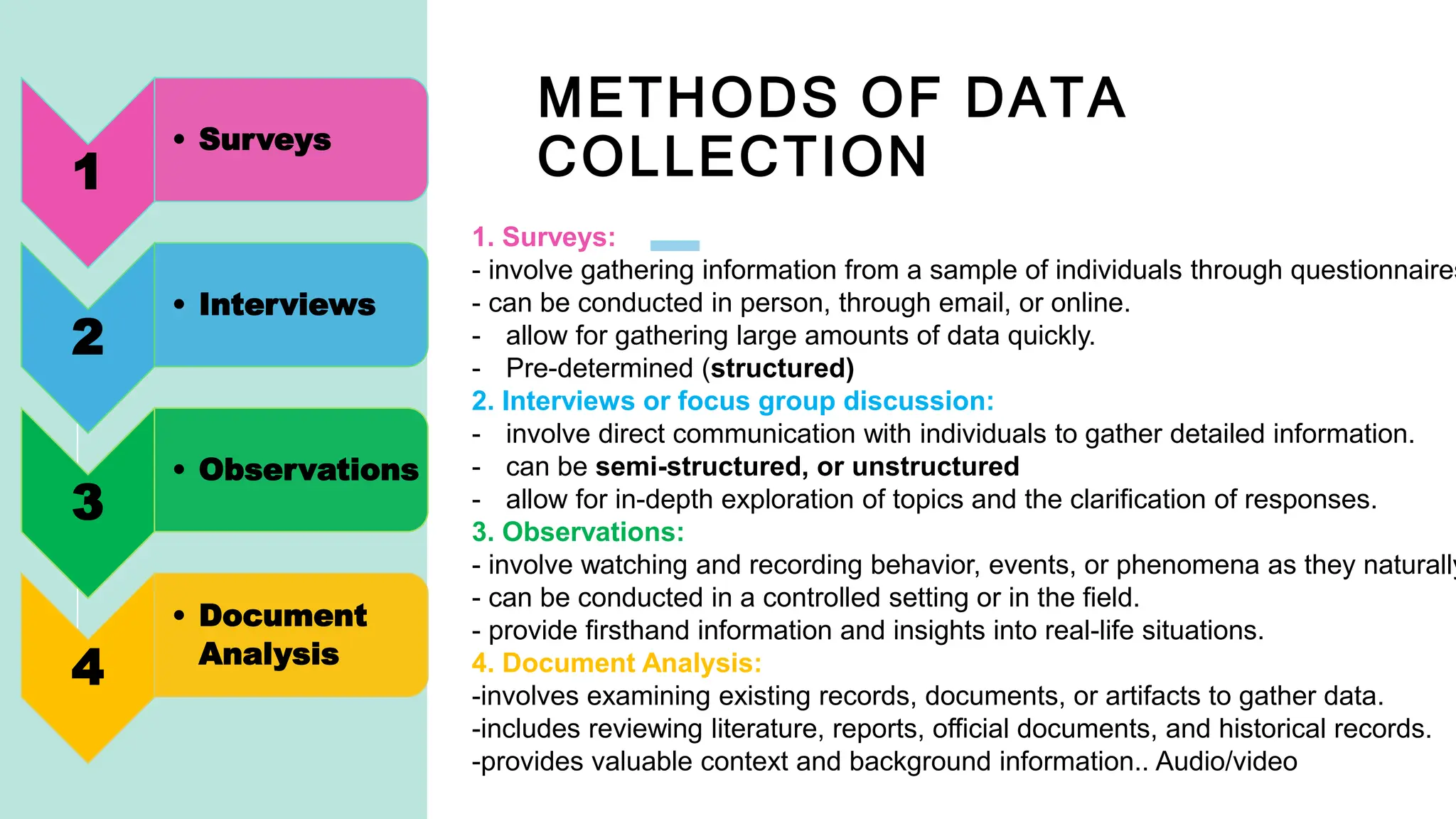
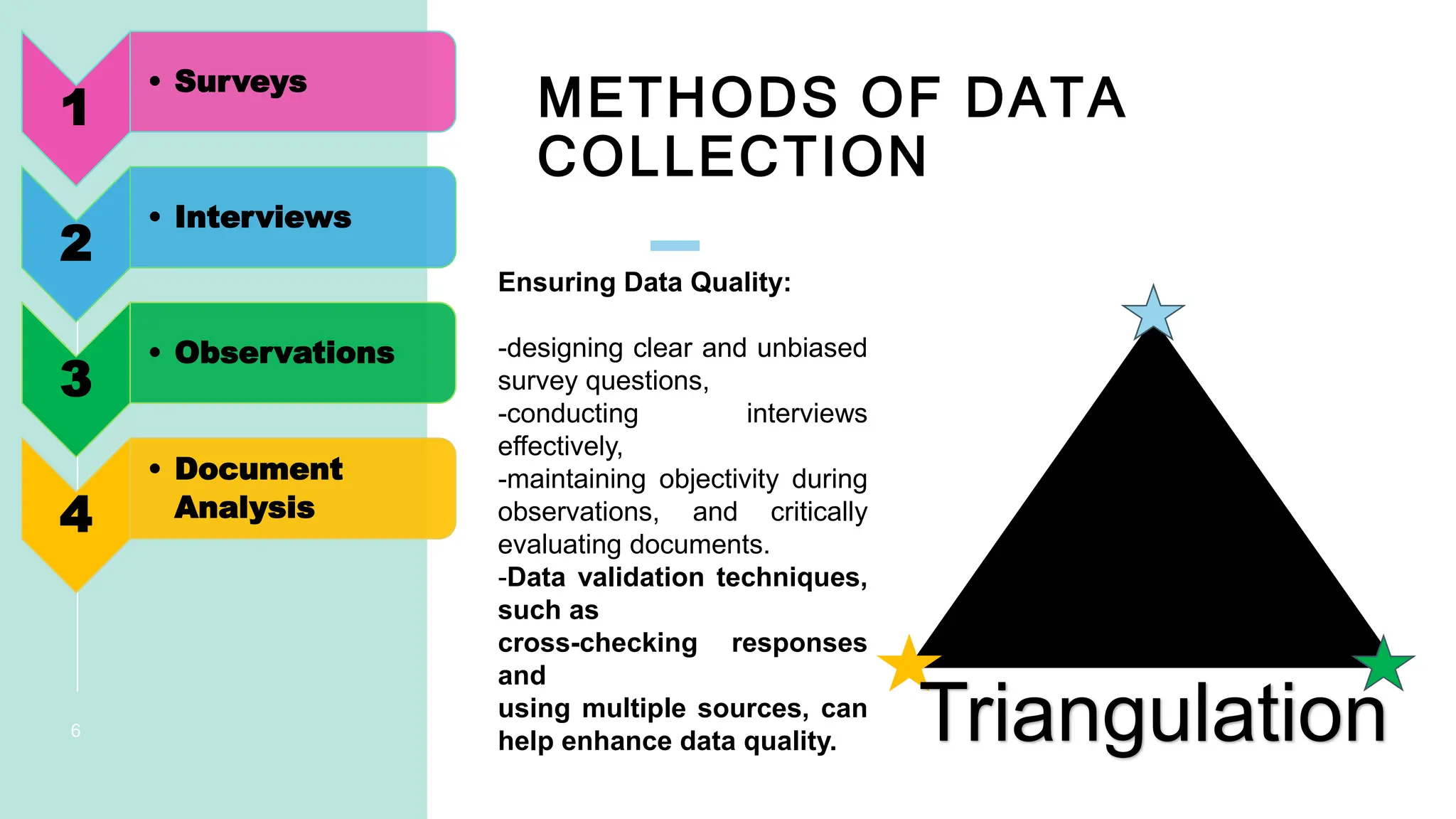
The document outlines essential methods for conducting research, emphasizing data gathering through surveys, interviews, observations, and document analysis. It stresses the importance of updating research methods with transparency and adhering to ethical guidelines, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring participant confidentiality. The content promotes rigorous data quality measures and ethical responsibility in research to maintain integrity and protect participants' rights.