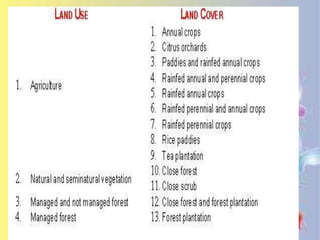
This document discusses different types of land resources including soil, natural vegetation, wildlife, and how land is used for cultivation, grazing, buildings, mining, and manufacturing. It also discusses physical factors like topography, soil, climate, water availability, and minerals that influence land use as well as economic and human factors like population, industrialization, and development level. The document also summarizes the three stages of soil formation and causes and methods of soil erosion. It provides key facts about water resources and their importance for irrigation, industry, drinking, power, and recreation as well as factors responsible for water scarcity. The document also discusses the role of natural vegetation in supporting ecosystems and providing resources and the importance of wildlife for food, pol