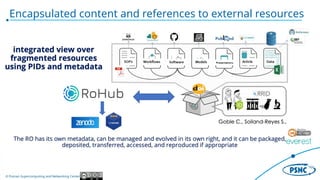
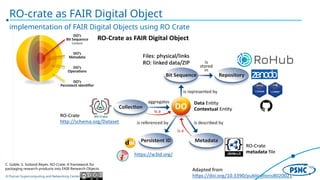
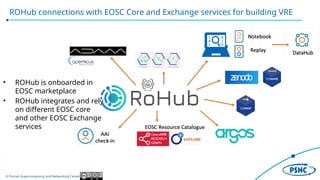
The document describes the Poznan Supercomputing and Networking Center's Research Object Management Platform, which aims to support FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) and open science. It outlines the motivation for managing research objects to enhance visibility, encourage reuse, and foster accessibility, providing mechanisms for collaboration and data management. Key features include a holistic solution for managing research objects, integration with various EOSC services, and tools for data analysis and dissemination.



![© Poznan Supercomputing and Networking Center
Research outcomes and related resources
Each object has its own metadata and repositories
All are first class citizens and are required to make research FAIR
[source RO-Crate: A framework for packaging research products into FAIR Research
Objects]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rohub-general-intro-240918121659-a6c89992/85/ROHub-RO-Crate-Research-Object-Management-Platform-General-Introduction-5-320.jpg)