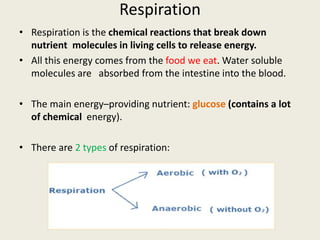
There are two types of respiration: aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration involves the breakdown of food substances in the presence of oxygen and releases a relatively large amount of energy. Anaerobic respiration involves the breakdown of food substances in the absence of oxygen and releases a relatively small amount of energy. Examples of processes that use anaerobic respiration include muscle activity during exercise and fermentation processes like winemaking, brewing, and baking.