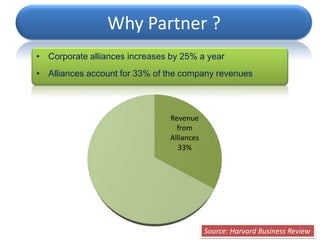
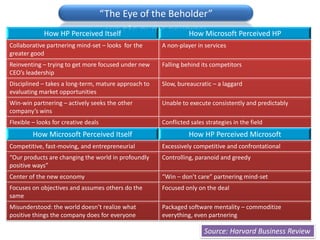
The document discusses Porter's stance on business strategy and the internet from 2000. Porter believed that companies should:
1) Vertically integrate and develop competencies internally instead of shifting strategies for the internet.
2) Use the internet as a complementary tool only and not as an emerging infrastructure for economic activity.
3) The internet would eventually lose its importance as a source of competitive advantage as all companies adopt it.
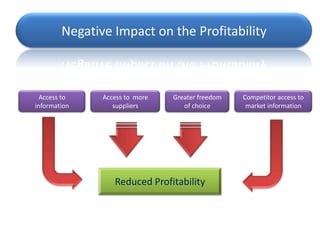
However, the document argues that Porter was wrong and that the internet enables new innovative business models, operational efficiencies, and improved customer relationships and services that provide long-term competitive advantages.





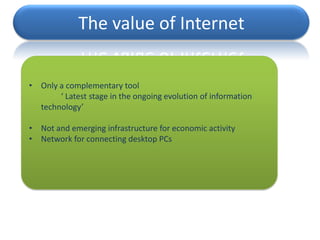
![The TRUE value of Internet
• A complete infrastructure and architecture
• More effective than earlier communication media
• Used for transactions
• Market Research
• Recruiting
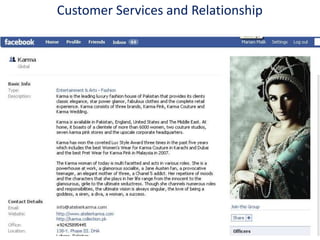
• Brings the company closer to the market [ better CRM, greater
customer insight]
• Allows for better governance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rethinkinghurrahscreativity-100415025307-phpapp02/85/Rethinking-HBR-Case-Study-Analysis-11-320.jpg)



![Competitive advantage of Internet
• “As the current technological revolution continues to change the face
of the world market, only the businesses that are the fastest to
anticipate change and to participate in the revolution will prosper”
Southwick ; keynote speaker at the New Jersey Software Forum 2000
• Once the second generation of eMarkets gets going, the cost of entry
will go up“; Bill Van Emburg, director of Quadrix Solutions
• Internet must not be considered only with reference to its present
existence [ nobody had imagined any thing such as the internet and
so cannot anticipate any future advancements]
• Internet would provide a basis for continuous innovation
• Unique Products
• operational efficiencies
• customer services and relationships](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rethinkinghurrahscreativity-100415025307-phpapp02/85/Rethinking-HBR-Case-Study-Analysis-15-320.jpg)