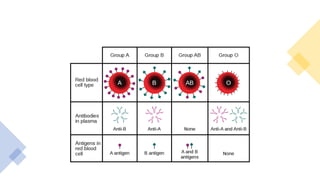
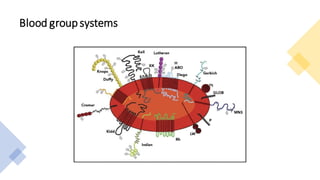
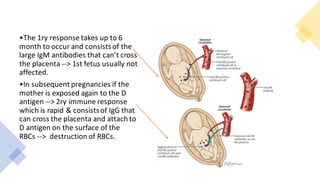
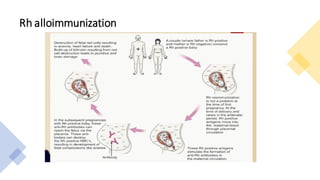
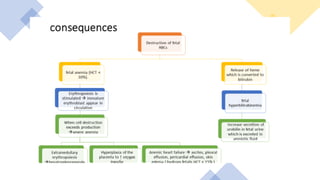
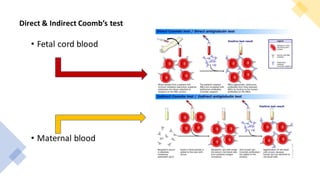
1) Rh isoimmunization occurs when an Rh-negative mother is exposed to Rh-positive fetal blood cells, leading to production of IgG antibodies that can cross the placenta and destroy fetal red blood cells.
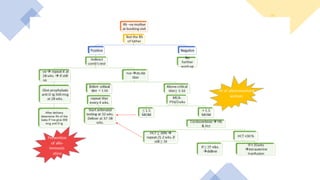
2) Prevention involves identifying at-risk Rh-negative mothers and administering anti-D immunoglobulin within 72 hours of potential fetal-maternal hemorrhage to suppress immunization.
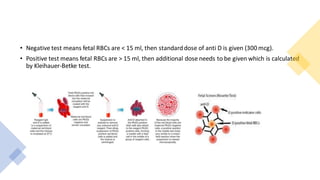
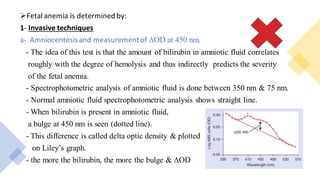
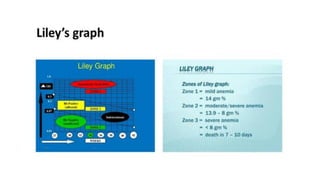
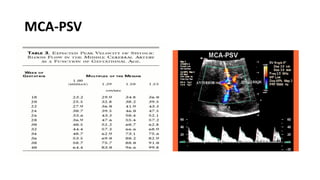
3) For sensitized pregnancies, fetal anemia is monitored through Doppler ultrasound or invasive tests, and treated with intrauterine transfusions if severe anemia is detected before 35 weeks.