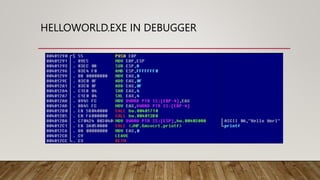
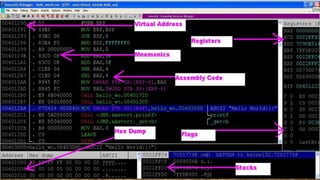
This document provides an introduction to reverse engineering basics. It discusses that reverse engineering involves analyzing a binary or executable to understand the underlying source code. It outlines tools used like debuggers to examine running programs, disassemblers to translate machine code to assembly, and decompilers to translate to high-level source code. The document explains that reverse engineering requires knowledge of operating systems, programming languages, and assembly. It also lists domains that benefit from reverse engineering like malware analysis, software cracking, and exploit development.