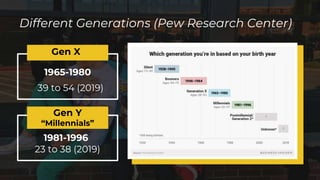
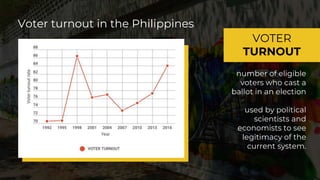
The document examines the social and political factors influencing the voting preferences of Generation X and Y voters in the Philippines, particularly during the 2016 presidential elections, which marked a significant increase in voter turnout among millennials. It aims to identify key factors determining these preferences in Metro Manila, utilizing qualitative research and insights from previous studies highlighting the importance of political experience and educational qualifications in candidate selection. The findings emphasize the interplay of social influences such as family and community, along with political considerations, in shaping the electoral behavior of younger voters.