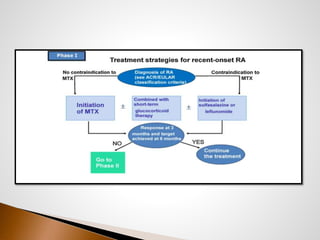
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that affects around 0.5% of adults worldwide, primarily women over 40. It causes inflammation and pain in the joints. While the exact cause is unknown, genetic and environmental factors are implicated. The disease is characterized by two subsets distinguished by the presence or absence of antibodies against citrullinated proteins. Treatment aims to reduce pain, swelling, and joint damage through medications like methotrexate and lifestyle changes such as exercise and heat/cold therapy. Ongoing research is exploring the immune system, genes, and new drug combinations to slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis.









![ Cipriani P, Ruscitti P, Carrubi F , Liakouli V, Giacomelli R. 2014.
Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Optimizing Therapy Among
Different Formulations. Current and Emerging Paradigms. Clinical
Therapeutics [Internet]; [cited 2014 Sep 25]. 36(3):427-
435.doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.01.014
Gaujoux-Vialaa C, Gossecb L, Cantagrelc A, Dougadosd M, Fautrelb
B, Mariettee X, Nataff H, Sarauxg A, Tropei S, Combej B. 2014.
Recommendations of the French Society for Rheumatology for
managing rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine [Internet]; [cited
2014 Oct 3]. 81(4)287-297.doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2014.05.002
Svendsen A, Kyvik K, Houen G, Junker P, Christensen K,
Christiansen L, Nielsen C, Skytthe A, Hjelmborg J. 2013. On the
Origin of Rheumatoid Arthitis: The Impact of Environment and
Genes-A Population Based Twin Study. PLoS One [Internet]; [cited
2014 Oct 31]. 8(2). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057304](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rheumatoidarthritis-141210205939-conversion-gate01/85/Rheumatoid-arthritis-Risk-Factors-and-Potential-Treatments-16-320.jpg)
