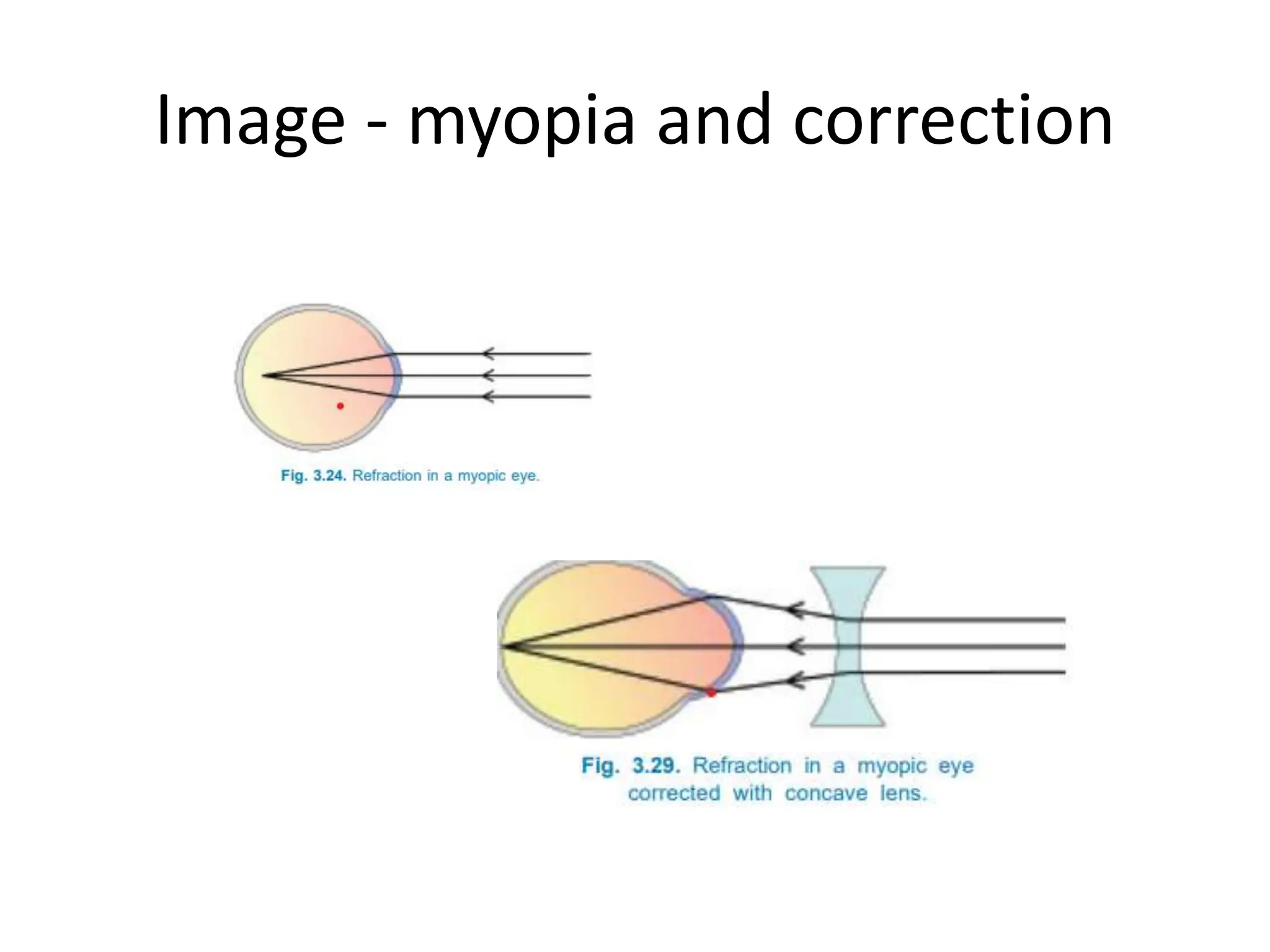
1. Myopia, also known as near-sightedness, occurs when rays of light focus anterior to the retina. It can be caused by disturbances in eye growth and degenerative changes, increased axial length and corneal curvature, or changes in the lens.
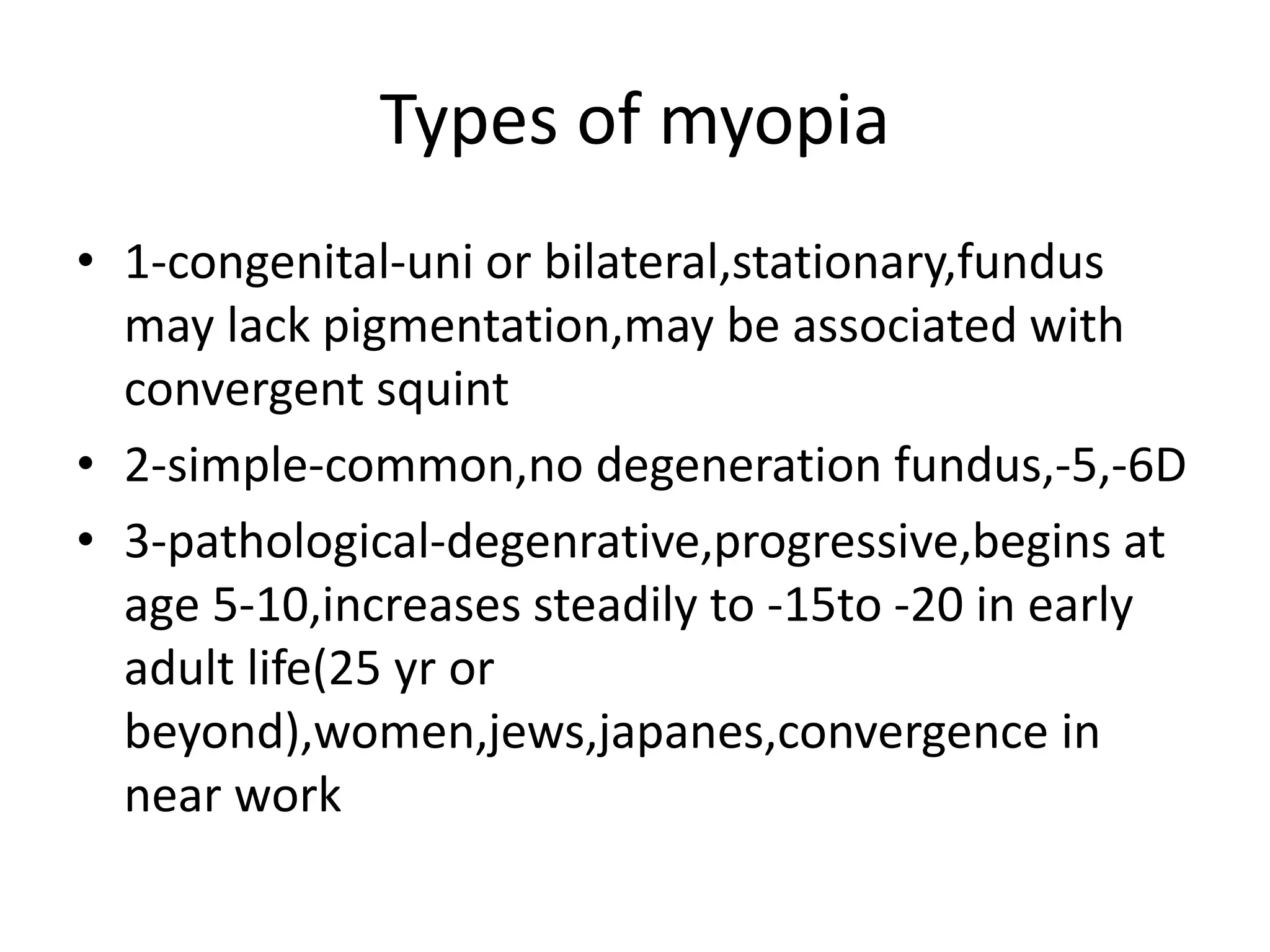
2. There are several types of myopia, including congenital, simple, and pathological. Pathological myopia tends to progress more rapidly and severely, especially in women, Jews, Japanese, and those who do close work.
3. Symptoms of myopia include indistinct distant vision, black spots, discomfort after near work, and flashes of light. Signs include a large pupil, prominent eye, and possible retinal damage or tearing seen on