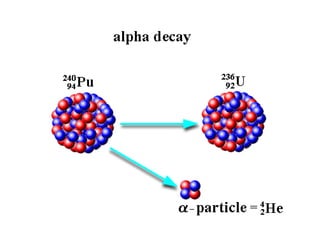
Radioactivity and the atomic nucleus were discovered in the late 19th century through experiments with uranium minerals. Three types of radiation - alpha, beta, and gamma - were identified. The atomic nucleus was determined to be stable when the ratio of protons to neutrons falls within the "band of stability." Nuclear models like the liquid drop and shell models were developed to explain nuclear stability. Radioactive decay follows first-order kinetics and half-lives can be used to date materials. Natural radioactivity occurs in uranium, thorium, and actinium decay series, while artificial radioactivity is induced through bombardment. Radiation poses health risks and proper safety measures should be taken when exposed.