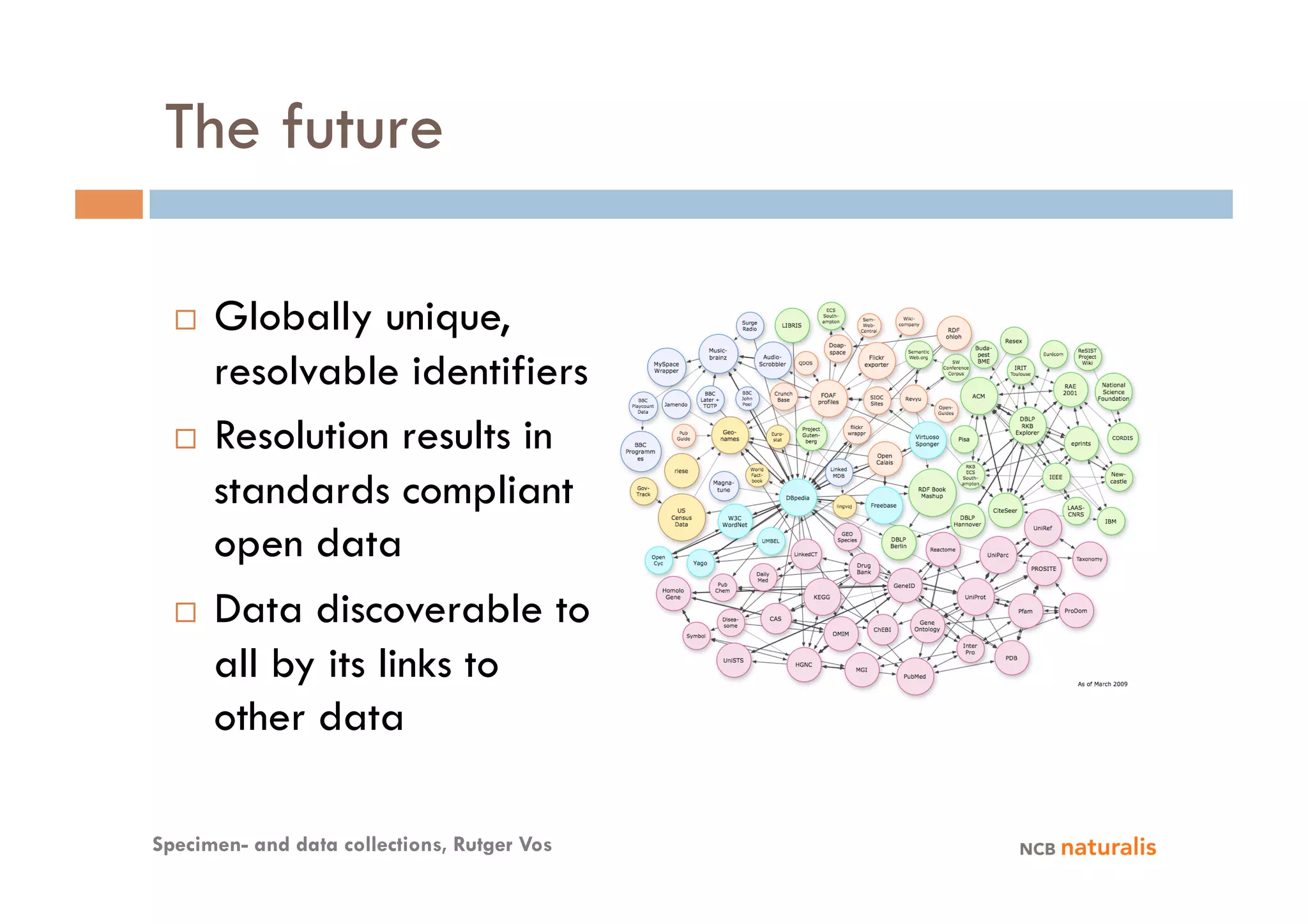
The document discusses the importance of specimen and data collections in natural history museums, particularly their evolution into professional biological disciplines and research tools. It highlights various research services, examples of collaborative projects, and the significance of linking physical specimens with digital data for future developments. The conclusion emphasizes the need for standards development and community engagement in improving data sharing and collaboration among stakeholders.