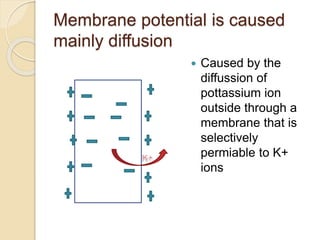
1. The document discusses resting potential and action potential in cells. The plasma membrane maintains electrochemical gradients between the intracellular and extracellular fluids through selective permeability to ions like sodium, potassium, and chloride.
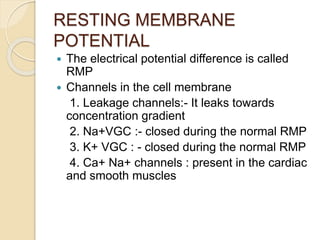
2. At resting potential, the plasma membrane is slightly permeable to sodium but freely permeable to potassium. The sodium-potassium pump actively transports sodium out and potassium into the cell. This establishes a resting membrane potential of around -70mV.
3. When a cell is stimulated, an action potential occurs involving rapid depolarization followed by repolarization. During depolarization, sodium channels open and the membrane potential increases to +55mV. Repolarization then returns the membrane to its resting potential through potassium channel opening












![Cont..
Na+ & K+ pump, pumps three Na+
ions outside the cell And two K+ ions
inside the cell by active transport [ by
using ATP present in the cell]
So that cell membrane get positive
charge on outer membrane And
negative charge on inner membrane.
So like this ,the RESTING
MEMBRANE POTENTIAL will be
established.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/restingpotentialactionpotential-2-240321041740-37098845/85/RESTING-POTENTIAL-ACTION-POTENTIAL-2-pptx-15-320.jpg)

![1.DEPOLARISATION
Depolarizationis the initial phase of action
potential in which the interior of the
muscle becomes “Positive” and Exterior
of the muscle becomes “negative”.
i.e., the polarized state[RMP] is
abolished resulting in depolarization.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/restingpotentialactionpotential-2-240321041740-37098845/85/RESTING-POTENTIAL-ACTION-POTENTIAL-2-pptx-17-320.jpg)
![2.REPOLARISATION
It is the phase of AP when the potential inside
the muscle reverse back to the resting
membrane potential[RMP].
i.e., within a short time after depolarization,
the interior of muscle becomes “negative”
And the outside becomes “positive” so the
polarized state of muscle is re-established.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/restingpotentialactionpotential-2-240321041740-37098845/85/RESTING-POTENTIAL-ACTION-POTENTIAL-2-pptx-18-320.jpg)


![Cont…
Latent period
This is the period when no change
occurs in the electrical potential
[immediately after applying of
stimulus]
It is a very short period with duration
of 0.5 -1 min.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/restingpotentialactionpotential-2-240321041740-37098845/85/RESTING-POTENTIAL-ACTION-POTENTIAL-2-pptx-21-320.jpg)

![DEPOLARISATION.
FIRING LEVEL AND
DEPOLARISTION.
Depolarisation starts after the latent period
Initially, it is very slow depolarisation about
15mV[upto -35mV]
The point at which the depolarisation
increases suddenly is called firing level
(threshold excitation)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/restingpotentialactionpotential-2-240321041740-37098845/85/RESTING-POTENTIAL-ACTION-POTENTIAL-2-pptx-23-320.jpg)