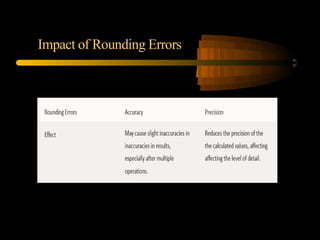
This document discusses approximation in numerical computation, specifically truncation and rounding errors. It begins with an introduction to numerical computation and the importance of approximation. It then defines truncation errors as arising from incomplete representation of infinite processes, such as truncating a Taylor series. Sources of truncation errors include discretization and complex algorithms. Rounding errors occur when approximating numbers to a specific precision. Sources include finite precision arithmetic and cumulative errors from computational iterations. The document discusses techniques to minimize these errors and concludes that continuous improvement in error reduction benefits many fields.