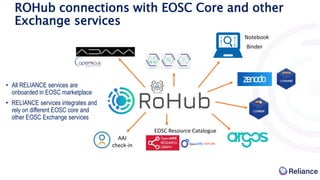
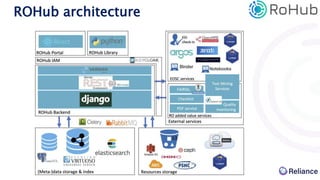
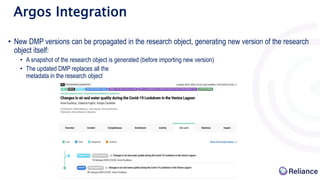
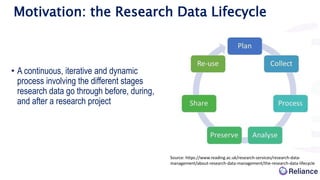
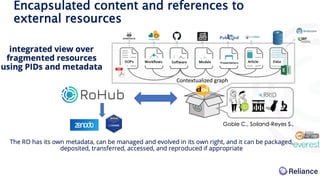
The document discusses the integration of Argos data management plans (DMPs) into the Research Object Hub (ROHub) platform. ROHub enables the creation and management of research objects (ROs) that package research outputs and metadata to support open science practices. The integration will allow Argos DMPs to be imported as ROs, with the DMP information encoded as machine-readable metadata. Updated DMP versions can then generate new versions of the associated RO. This will help support the full research data lifecycle from planning to publication.



![Research outcomes and related resources
Each object has its own metadata and repositories
All are first class citizens and are required to make research FAIR
[source RO-Crate: A framework for packaging research products into
FAIR Research Objects]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rohub-argos-final-230314072111-a0d752ac/85/ROHub-Argos-integration-6-320.jpg)
![Research objects: Self-describing, chiefly
metadata, objects
[source RO-Crate: A framework for packaging research products into
FAIR Research Objects]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rohub-argos-final-230314072111-a0d752ac/85/ROHub-Argos-integration-8-320.jpg)
![Research objects: Self-describing, chiefly
metadata, objects
[source RO-Crate: A framework for packaging research products into
FAIR Research Objects]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rohub-argos-final-230314072111-a0d752ac/85/ROHub-Argos-integration-9-320.jpg)
![Summary: RO-Crate in a nutshell
[source RO-Crate: A framework for packaging research products into
FAIR Research Objects]
RO-Crate (Research Object Crate): Practical lightweight approach
to packaging research data entities (any object) with metadata
Aggregate files and/or any URI-addressable content, with
contextual information to aid decisions about re-use: Who What
When Where Why How.
Web Native Machine readable. Human readable. Search engine
friendly. Familiar.
Extensible and Incremental: add additional metadata; nested
and typed by their profile.
Open Community effort](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rohub-argos-final-230314072111-a0d752ac/85/ROHub-Argos-integration-10-320.jpg)