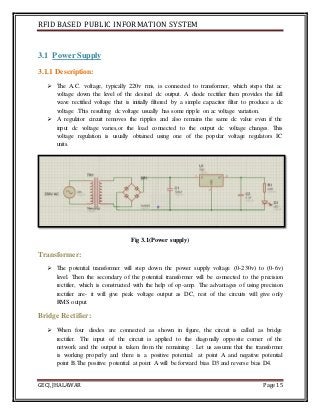
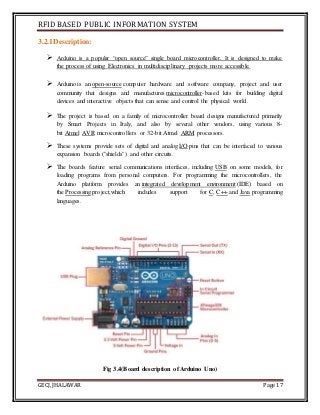
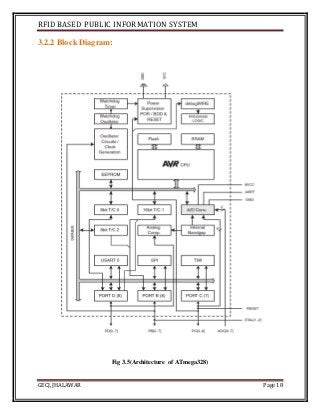
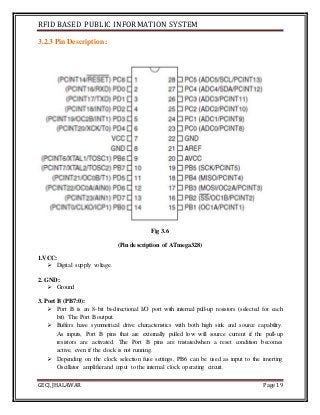
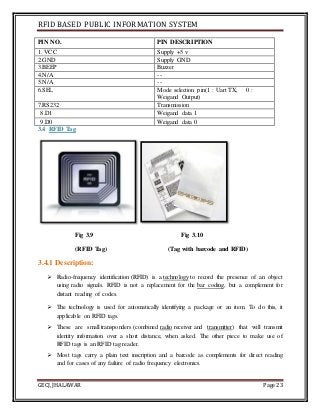
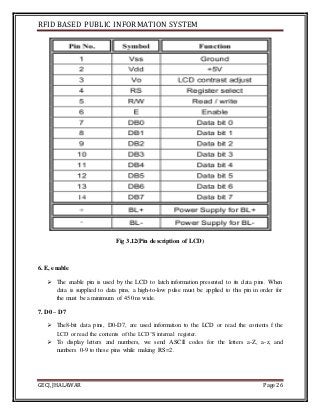
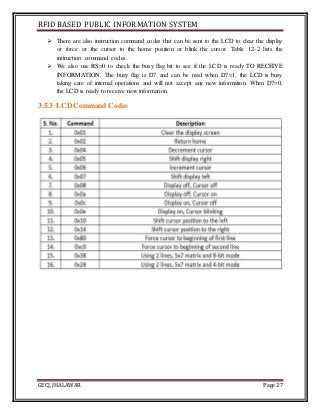
The document discusses the development of an RFID-based public information system for institutions, focusing on its implementation as a solution to manage identification and attendance using RFID tags and a microcontroller. It outlines the project methodology, hardware design, and the technological components involved, such as Arduino Uno, RFID readers, and LCD displays. The project's aim is to facilitate efficient identification and attendance management in various public settings.