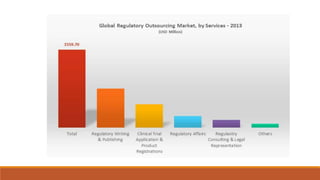
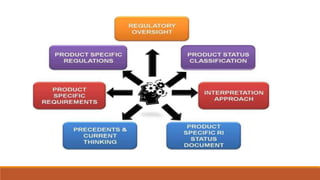
Regulatory intelligence plays an important role in the pharmaceutical industry by helping companies stay compliant, influence regulations, and make strategic decisions. Key responsibilities of regulatory intelligence functions are to identify regulatory changes, conduct analyses to facilitate decision making, and serve as internal consultants. Having access to sources like regulatory authorities and trade associations helps with identifying opportunities, reducing costs and time to market, and increasing compliance. However, challenges include the large volume of information, regional differences, and unclear agency expectations that require regulatory professionals to "read between the lines".