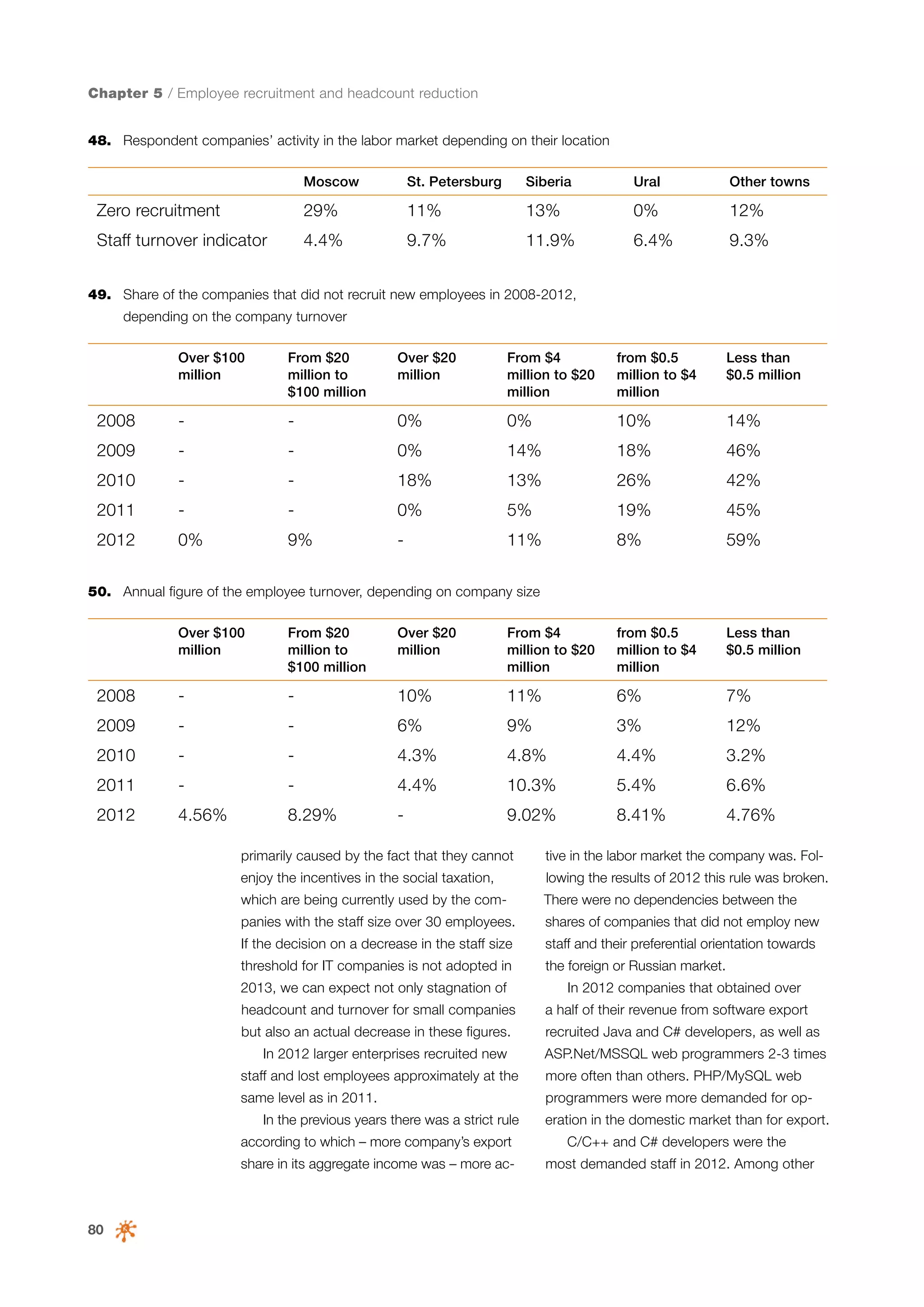
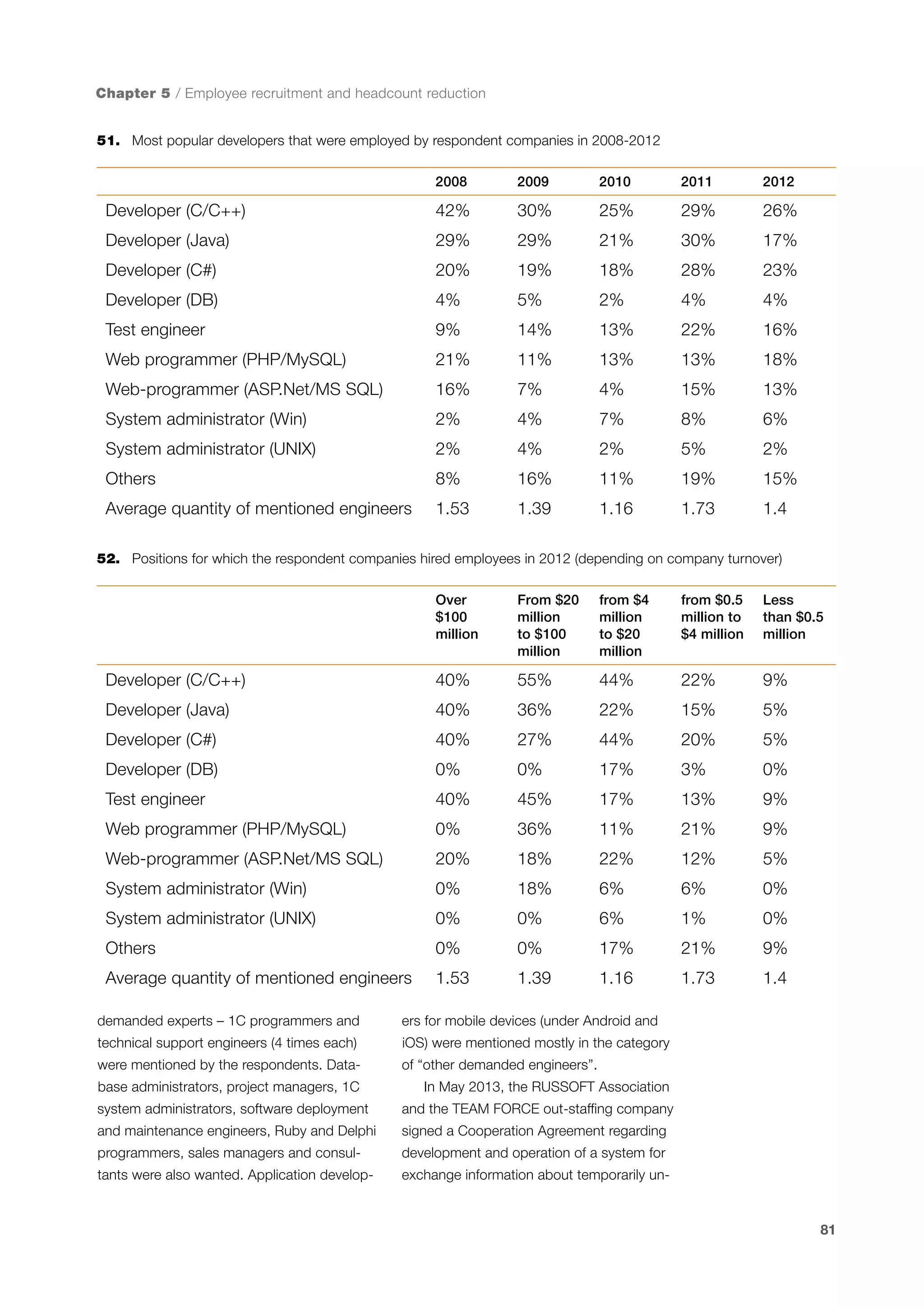
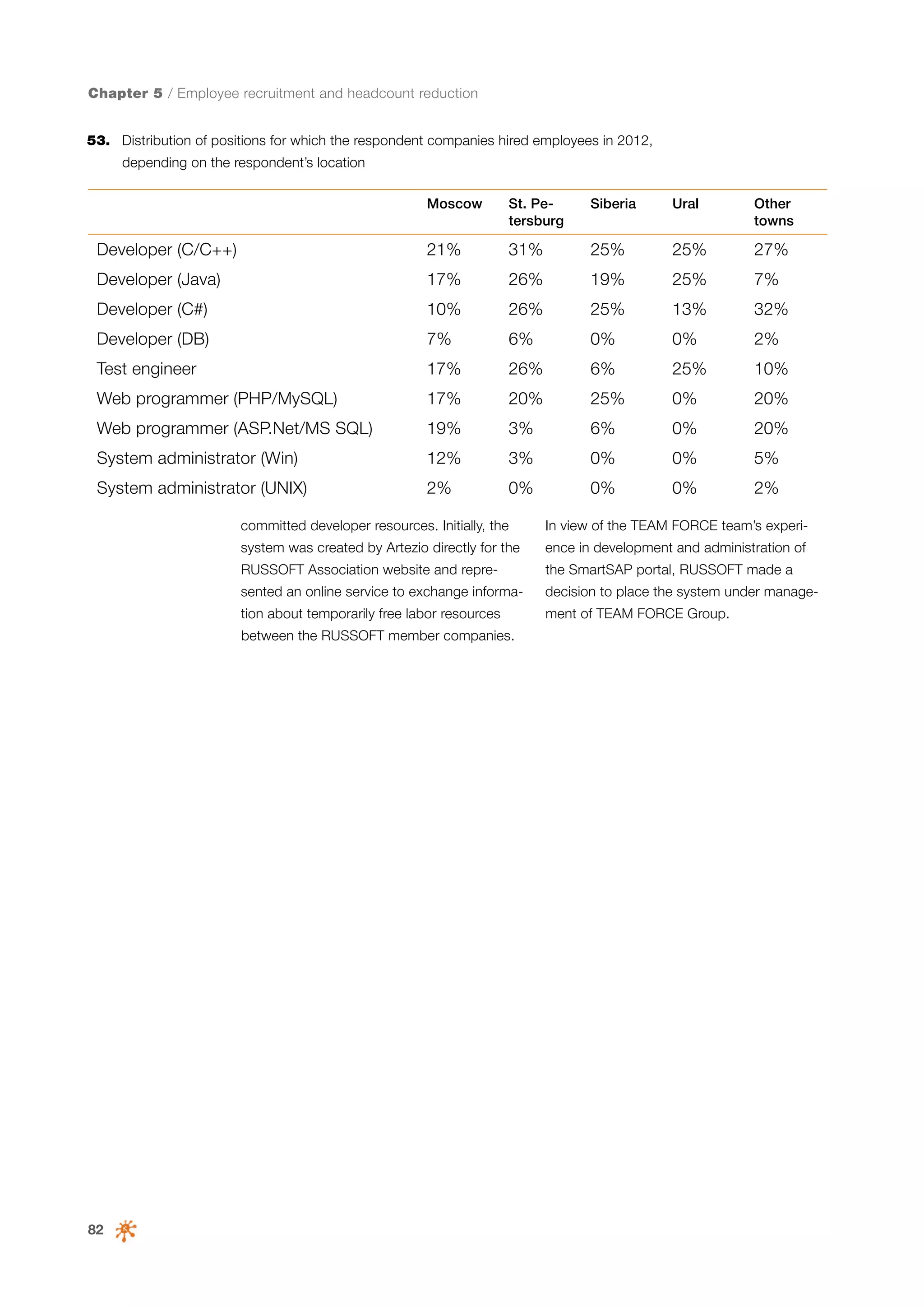
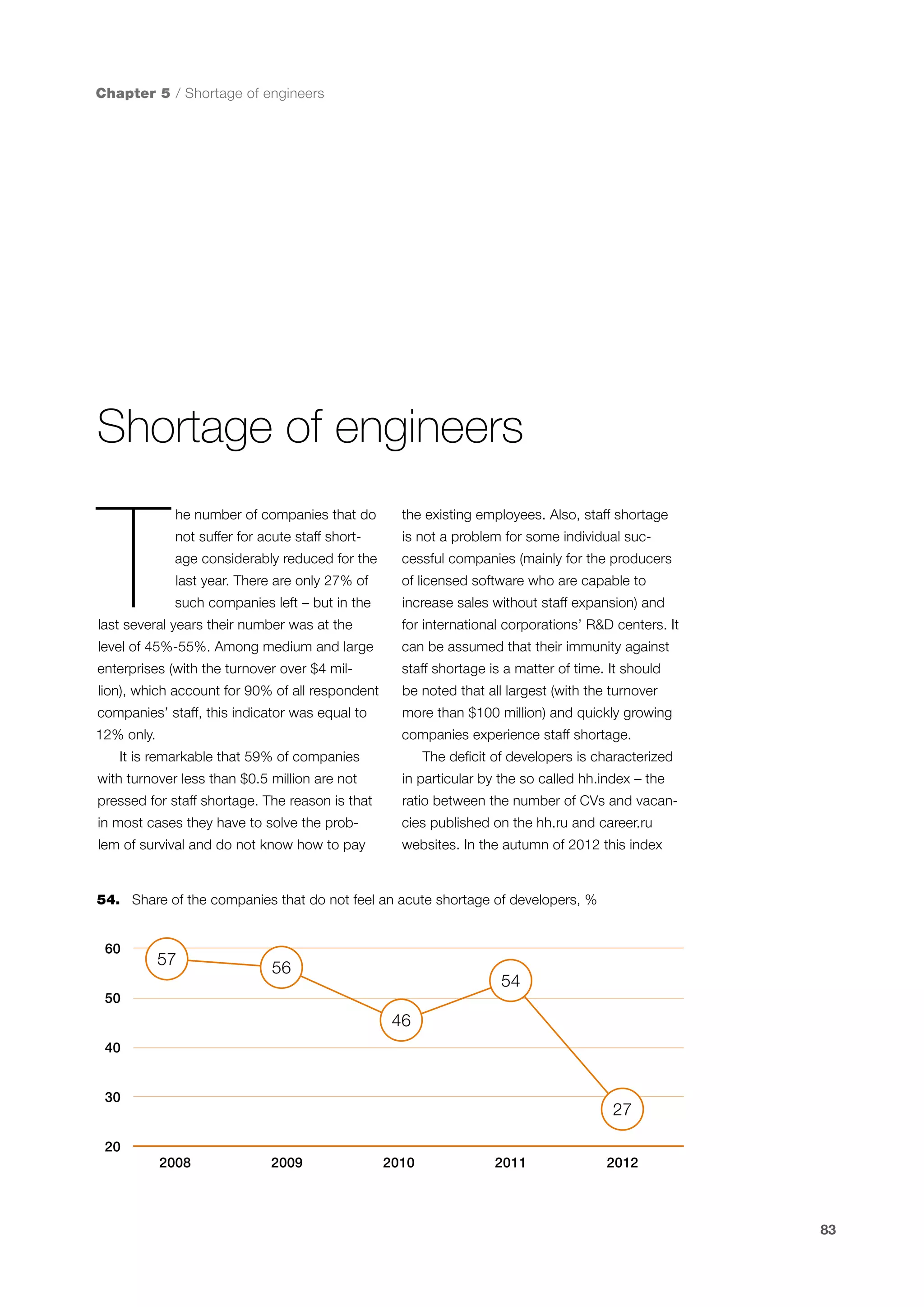
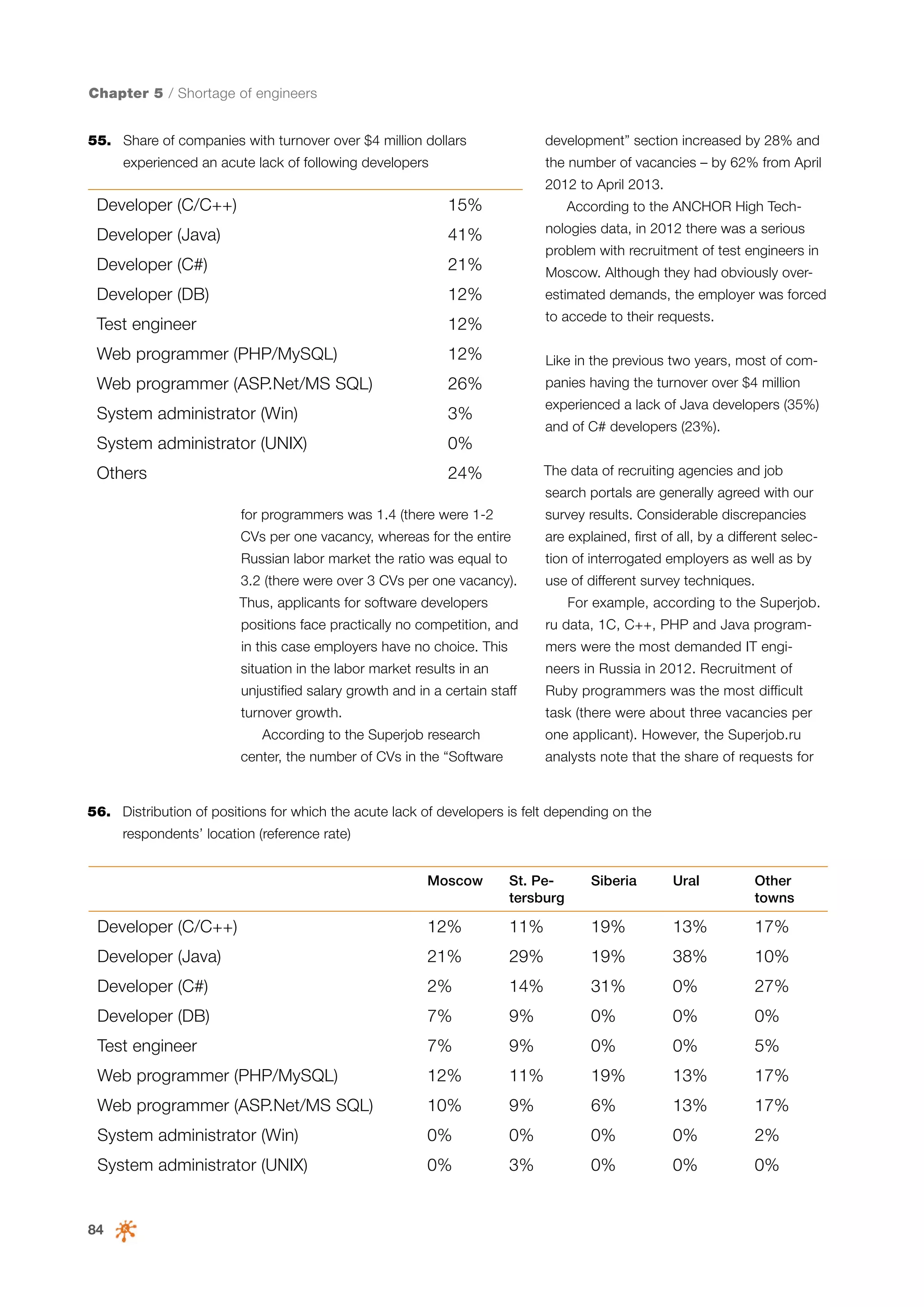
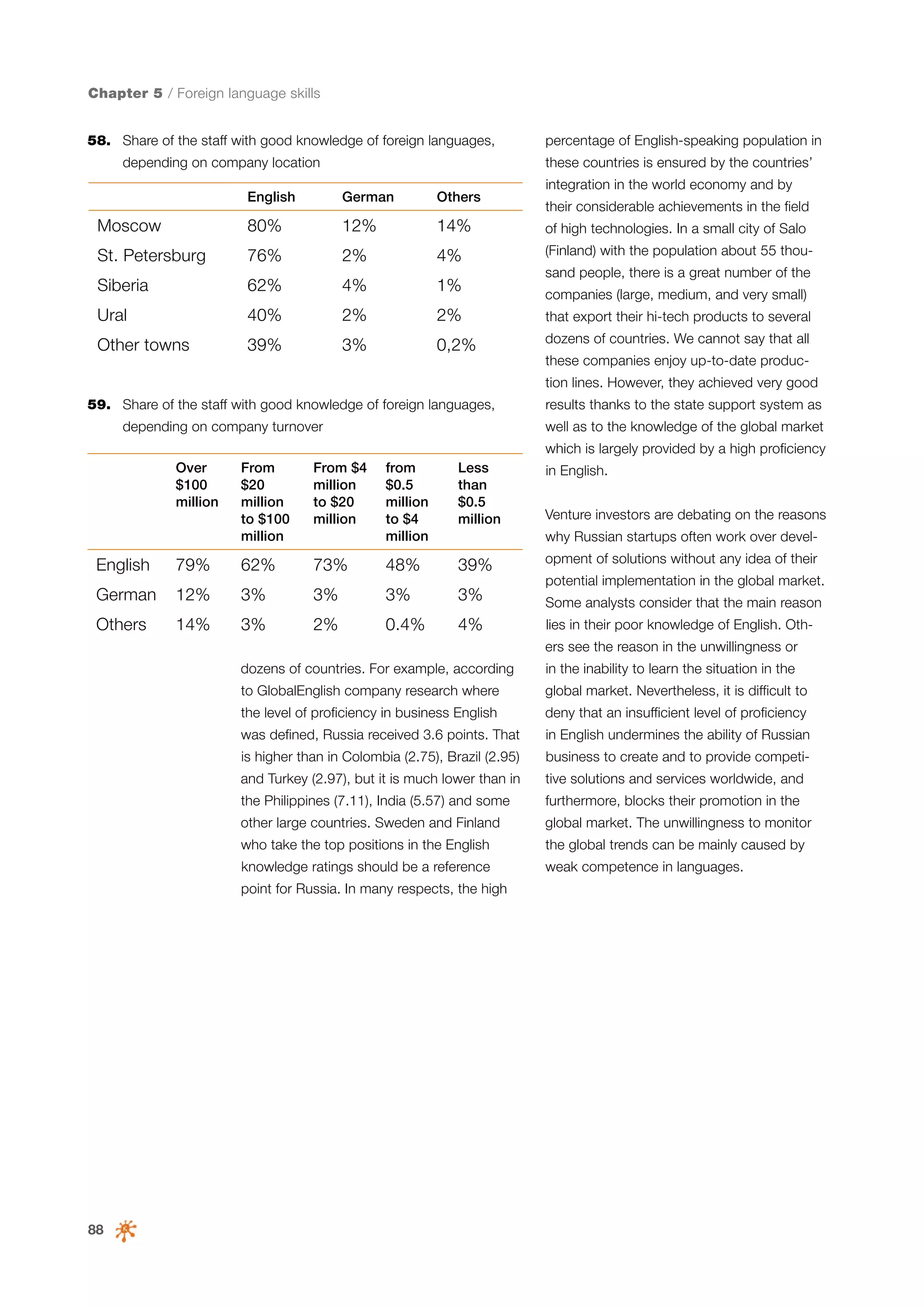
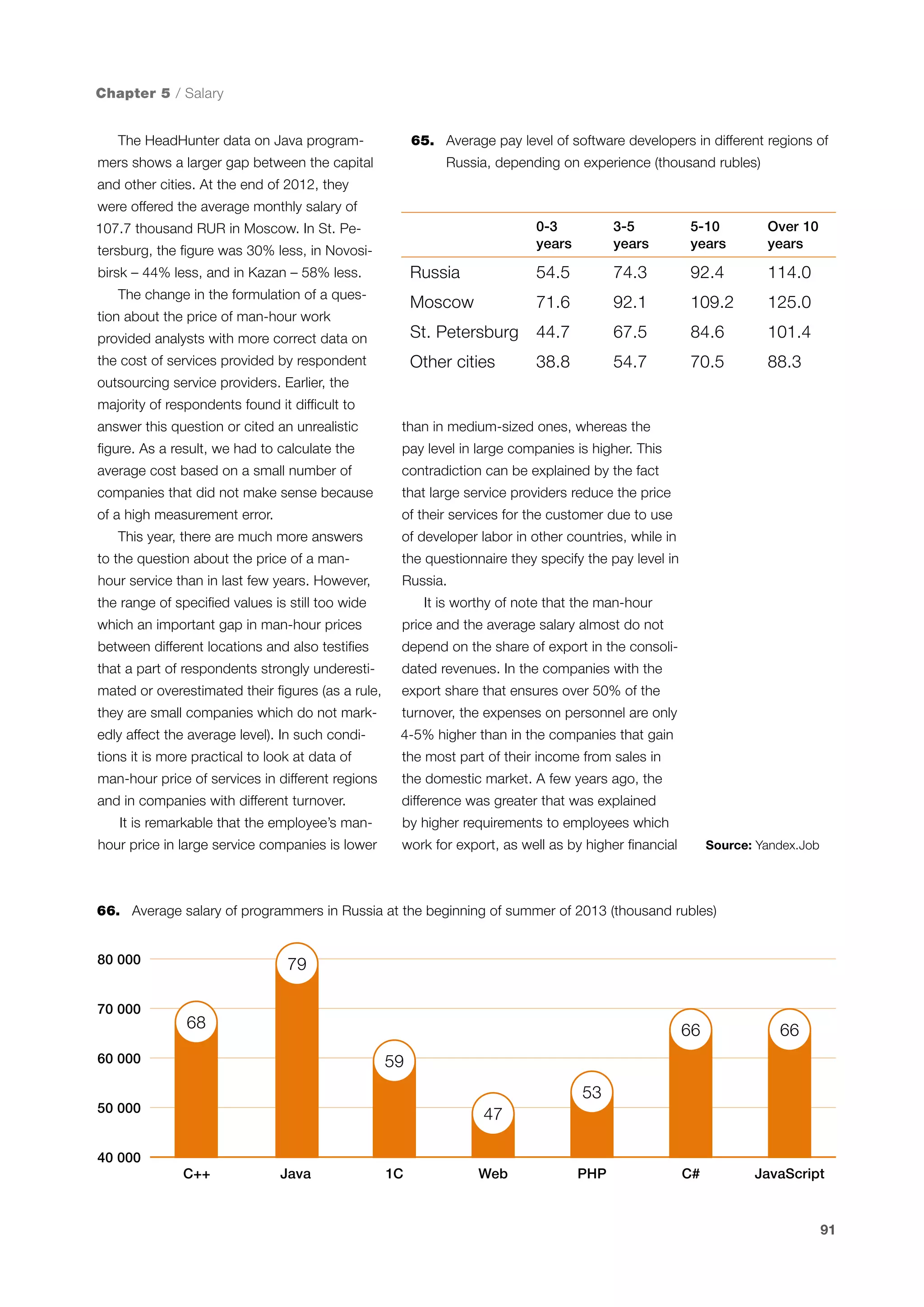
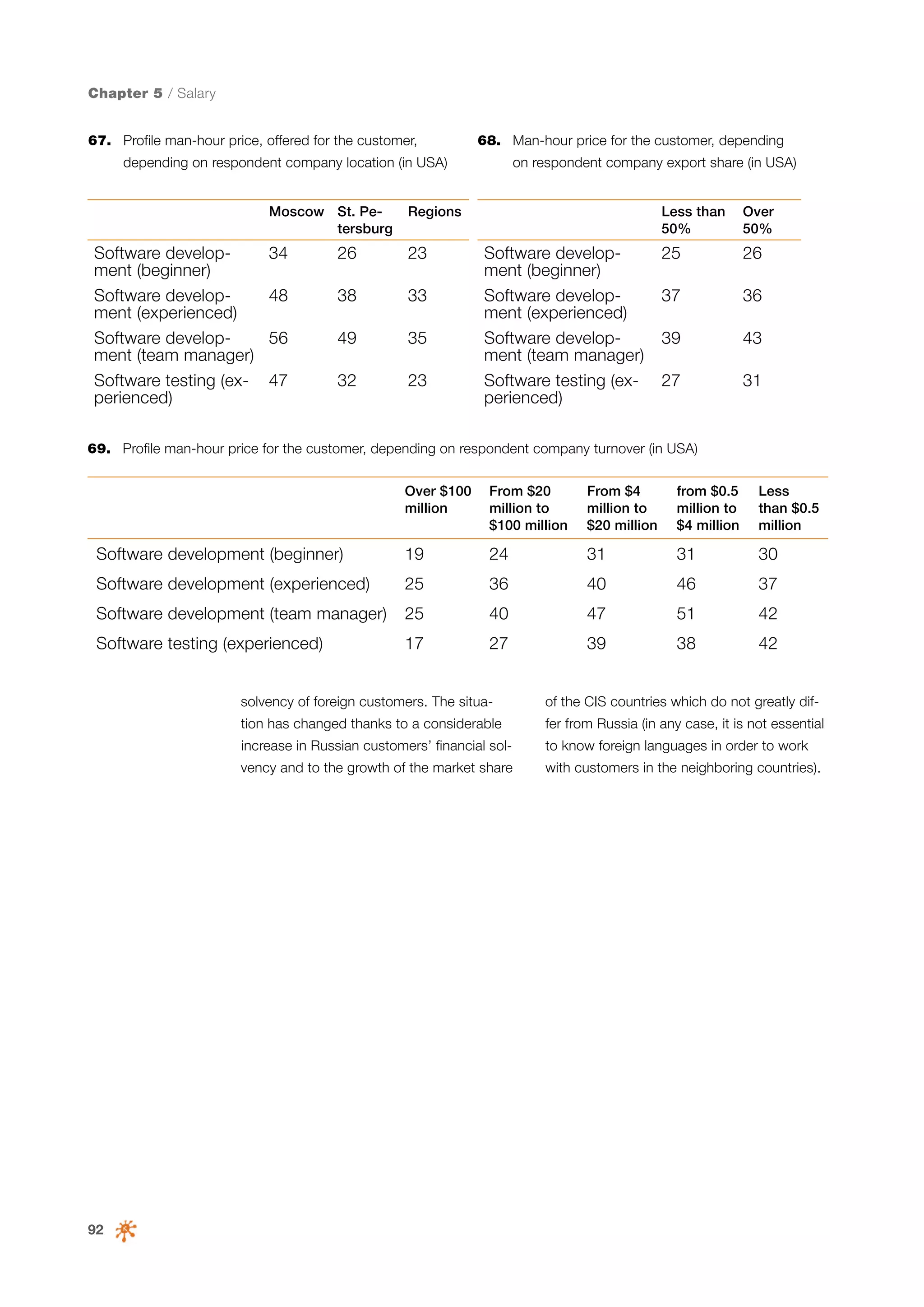
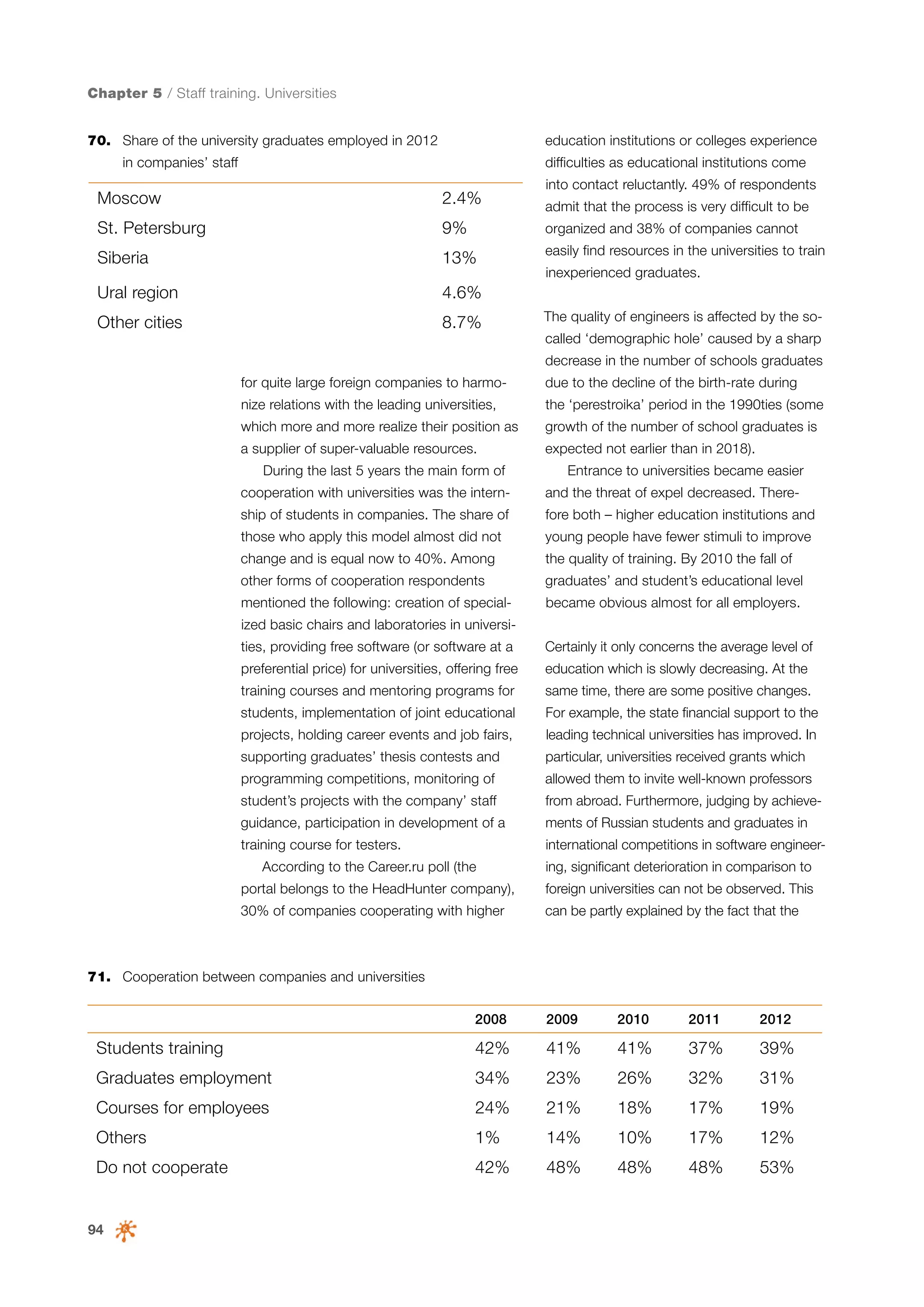
This document is a 10-year survey of the Russian software development industry and software exports from 2013. It provides an introduction and discusses the methodology used in the survey. The survey questioned over 140 market players in the software industry from February to April 2013. It aims to analyze the position and development of the Russian software industry in global markets over the past decade. The document is divided into several chapters covering topics such as Russia's position in global IT ratings, the volume and structure of Russian software exports, major trends in the industry, the geographic and market reach of Russian software companies, human resources and technology.