Embed presentation
Download to read offline


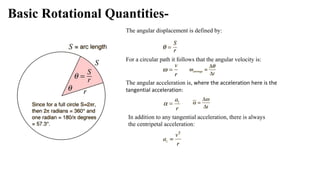

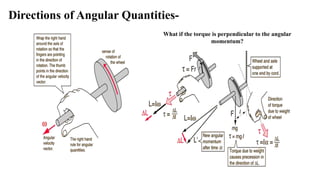
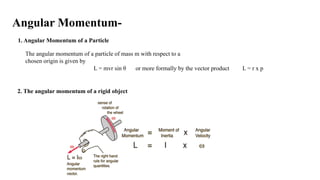






Rigid Body Dynamics discusses rotational motion and angular quantities. A rigid body is a system of particles where external forces do not change the distance between particles. Angular displacement, velocity, and acceleration are defined. Angular momentum is calculated as the cross product of position and linear momentum vectors. Angular momentum is conserved for a closed system. Precession motion occurs when a torque acts perpendicular to the angular momentum vector. Gyroscopes demonstrate precession, where the axis of rotation precesses about the applied torque.











