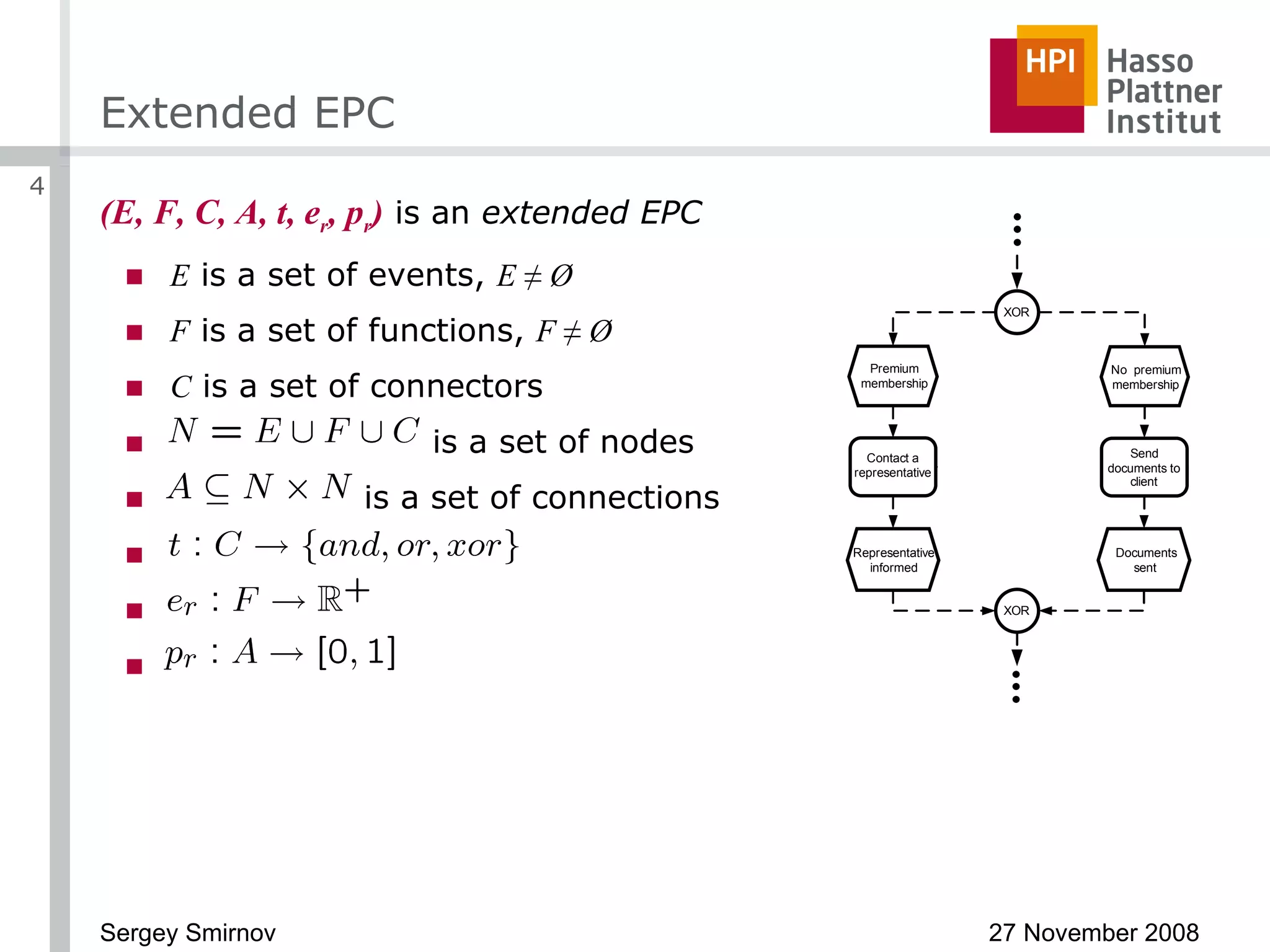
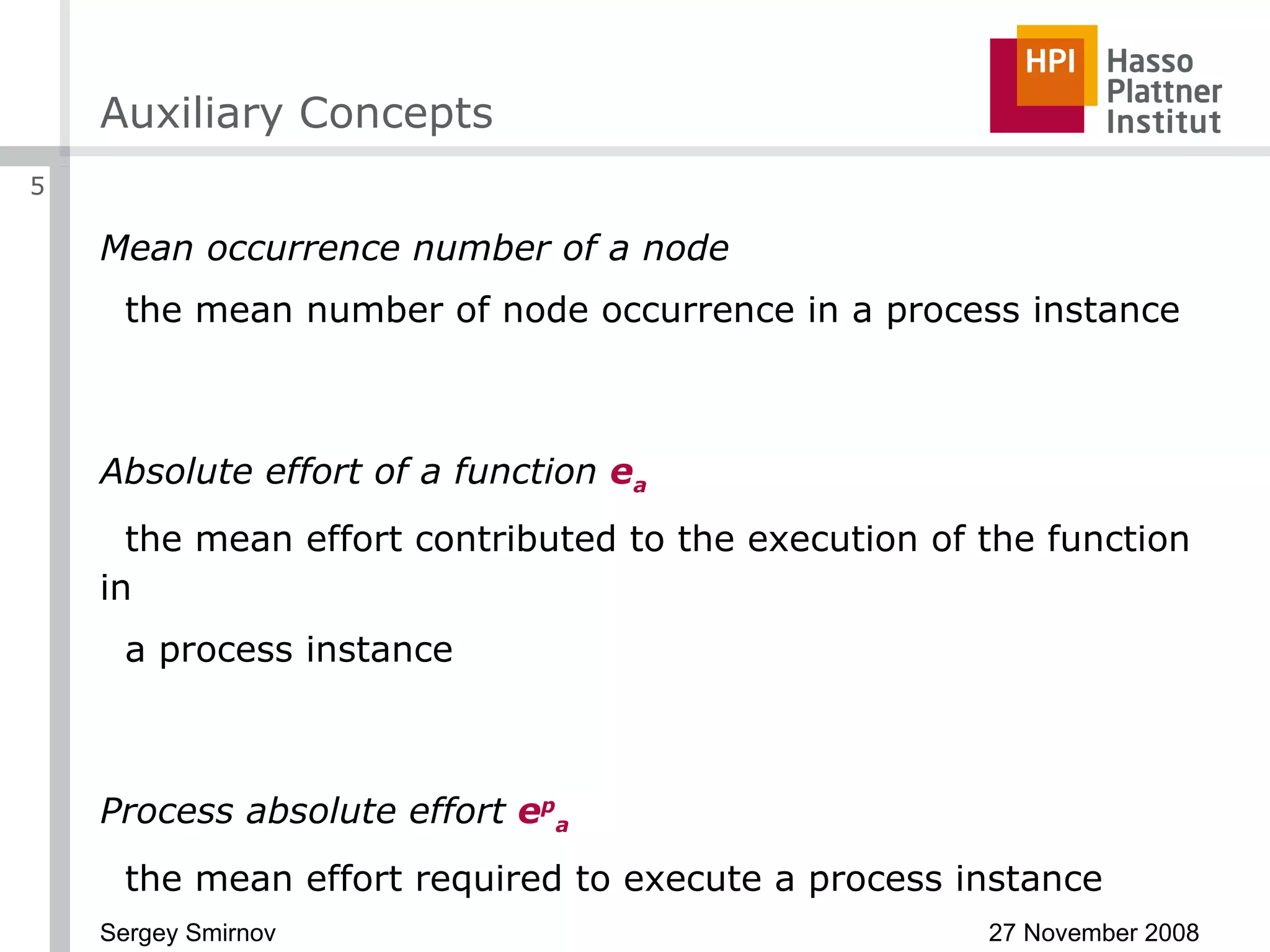
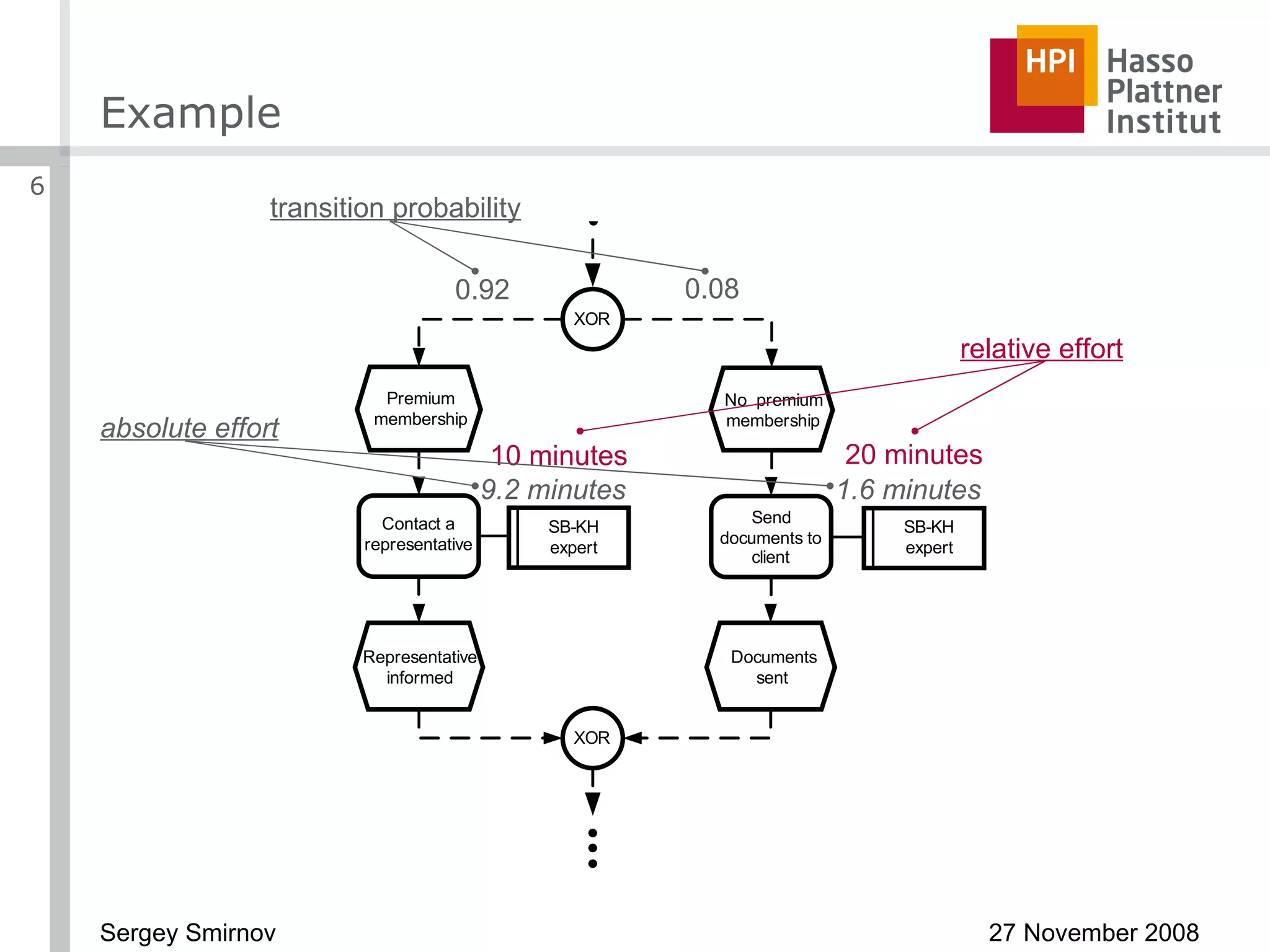
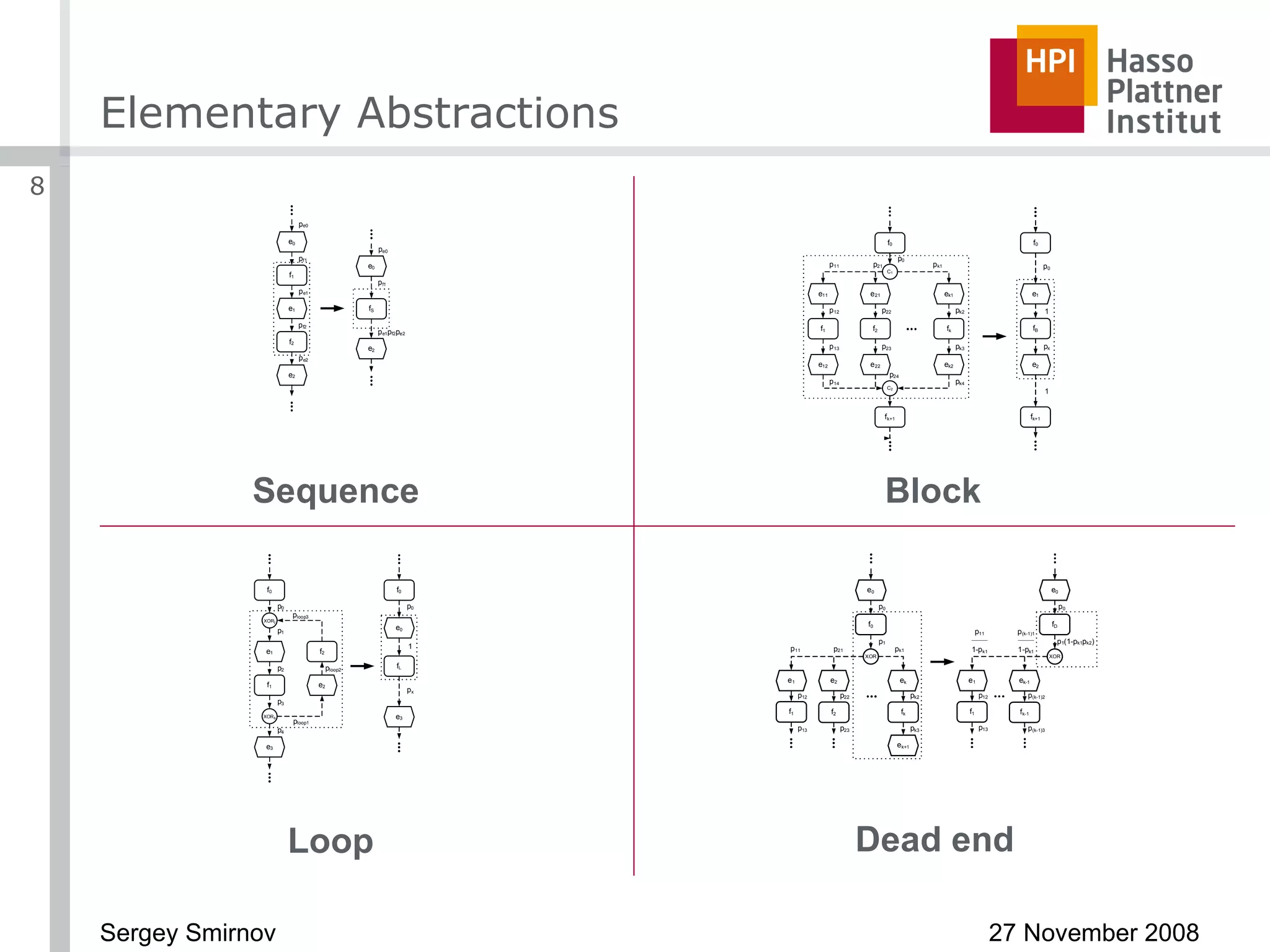
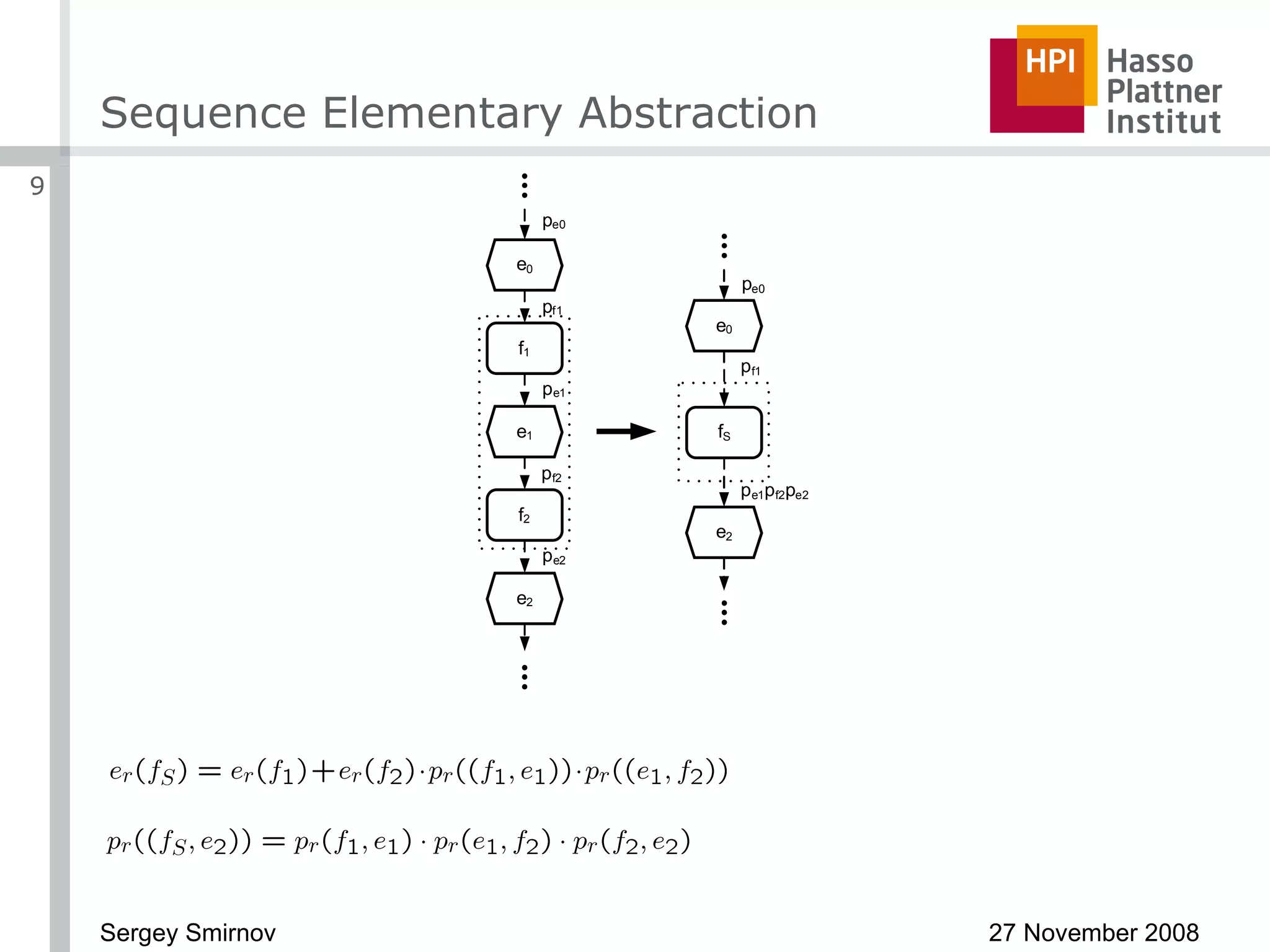
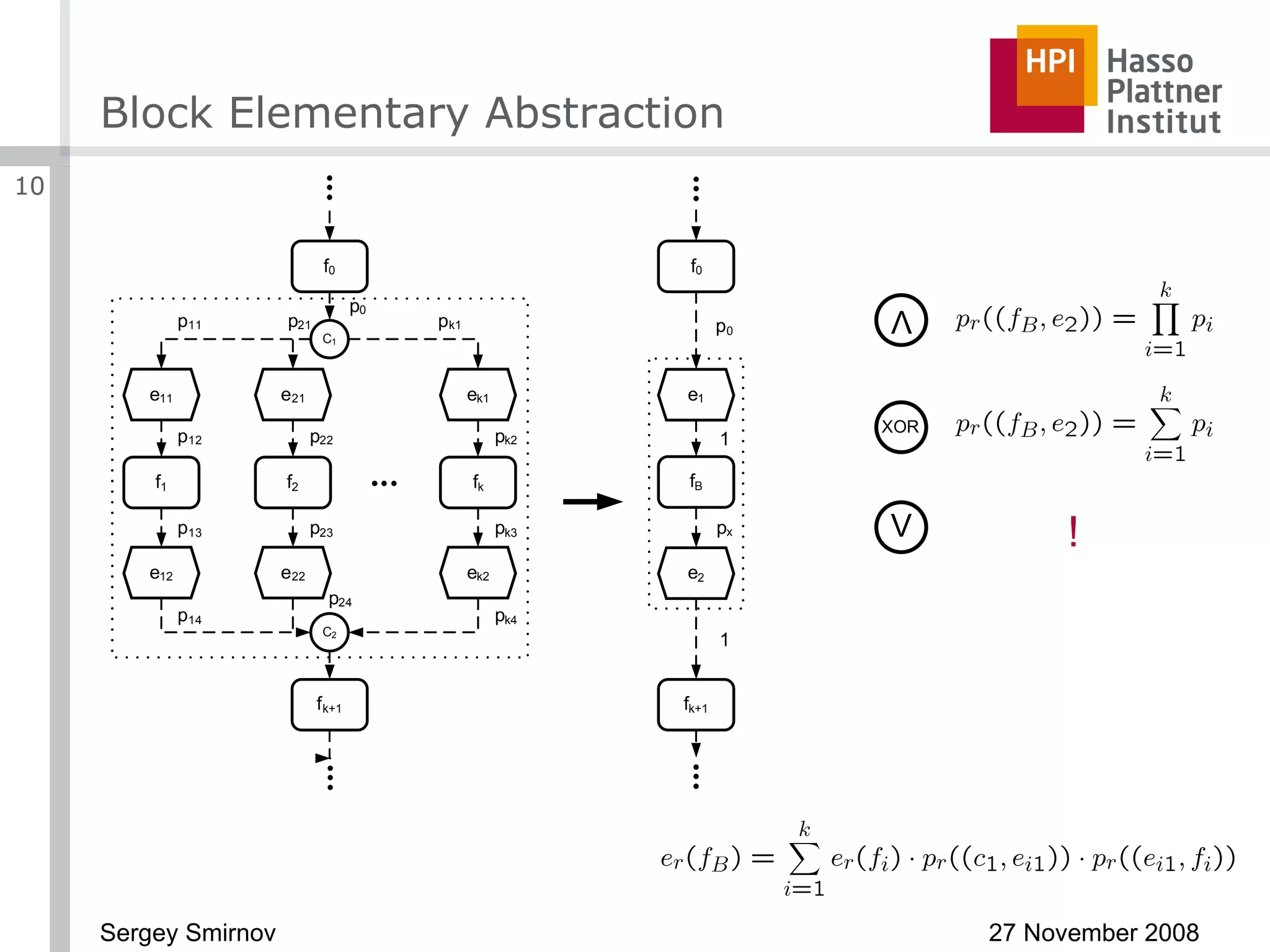
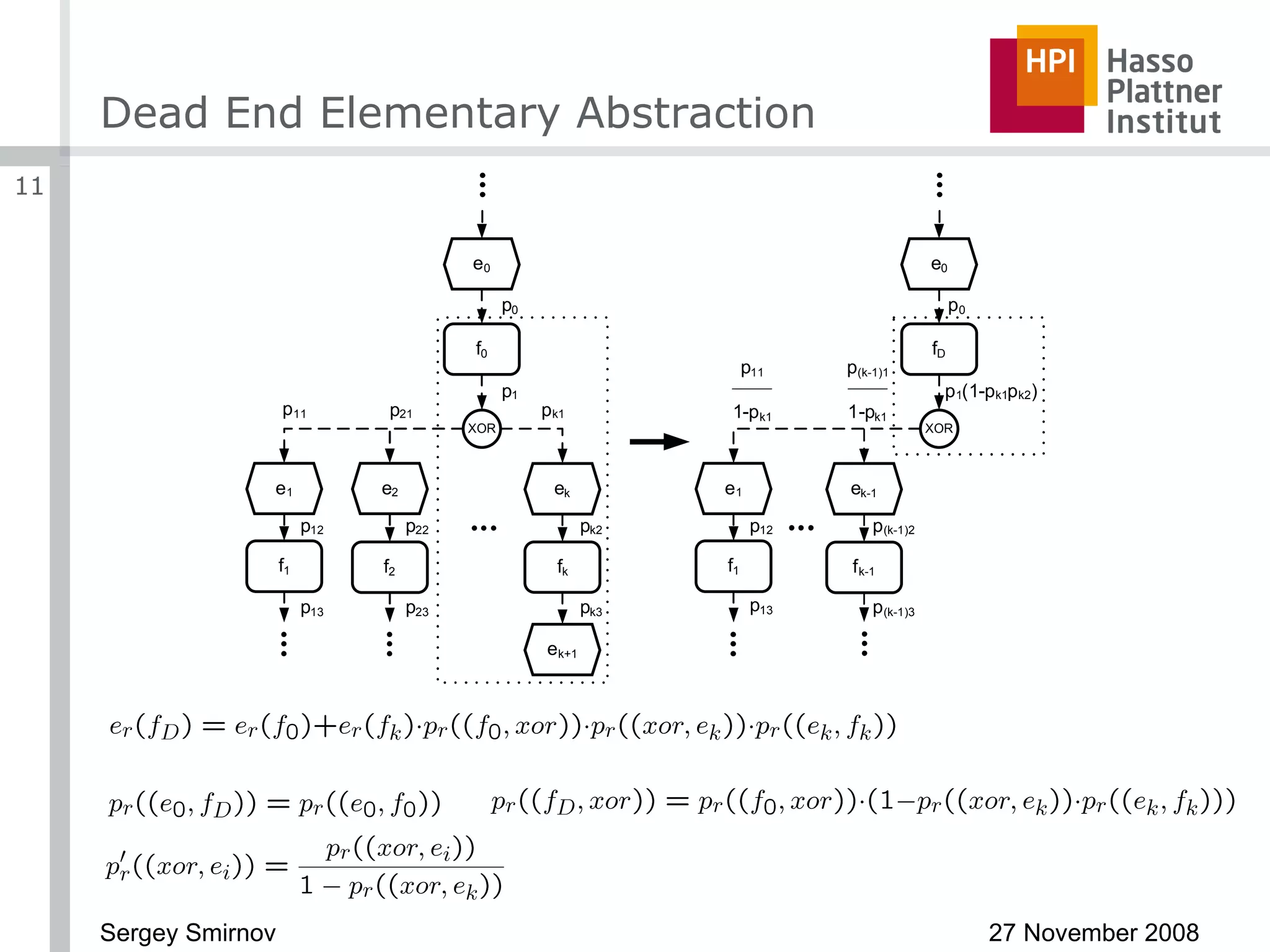
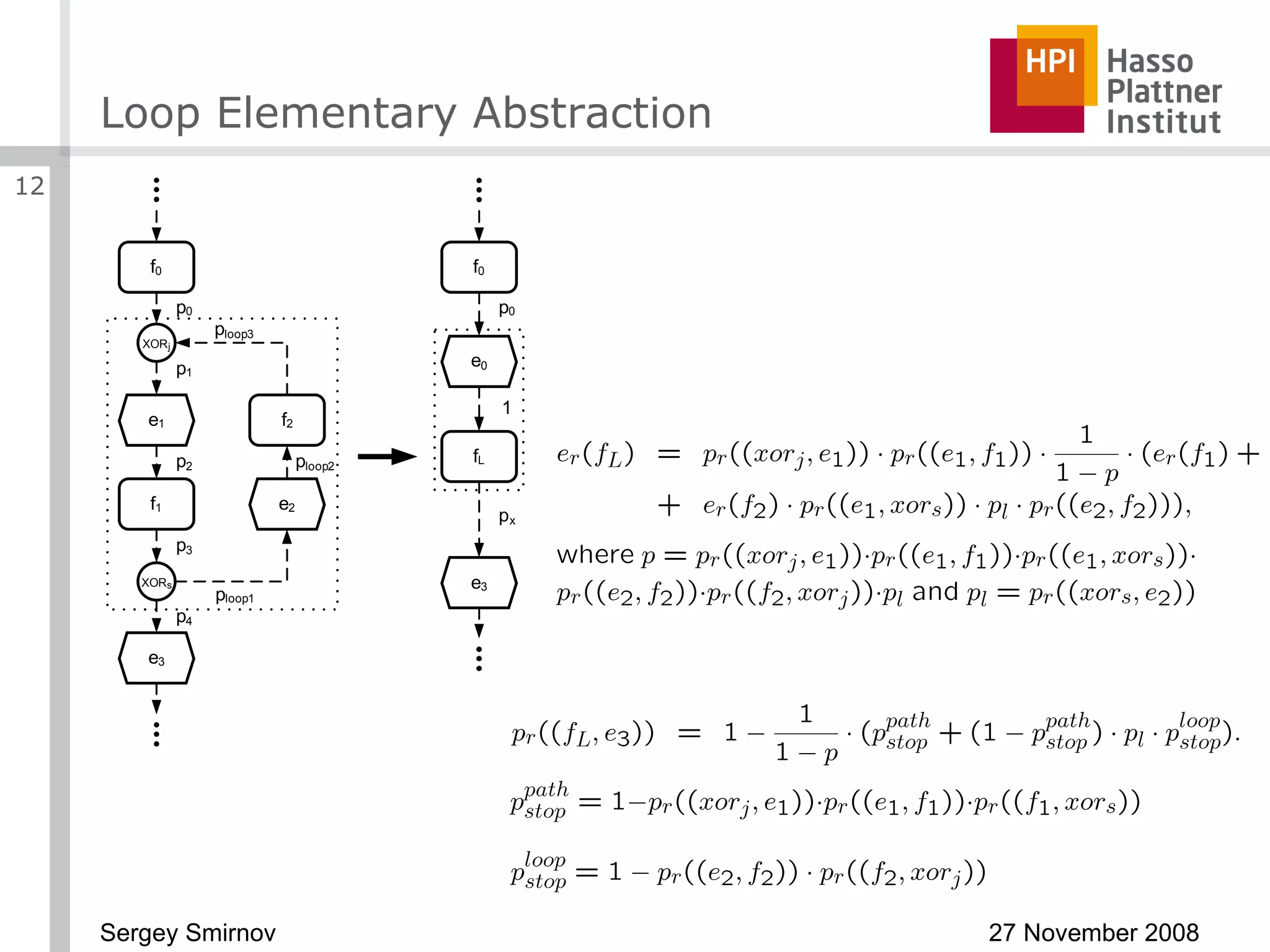
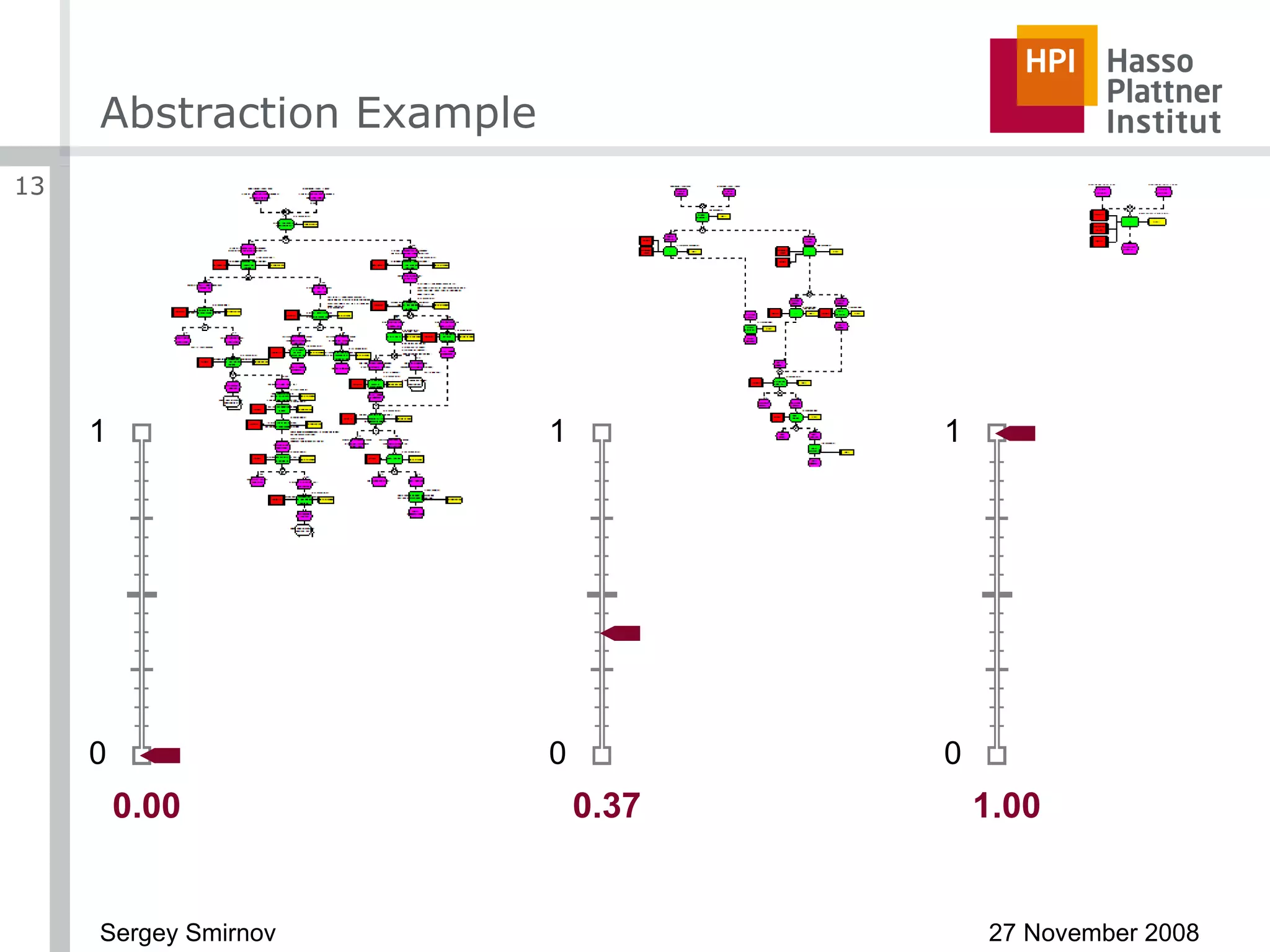
The document discusses reducing complexity in large event-driven process chains (EPCs) through abstraction. It proposes an approach to abstract insignificant model elements based on elementary abstractions like blocks, dead ends, sequences and loops. These elementary abstractions transform fragments of the model based on rules regarding structural elements and non-functional properties like execution time and effort. The goal is to create abstract process models from detailed models containing thousands of elements while preserving the overall execution time of each process.