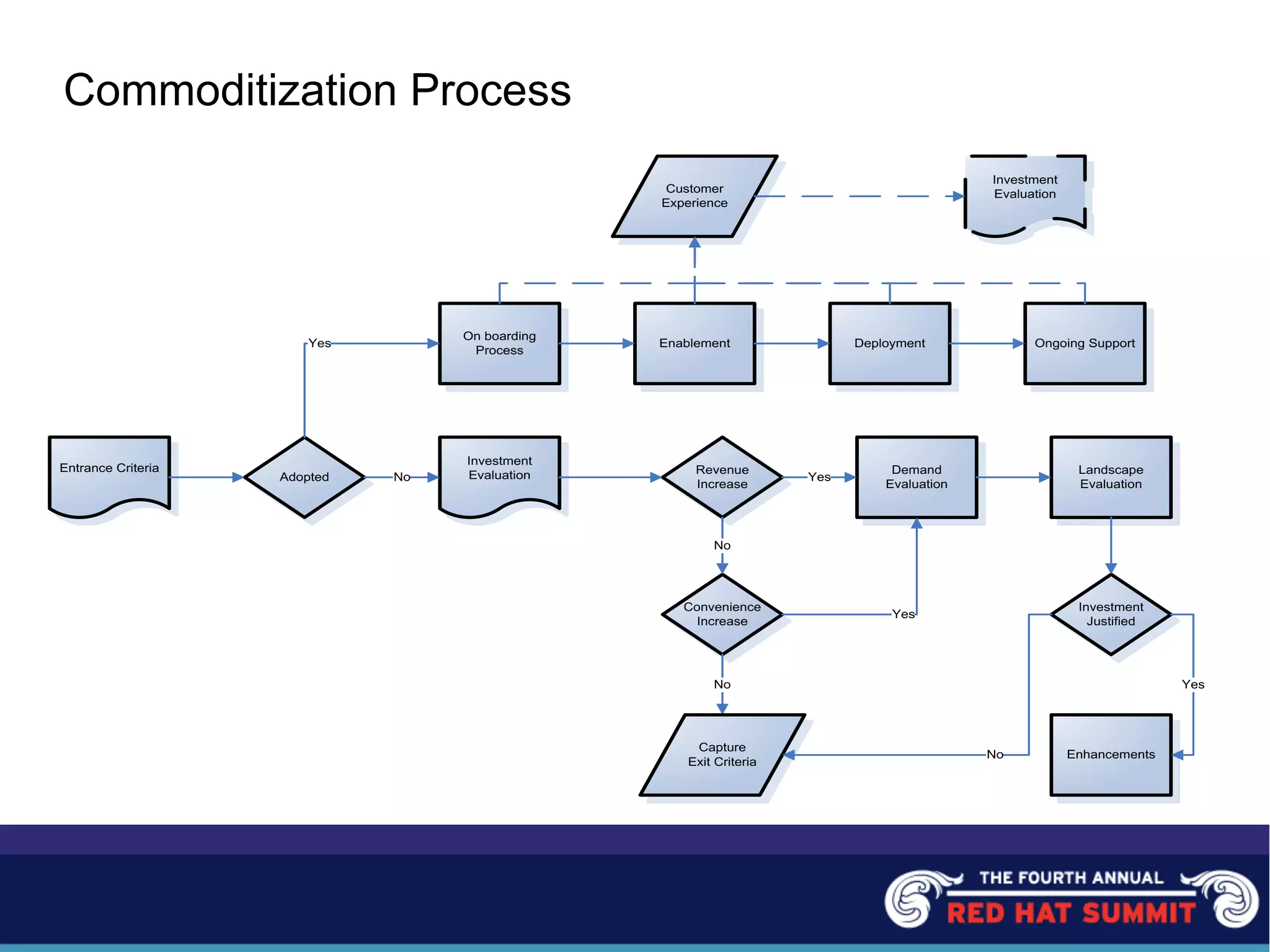
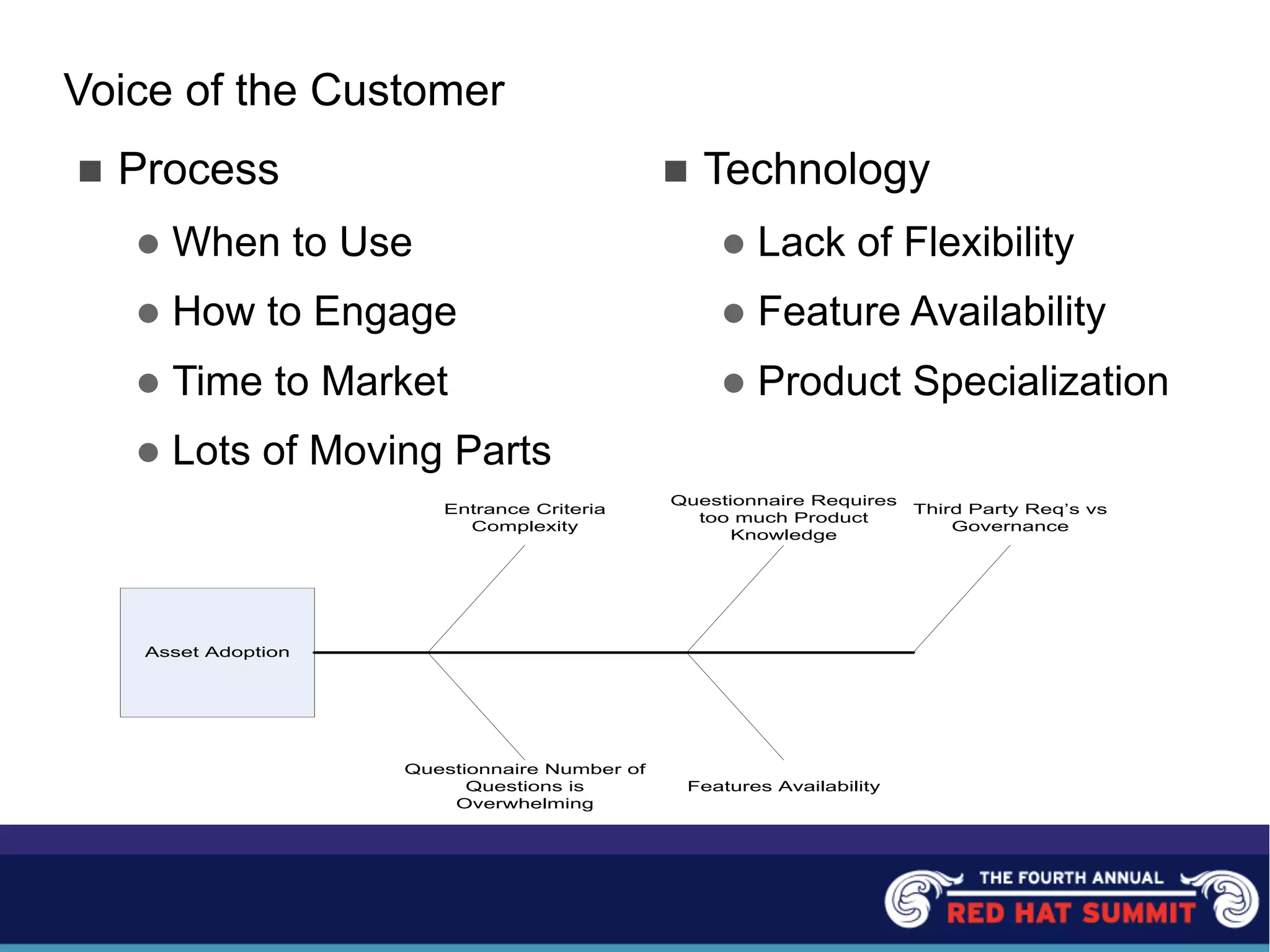
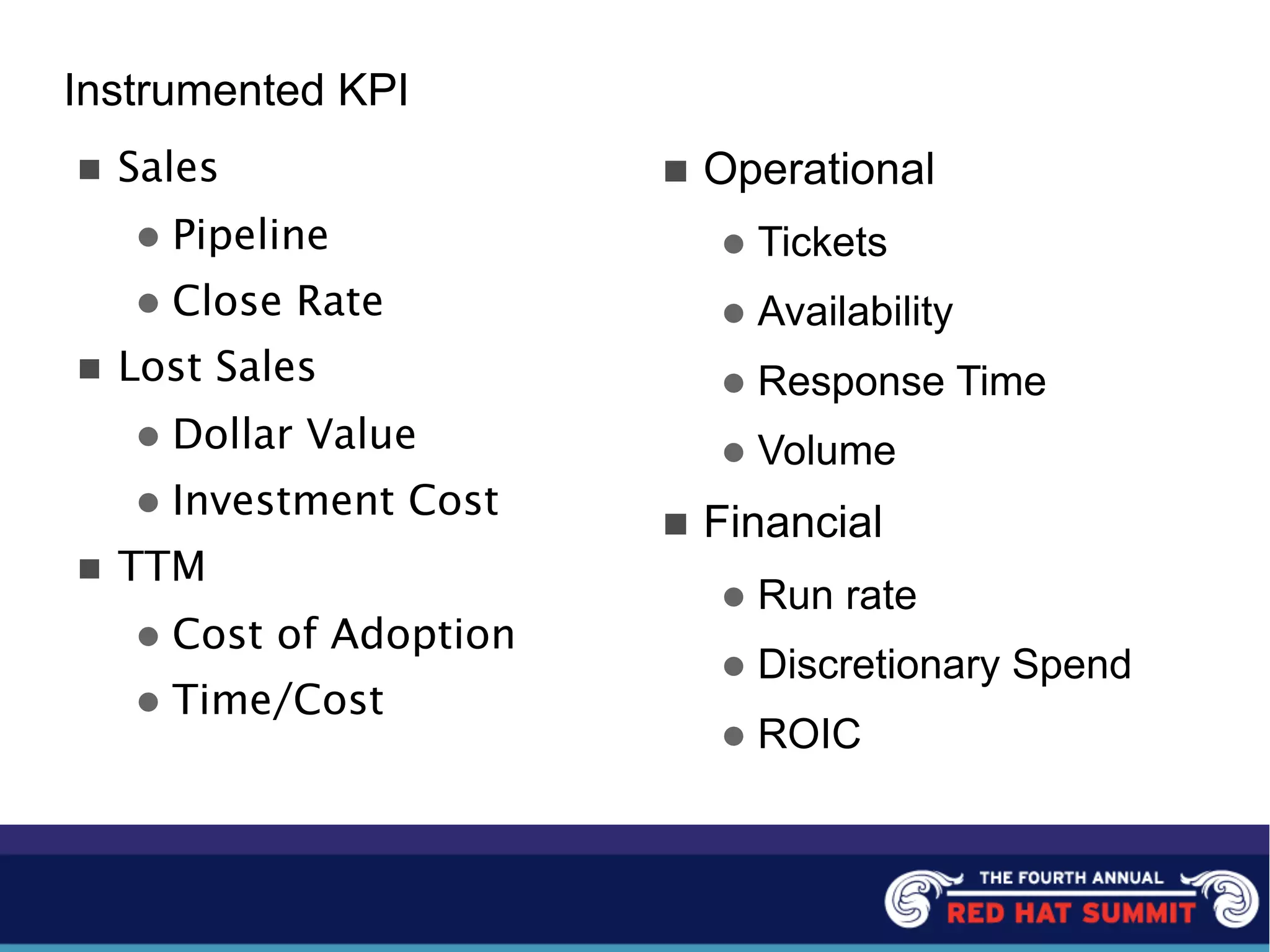
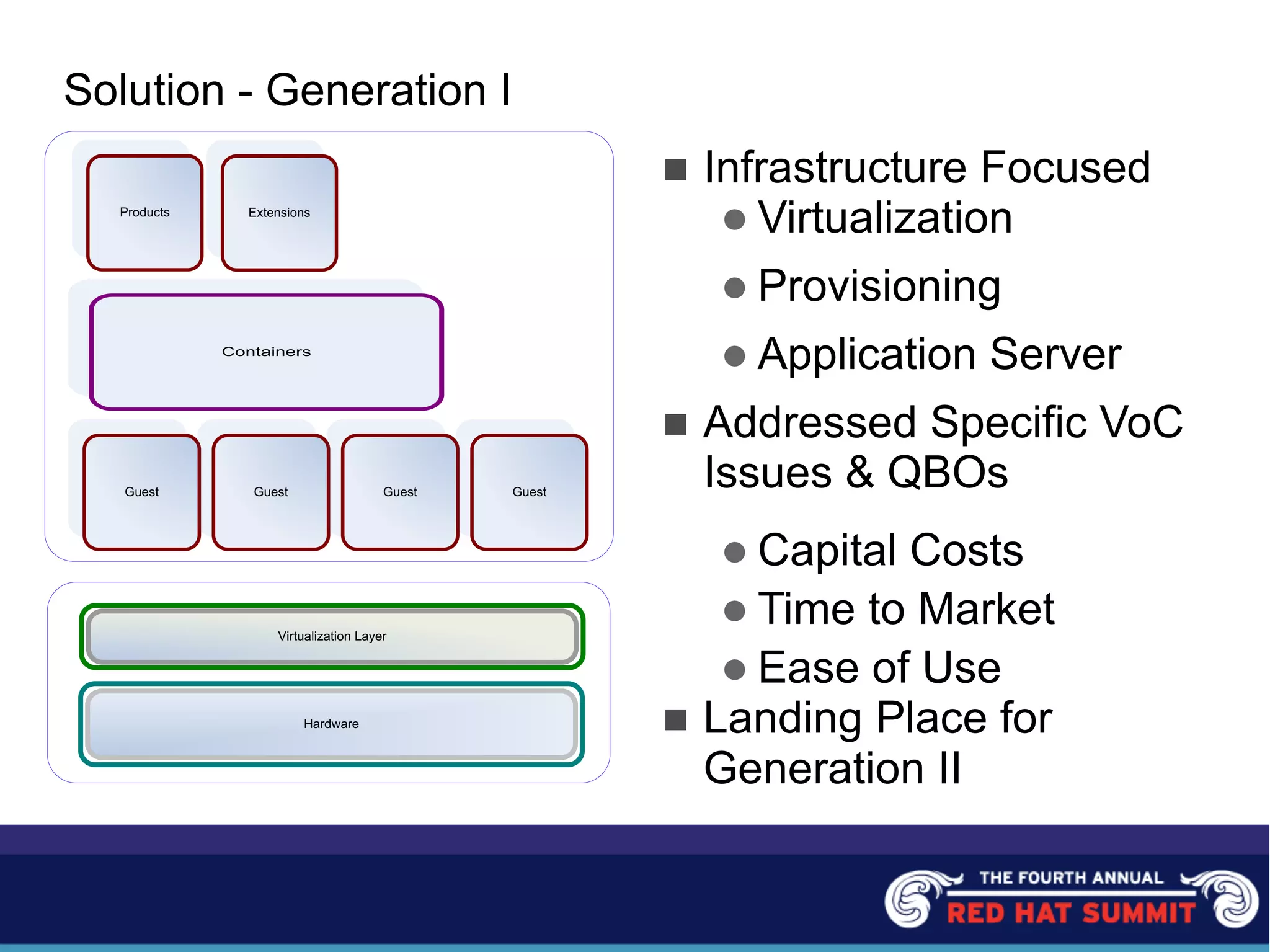
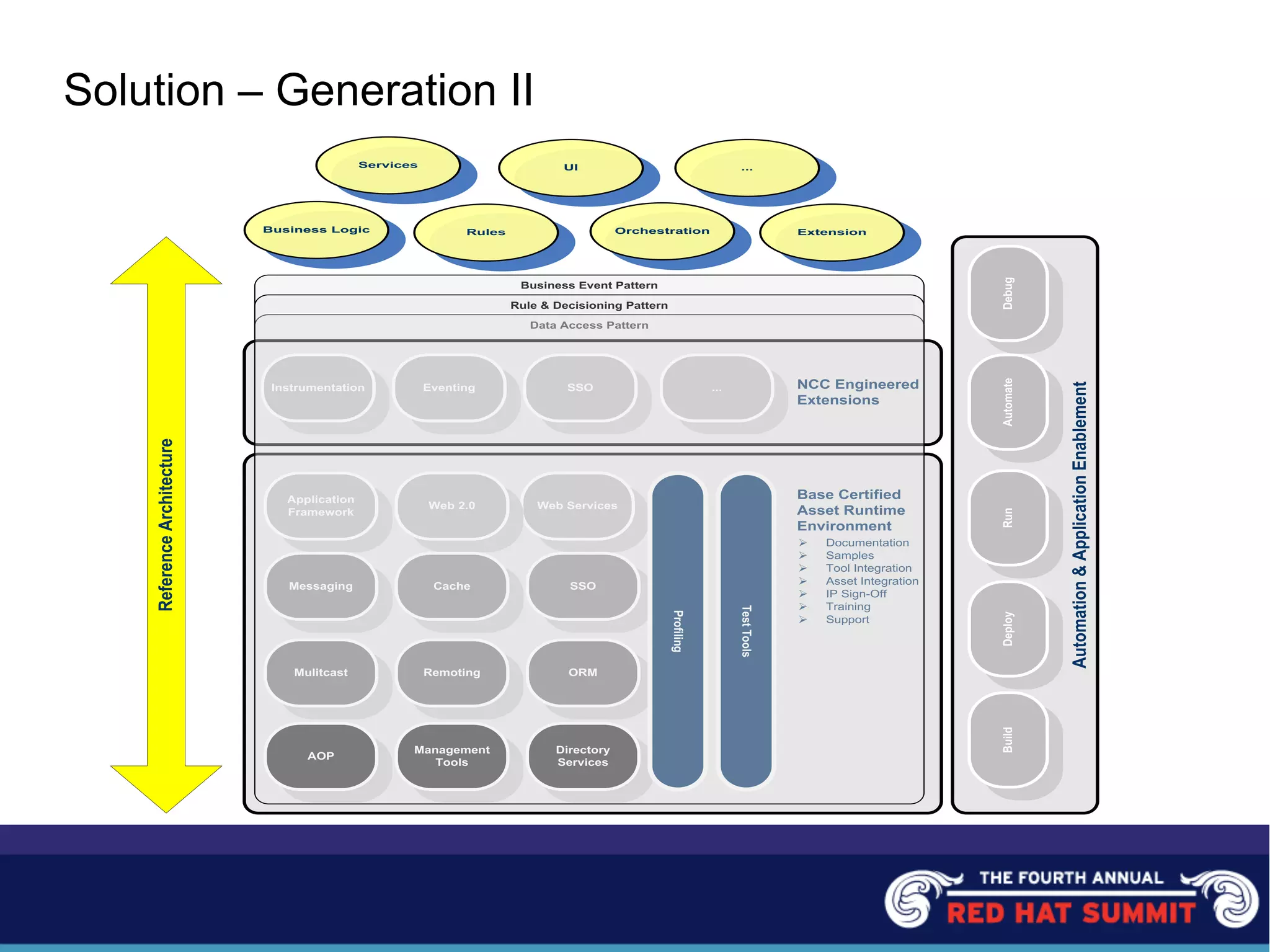
The document outlines the challenges and solutions related to server management and technology integration at National City Corporation. It highlights the need for improved efficiency and reduced costs through better product development and the adoption of standardized platforms like JEE and virtualization technologies. The summary includes financial impacts and future strategies aimed at enhancing customer experiences and driving product innovation.